wireless backhaul
What is wireless backhaul?
Wireless backhaul is the use of wireless communication systems to transport data between the internet and subnetworks. It can help an organization or mobile network eliminate the need for physical cabling. Rather than having a facility where all the internet hubs connect via wires to the internet, the connection happens wirelessly using either microwaves or radio waves to transmit signals between wireless access points.
One example of wireless backhaul is a smartphone that connects to the internet by receiving data from a cell tower or another kind of base station. The connection between the cell tower and the smartphone is the wireless backhaul.
What is the difference between wireless backhaul and backhaul?
Wireless backhaul and Backhaul are not the same thing. In the smartphone example, the connection happens over the air; thus it is wireless backhaul.
Backhaul is similar because it connects a device to the internet, but it uses wires or cables. For example, a tablet connected to a Wi-Fi router via an Ethernet cable is an example of a backhaul system. The router connects to the internet using a data line. If the user connects to an LTE (Long Term Evolution) or 5G network, they directly access the internet using a wireless backhaul connection.
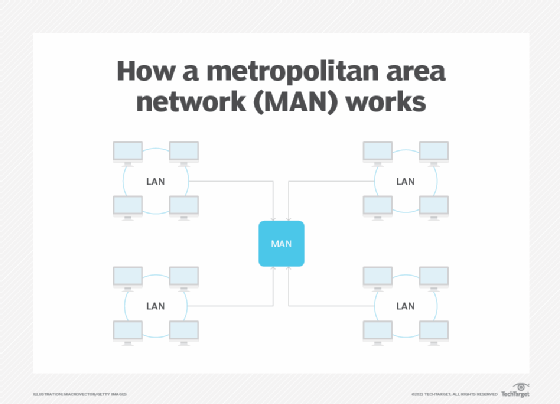
Several cities use metropolitan area networks (MANs), which essentially use wireless backhaul to cast a high-bandwidth "Wi-Fi net" around an area. Users or subscribers can connect to this network without having cabling set up in their homes or offices. They can also rely on this network because the wireless backhaul enables stable connections in stores, the park and even on the street.
Wireless backhaul applications
Wireless backhaul today is becoming more common than wired cable systems, as there are more applications and fewer limitations to the technologies behind it. Data centers can now reliably use wireless backhaul to connect with remote offices.
Similarly, organizations can better secure their operations. For example, surveillance networks monitor crime, but the system may miss a critical moment if the connection falters. Wireless backhaul strengthens this connection and provides last-mile aggregation. Rather than jumping through many hoops to reach the internet, there is direct access. These wireless networks can deliver hundreds of data streams and enable efficient and unbound throughput for data, video and voice.
The most relevant and growing application of wireless backhaul is 5G. 5G backhaul architecture -- which comes in wired, fiber-optic and wireless forms -- presents numerous opportunities to grow and expand broadband connectivity for mobile operators and their customers as well as in private enterprise 5G networks.
What is wireless mesh?
Wireless backhaul is not only a helpful tool for telecommunication networks and cities, but it is also ideal for commercial facilities and residential neighborhoods. In these settings, wireless backhaul comes in the form of wireless mesh network (WMN) systems.
A wireless mesh (or Wi-Fi mesh) system essentially creates many access points for wirelessly connecting to the internet. Users can distribute these wireless access points -- all with the same secure and fast direct link to the internet -- throughout a home, school or office.
By contrast, standard backhaul systems use wires to connect all access points back to a main central hub, which is the only access point to the internet. Devices that connect to noncentral points may experience latency and be less reliable. Wireless backhaul, in conjunction with wireless mesh systems, minimizes -- if not eliminates -- these issues.
What is microwave backhaul?
Microwave wireless backhaul is becoming one of the most prominent forms of wireless backhaul. It is already in use in many areas and is predicted to make up around 65% of the global backhaul by 2027, according to ABI Research. Where an organization cannot support or deploy fiber, microwave wireless backhaul is an excellent option, as it can be deployed quickly and economically. These systems also support high data rates, decrease latency and increase reliability. Microwave backhaul can also scale to meet increasing traffic demands.
Advantages of wireless backhaul
Wireless backhaul offers scalable, flexible alternatives to wire and fiber backhaul and can be quickly deployed. These links decrease operating costs, as there is no need to pay for fiber or leased lines.
As traffic increases, wireless backhaul systems adapt to demand. They can overcome the barriers associated with a wired network.
Wireless backhaul and 5G
5G presents opportunities for enterprises across a wide range of industries and cities worldwide. From virtual reality and augmented reality to autonomous cars, these technologies need concrete infrastructure and transport technologies.
Before deploying 5G, a mobile network operator must establish the right transport technology, however. This technology must meet stringent requirements for reliability, latency and throughput.
While wireless backhaul is a term that has long been in use, new wireless backhaul types are emerging. These technologies elevate the potential for internet connectivity around the world. They will open up accessibility to populated urban centers and, soon, to every edge of the planet.







