What is green networking?
Green networking is the practice of selecting energy-efficient networking technologies and products to minimize resource use whenever possible.
Although investing in green networking might require an initial cash outlay, the products, services and practices involved typically save money over time.
Green networking practices include the following:
- Updating IT policies to support the use of green technologies and resources.
- Increasing the use of off-premises networking, such as cloud services.
- Updating office space and data centers to be more energy-efficient, such as implementing network virtualization and practicing server consolidation.
- Upgrading older equipment for newer, more energy-efficient products.
- Employing systems management to increase efficiency.
- Substituting remote working, remote administration and video conferencing for travel.
- Organizing periodic reviews by environmental experts to validate green activities.
What is the goal of green networks?
A green data center typically houses the nerve center of a company's networking infrastructure. It stores, manages and disseminates network data. The physical components of the building structure -- environmental and security systems, lighting, electrical and computing resources -- are selected and deployed to minimize the environmental effect, while maximizing energy efficiency.
Green data centers, which also house network operations centers (NOCs), use the following technologies and strategies:
- Redesigned footprints that take up less space.
- Catalytic converters on backup generators.
- Low-emission building materials, carpets and paints.
- Energy-efficient entry points, exit points and window glass.
- Sustainable landscaping.
- E-waste recycling.
- Energy-optimized systems, such as solar farms, data center evaporative cooling and heat pumps.
- Hybrid or electric vehicles.
Building and certifying a green data center or other facility that supports green networking operations can be costly upfront. But, over time, organizations can save on energy, heating and cooling; networking operations; and systems maintenance.
For businesses, the goal of green networks is to cut energy consumption and emissions to improve air quality and the overall environment. An environmentally clean and friendly organization is also healthy for employees. Local communities also appreciate green networking facilities.
Another goal of green networks is to address and assuage environmental groups' concerns. Organizations that use environmentally responsible technologies might also receive governmental financial incentives.
Green networking approaches
An organization's commitment to green networking is essential for a successful green strategy.
At a fundamental level, network infrastructure configuration doesn't need to change in a green network. However, this assumes the existing configuration already provides necessary services, desired data throughput, latency control and security measures to protect the network and its perimeter from cybersecurity threats.
The principal approach to green networking is to replace existing network components with energy-efficient units. If the building that houses network elements doesn't change to a more environmentally friendly facility, then the organization can't significantly optimize the network. However, energy-efficient units can replace the following equipment:
- Backup power systems.
- Heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems.
- Building security systems.
- Window glass.
Figure 1 depicts a data center with a green NOC that has energy-efficient systems and technologies to improve the building's environmental footprint. Organizations can implement many of these energy improvements as part of a NOC upgrade.
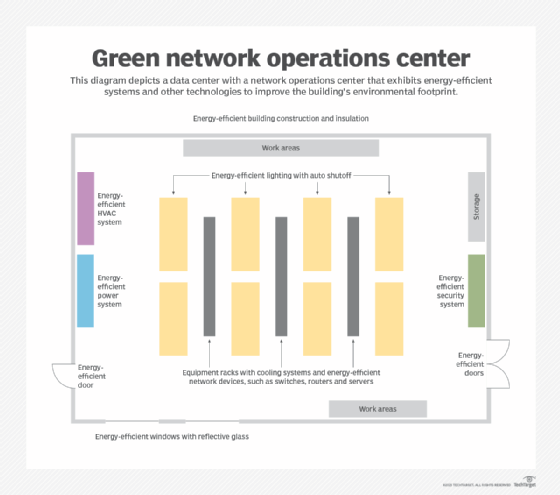
The bulk of a network infrastructure is often external to an organization. Organizations should query the carriers providing connectivity to understand their approach to green technology. Observe and validate the carriers' green activities in switching centers and data centers. Reports on energy savings and other environmental metrics should be available for customers to review.
Certain metrics demonstrate and certify that buildings are energy-efficient and minimize environmental damage. Green networking centers conform to one or both of two metrics that measure energy usage and sustainability.
- Power usage effectiveness. Introduced by The Green Grid -- an affiliate member of the Information Technology Industry Council -- in 2007, power usage effectiveness (PUE) measures a data center's power consumption and assesses efficiency. It is the data center's total power divided by the power the equipment uses. The goal is to have the ratio come as close to one as possible, which indicates effective power usage. Networking equipment is among the many components found in data centers. Many networking devices, such as servers, switches, firewalls and routers, have environmentally friendly options.
- Carbon usage effectiveness. The Green Grid also developed CUE, the ratio of carbon dioxide emissions a data center generates divided by the equipment's energy consumption. Much like PUE, CUE aims to have the lowest possible value. This indicates the data center and NOC effectively control carbon dioxide emissions and reduce the data center's carbon footprint.
Green networking certifications
In addition to PUE and CUE, two certifications are available to validate that a building or IT device is energy-efficient and environmentally friendly:
- Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design. Developed by the U.S. Green Building Council, LEED is a building certification. LEED means a building has satisfied the criteria for lowering energy consumption and being environmentally friendly.
- Energy Star. Developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the U.S. Department of Energy, the Energy Star designation certifies a device's energy efficiency. Since 1992, Energy Star products have saved residential and business users 5 trillion kilowatt-hours of electricity. In May 2025, the U.S. government announced plans to end the Energy Star program.

The benefits of green networking
Energy consumption is one of the largest budget items of a data center. It's also among the top 10 issues that concern data center operators and, by extension, network operations managers.
By committing to green networking, organizations can reap certain benefits. Over time, they could see a reduction in the following:
- Operating costs.
- Electricity consumption.
- Physical space.
- Carbon footprint.
- Carbon emissions.
- Water use.
- Waste output.
Green networks and the cloud
The components in a green NOC are energy-efficient as compared to data centers without such operational and environmental controls. To go green, the network configuration does not need to change -- only the physical components.
Migrating network components into a cloud or managed service provider environment can also increase the green factor. This eliminates the need for a physical NOC, as dashboards and other administrative tools can handle most network management tasks.
Cloud service providers have grown in popularity, and many of the key providers, such as Amazon, Google and Microsoft, use environmentally friendly data centers. Many network service providers, such as local telephone companies, also institute green measures in their central offices.








