
Getty Images
GitHub Copilot Autofix tackles vulnerabilities with AI
GitHub says Copilot Autofix drastically reduced the median time to remediate vulnerabilities in beta testing from 90 minutes for manual fixes to 28 minutes with the GenAI tool.
GitHub on Wednesday launched Copilot Autofix, an AI-powered tool designed to find and remediate software vulnerabilities.
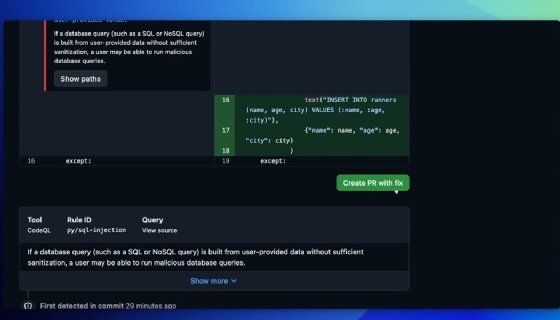
Copilot Autofix was first unveiled by GitHub in March and has been in public beta since that time. The tool combines GitHub's CodeQL scanning engine and GPT-4o, along with heuristics and Copilot APIs, to create code suggestions for users. Copilot Autofix offers large language model prompts based on CodeQL analysis and snippets of code around the flow path; users can choose to accept, edit or reject suggestions the tool makes.
In a blog post published Wednesday, Mike Hanley, CSO and senior vice president of engineering at GitHub, said developers and security teams are struggling to make progress with backlogs of existing vulnerabilities that need to be addressed. "Code scanning tools detect vulnerabilities, but they don't address the fundamental problem: remediation takes security expertise and time, two valuable resources in critically short supply," Hanley said. "In other words, finding vulnerabilities isn't the problem. Fixing them is."
GitHub said the results of the private beta showed that the median time for customers to respond to a CodeQL alert and automatically remediate a vulnerability in a pull request was 28 minutes, compared with 90 minutes to manually resolve the same alerts. Copilot Autofix provided even faster results for common vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting flaws, which were remediated on average in 22 minutes compared with three hours for manual fixes, and SQL injections, which took 18 minutes compared with almost four hours.
Hanley compared Copilot Autofix's ability to remediate vulnerabilities at a quicker pace to GitHub Copilot's ability to produce code for developers at a faster clip. GitHub Copilot, a generative AI coding assistant that was released in 2022, has become an increasingly popular tool for developers. However, some cybersecurity vendors have observed that GitHub Copilot and other GenAI coding assistants are often replicating existing vulnerabilities in users' codebases.
Katie Norton, an industry analyst and research manager at IDC, said the speed at which AI coding assistants are creating new software might be a bigger security issue than the replication of vulnerabilities. Chris Wysopal, CTO and co-founder at Veracode, echoed that concern during a Black Hat USA 2024 session last week in which he said increased coding velocity has created more software and larger backlogs of vulnerabilities for development teams to address.
Norton said the pileup of vulnerabilities has put a growing amount of security responsibility on developers, but AI-powered tools like Copilot Autofix could help reduce those backlogs and enable them to remediate bugs without having to become security experts. She noted that other vendors offer AI-powered autoremediation tools and features, including Mobb and Snyk.
"Who does the remediation for these backlogs [of vulnerabilities]? The majority of the work goes to developers, and it's either a disruption to their workflows or the vulnerabilities sit in a backlog," Norton told TechTarget Editorial. "The prioritization and remediation process is really challenging right now for organizations, and I think Autofix could help with the remediation part."
Copilot Autofix initially supported JavaScript, TypeScript, Java and Python in the public beta; GitHub told TechTarget Editorial the tool now supports C#, C/C++, Go, Kotlin, Swift and Ruby as well.
In addition to helping organizations tackle their own vulnerabilities, Hanley said Copilot Autofix will also benefit the open source software market. GitHub previously gave open source maintainers free access to several enterprise security tools for code scanning, secret scanning and dependency management; in September, the company will add Copilot Autofix to the list of free tools for maintainers, he said.
"As the global home of the open source community, GitHub is uniquely positioned to help maintainers detect and remediate vulnerabilities so that open source software is safer and more reliable for everyone," Hanley said.
Copilot Autofix is now generally available to all GitHub customers in all regions.
Rob Wright is a longtime reporter and senior news director for TechTarget Editorial's security team. He drives breaking infosec news and trends coverage. Have a tip? Email him.






