What is a large language model (LLM)?
A large language model (LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence algorithm that uses deep learning techniques and massively large data sets to understand, summarize, generate and predict new content. The term generative AI is also closely connected with LLMs, which are a type of generative AI architected specifically to help generate text-based content.
Over millennia, humans developed spoken languages to communicate. Language is at the core of all forms of human and technological communications; it provides the words, semantics and grammar needed to convey ideas and concepts. In the AI world, a language model serves a similar purpose, providing a basis to communicate and generate new concepts.
The first AI language models trace their roots to the earliest days of AI. The Eliza language model debuted in 1966 at MIT and is one of the earliest examples of an AI language model. All language models are first trained on a set of data, then use various techniques to infer relationships before ultimately generating new content based on the trained data. Language models are commonly used in natural language processing (NLP) applications, where a user inputs a query in natural language to generate a result.
An LLM is the evolution of the language model concept in AI that dramatically expands the data used for training and inference. It increases AI model capabilities massively. Parameters are a machine learning (ML) term for the variables present in the model on which it was trained that can be used to infer new content. An LLM typically has at least one billion or more parameters, though there isn't a universally accepted figure for how large the data set for training should be.
This article is part of
What is GenAI? Generative AI explained
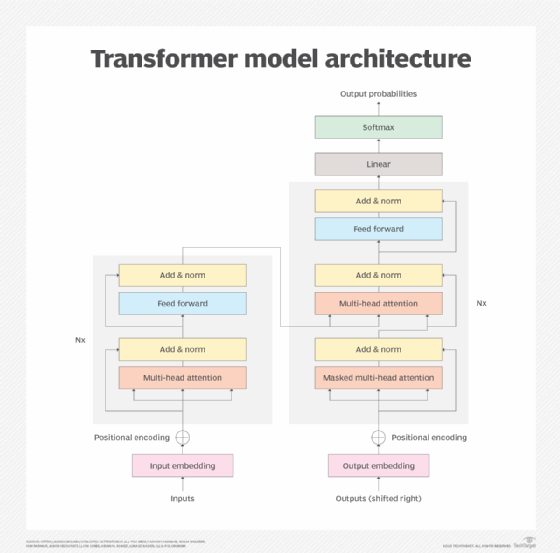
Modern LLMs emerged in 2017 and use transformer models, which are neural networks commonly called transformers. With a large number of parameters and the transformer model, LLMs can understand and generate accurate responses rapidly, which makes the AI technology applicable broadly across many different domains.
Some LLMs are called foundation models, a term the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence coined in 2021. A foundation model is so large and impactful that it serves as the foundation for further optimizations and specific use cases.
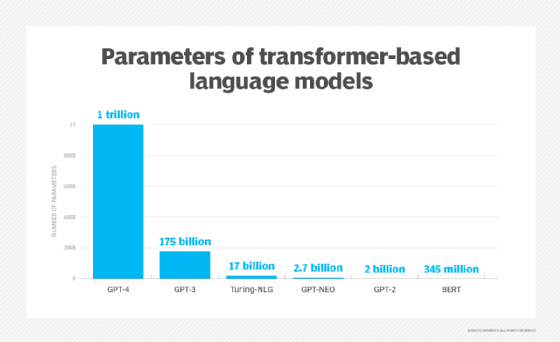
Examples of LLMs
Here's an alphabetized list of the top 10 LLMs on the market based on internet research:
- Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT).
- Claude.
- Cohere.
- Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration (Ernie).
- Falcon 40B.
- Galactica.
- Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3).
- GPT-3.5.
- GPT-4.
- GPT-5.
- Language Model for Dialogue Applications (Lamda).
You can learn more about these and other leading LLMs.
Why are LLMs becoming important to businesses?
As AI evolves, its playing an increasingly dominant role in business. This is seen in the use of LLMs and ML tools. In composing and applying ML models, simplicity and consistency should be primary goals. Identifying the issues that must be solved is also essential, as is comprehending historical data and ensuring accuracy.
ML benefits are often grouped into four categories: efficiency, effectiveness, experience and business evolution. As these continue to emerge, businesses invest in this technology.
How do LLMs work?
LLMs take a complex approach that involves multiple components.
At the foundational layer, an LLM must be trained on a large volume -- sometimes called a corpus -- of data typically petabytes in size. The training can take multiple steps, usually starting with an unsupervised learning approach. In that approach, the model is trained on unstructured data and unlabeled data. The benefit of training on unlabeled data is that there's often vastly more data available. At this stage, the model begins to derive relationships between different words and concepts.
The next step for some LLMs is training and fine-tuning with a form of self-supervised learning. Here, some data labeling has occurred, assisting the model to identify different concepts more accurately.
Next, the LLM undertakes deep learning as it goes through the transformer neural network process. The transformer model architecture enables the LLM to understand and recognize the relationships and connections between words and concepts using a self-attention mechanism. That mechanism can assign a score, commonly called a weight, to a given item -- called a token -- to determine the relationship.
Once an LLM is trained, a base exists on which the AI can be used for practical purposes. By querying the LLM with a prompt, the AI model inference can generate a response, which could be an answer to a question, newly generated text, summarized text or a sentiment analysis report.
What are LLMs used for?
LLMs are popular because of their utility for a broad range of NLP tasks, including the following:
- Text generation. The ability to generate text on any topic the LLM has been trained on is a primary use case.
- Translation. For LLMs trained on multiple languages, the ability to translate from one language to another is a common feature.
- Content summary. Summarizing blocks or multiple pages of text is a useful function.
- Rewriting content. Rewriting a section of text is valuable.
- Classification and categorization. An LLM can classify and categorize content.
- Sentiment analysis. Most LLMs support sentiment analysis to help users better understand the intent of a piece of content or a particular response.
- Conversational AI and chatbots. LLMs can enable a conversation with a user in a way that is typically more natural than older AI technologies.
Conversational AI is used commonly through a chatbot, which can exist in several different forms where a user interacts in a query-and-response model. The most widely used LLM-based AI chatbot is ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI. ChatGPT currently is based on the GPT-3.5 model, although paying subscribers can use the newer GPT-4 LLM.
What are the advantages of LLMs?
LLMs provide numerous advantages:
- Extensibility and adaptability. LLMs can serve as a foundation for customized use cases. Additional training on top of an LLM can create a finely tuned model for an organization's specific needs.
- Flexibility. One LLM can handle many different tasks and deployments across organizations, users and applications.
- Performance. Modern LLMs are typically high-performing and can generate rapid, low-latency responses.
- Accuracy. As the number of parameters and volume of trained data grow in an LLM, the transformer model can deliver increasing levels of accuracy.
- Ease of training. Many LLMs are trained on unlabeled data, which can accelerate the training process.
- Efficiency. LLMs can save employees time by automating routine tasks.
What are the challenges and limitations of LLMs?
Some challenges and limitations of using LLMs include the following:
- Development costs. LLMs require large quantities of expensive graphics processing unit hardware and massive data sets.
- Operational costs. After the training and development period, the cost of operating an LLM can be quite high.
- Bias. A risk with any AI trained on unlabeled data is bias; whether known bias has been removed is often unclear.
- Ethical concerns. LLMs can introduce data privacy issues and create harmful content.
- Explainability. How an LLM generated a specific result often is not explained easily.
- Hallucination. AI hallucination occurs when an LLM provides an inaccurate response that is not based on trained data.
- Complexity. With billions of parameters, modern LLMs are exceptionally complicated technologies; troubleshooting is correspondingly complex.
- Glitch tokens. Maliciously designed prompts that cause an LLM to malfunction, known as glitch tokens, have been part of an emerging trend since 2022.
- Security risks. LLMs can be used to improve phishing attacks on employees.
What are the different types of LLMs?
There's an evolving set of terms to describe the different types of LLMs. These are some common types:
- Zero-shot model. This is a large, generalized model trained on a generic corpus of data that can give a fairly accurate result for general use cases without the need for additional training. GPT-3 is often considered a zero-shot model. Few shot models have also emerged.
- Fine-tuned or domain-specific models. Additional training on top of a zero-shot model such as GPT-3 can lead to a fine-tuned, domain-specific model. One example is OpenAI Codex, a domain-specific LLM for programming based on GPT-3.
- Language representation model. One example of a language representation model is Google's Bert, which uses deep learning and transformers well suited for NLP.
- Multimodal model. Originally, LLMs were tuned specifically just for text, but with the multimodal approach, it's possible to handle both text and images. GPT-4 is this type of model.
The future of LLMs
The future of LLMs remains in the hands of humans who are developing the technology, though there could be a future in which LLMs write themselves. The next generation of LLMs will not likely be artificial general intelligence or sentient, but will improve and get "smarter" continuously.
LLMs will also support more business applications. Their ability to translate content across different contexts will grow further, making them more usable by business users with different levels of technical expertise.
LLMs will continue to be trained on ever larger sets of data, and that data will increasingly be better filtered for accuracy and potential bias, partly through the addition of fact-checking capabilities. LLMs of the future will likely do a better job than the current generation in providing attribution and better explanations for how a result was generated.
Also expected is enabling more accurate information through domain-specific LLMs developed for individual industries or functions. Expanded use of techniques such as reinforcement learning from human feedback, which OpenAI uses to train ChatGPT, could help improve LLM accuracy. A class of LLMs based on the concept known as retrieval-augmented generation -- including Google's Retrieval-Augmented Language Model (Realm) -- will enable training and inference on a highly specific corpus of data, much like how a user today can specifically search content on a single site.
There's also ongoing work to optimize the overall size and training time required for LLMs, including development of Meta's Llama model. Llama 2, released in July 2023, had less than half the parameters of GPT-3 and a fraction of the number GPT-4 contains, though its backers claimed it could be more accurate. Meta has recently released Llama 4. The several models in the Llama 4 family use a mixture-of-experts architecture where only some of all the available parameters activate for an input token. This is a way to achieve power with better efficiency.
The use of LLMs could drive new instances of shadow IT in organizations. CIOs will need to implement usage guardrails and provide training to avoid data privacy problems and other concerns. LLMs could introduce new cybersecurity challenges by enabling attackers to write more persuasive, realistic phishing emails or other malicious communications. Despite such concerns, the future of LLMs will likely remain bright as the technology evolves in ways that help improve human productivity.