SQL injection (SQLi)
What is a SQL injection (SQLi)?
A SQL injection (SQLi) is a technique that attackers use to gain unauthorized access to a web application database by adding a string of malicious code to a database query.
A SQL injection manipulates Structured Query Language code to provide access to protected resources, such as sensitive data, or execute malicious SQL statements. When executed correctly, a SQL injection can expose intellectual property, customer data or the administrative credentials of a private business.
SQL injection attacks can be used to target any application that uses a SQL database, with websites being the most common prey. Common SQL databases include MySQL, Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server.
How does a SQL injection attack work?
A SQL query is a request for some action to be performed on an application database. Queries can also be used to run operating system commands. Each query includes a set of parameters that ensure only desired records are returned when a user runs the query. During a SQL injection, attackers exploit this by injecting malicious code into the query's input form.
The first step of a SQL injection attack is to study how the targeted database functions. This is done by submitting a variety of random values into the query to observe how the server responds.
Attackers then use what they've learned about the database to craft a query the server interprets and then executes as a SQL command. For example, a database may store information about customers who have made a purchase with customer ID numbers. Instead of searching for a specific customer ID, an attacker may insert "CustomerID = 1000 OR 1=1" into the input field. Since the statement "1=1" is always true, the SQL query would return all available customer IDs and any corresponding data. This enables the attacker to circumvent authentication and gain administrator-level access.
In addition to returning unauthorized information, SQL attacks can be written to delete an entire database, bypass the need for credentials, remove records or add unwanted data.
How many types of SQL injection attacks are there?
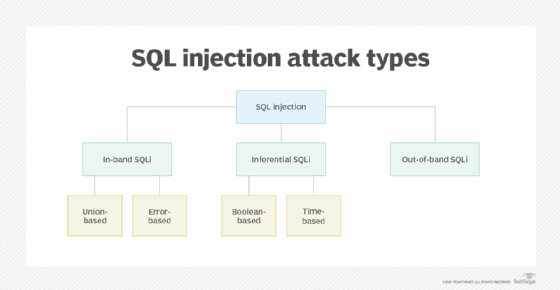
There are a few different types of SQL injection attacks.
In-band SQLi
Also known as classic SQLi, in-band SQLi is when hackers use the same channel -- or band -- to launch database errors and to collect the results from an attack. In-band SQLi is most commonly achieved through two methods:
- Error-based injection techniques force the database to produce error messages that reveal information about the structure of the database.
- Union-based attacks use prepared statements that exploit the SQL union function, which combines the results of multiple queries into one result.
Inferential SQLi
Also known as blind SQLi, inferential SQLi is when hackers send data payloads to a database server to observe its response and behavior without being able to see what is occurring within the database. The server's response provides attackers with clues that they can use to adjust their attack strategy.
Inferential SQLi can be either Boolean-based or time-based. Boolean SQLi uses true or false statements to solicit a response, while time-based SQLi sets a designated response period.
Out-of-band SQLi
Out-of-band SQLi is when hackers take advantage of domain name system or Hypertext Transfer Protocol requests to retrieve data. Out-of-band SQLi is usually only performed when a web server is too slow or when in-band SQLi is not possible to execute.
How can a SQL injection attack be detected and prevented?
If a SQL injection attack is successfully carried out, it could cause extensive damage by exposing sensitive data and damaging customer trust. That's why it is important to detect this type of attack in a timely manner.
Web application firewalls (WAFs) are the most common tool used to filter out SQLi attacks. WAFs are based on a library of updated attack signatures and can be configured to flag malicious SQL queries in web applications.
To prevent a SQL injection attack from occurring, businesses can follow these practices:
- Train employees on prevention methods. It's important that IT teams -- including DevOps, system administrators and software development -- receive proper security training to understand how SQLi attacks happen and how they can be prevented in web applications.
- Don't trust user input. Any user input provided in a SQL query increases the likelihood for a successful SQL injection. The best way to mitigate this type of risk is to put security measures around user input.
- Use an allowlist instead of a blocklist. Validating and filtering user input via an allowlist, as opposed to a blocklist, is recommended because cybercriminals can usually bypass a blocklist. This is because a blocklist includes a list of all the applications or executables that might pose a threat to the network. Therefore, everything on the network can operate besides the items on the blocklist. Unfortunately, thousands of new malware and virus samples are created every day, and it's impossible for administrators to keep the blocklists updated with newer attack variants and zero-day vulnerabilities, so a security breach is entirely possible before the list is updated.
- Perform routing updates, and use the newest version of applications. One of the most common SQL injection vulnerabilities is outdated software. Not only is older technology unlikely to have built-in SQLi protection, but unpatched software is also often easier to manipulate. This includes programming languages, too. Older languages and syntax are more vulnerable. For example, use PHP Data Objects as a substitute for older MySQL.
- Use validated prevention methods. Query strings written from scratch offer insufficient protection against SQLi. The best way to protect web applications is through input validation, prepared statements and parameterized queries.
- Perform regular security scans. Regularly scanning web applications catches and remedies potential vulnerabilities before they do serious damage.
Some database administrators believe that a stored procedure statement can often aid in the prevention of SQL injection attacks by restricting the types of statements that can be supplied to its parameters. However, this doesn't prevent all exploits, as there are numerous workarounds and intriguing statements that can still be provided to stored procedures.
The impact of SQL injection attacks for your business
SQL injection attacks can seriously harm a business or organization. The negative effects could include the following:
- Cybercriminals could gain unwanted or administrative access to private information and resources.
- Potential data breaches can occur as a result of unauthorized access to resources.
- The data can be altered, or entire database tables can be deleted by cybercriminals.
- Database infiltration can enable threat actors to penetrate entire networks or systems.
- Customers may lose trust in the business, which can ultimately result in decreased revenue.
- It may take time and resources to recover from the attack and implement new security measures to prevent future incidents.
- While the immediate effect of a successful SQL injection attack may be difficult to quantify, the long-term damage caused by reputation loss, legal costs and lost business opportunities can have far-reaching consequences.
A few well-known companies that have experienced SQL injection attacks include Target, Yahoo, LinkedIn, Sony Pictures and 7-Eleven.
Examples of SQL injection attacks
There are numerous SQL injection vulnerabilities, attacks and strategies that can occur in a variety of settings.
The following are some common SQL injection examples:
- Changing SQL query. To retrieve hidden data, a SQL query can be changed by cybercriminals to reveal additional information.
- Login bypass. To get around authentication and access the program or website, a hacker can inject a SQL command into a login form.
- Undermining application logic. This is where a cybercriminal alters a query to obstruct the logic of the application.
- Union attacks. These attacks enable the retrieval of data from many database tables.
- Database analysis. This is where the cybercriminals analyze the database to glean information about its version and structure.
- Blind SQL injection. During a blind SQL injection, no error messages are received from the database.
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. During this attack, an attacker injects a SQL statement to generate a DoS or DDoS attack, overwhelming a system.
The following are some examples of real-life SQL injection vulnerabilities:
- Tesla vulnerability. In 2014, security researchers revealed that they were able to penetrate Tesla's website via a SQL injection, get administrative privileges and steal user data.
- Fortnite vulnerability. Fortnite is a popular online game with over 350 million players. A SQL injection vulnerability was discovered in 2019 that could enable attackers to access user accounts. However, this vulnerability was patched.
- Cisco vulnerability. A SQL injection vulnerability in Cisco Prime License Manager was discovered in 2018. The flaw enabled attackers to get shell access to computers where the license management was installed. Cisco has addressed the issue.
History of SQL injections
SQL injection attacks have been around for over two decades since they were first documented by cybersecurity researcher and hacker Jeff Forristal in 1998. However, they didn't appear to get much attention until 2002.
SQL injections are considered one of the most common security exploits, as evidenced by their presence on the list of Open Web Application Security Project's top 10 threats to web application security. The risk of SQLi exploits and the damage they can cause have both grown with the availability of automated tools for executing SQL injections. In the past, the likelihood of an enterprise being targeted with a SQL injection was somewhat limited because attackers had to carry out these exploits manually.
These attacks have now become one of the most common and continuously rated top security exploits in database software history, with a succession of high-profile attacks on large organizations, such as TalkTalk, where an outdated database was the main factor behind the breach.
Successful SQL injection attacks enable attackers to modify database information, access sensitive data, perform administrative activities on the database and recover files from the database.
SQL injections and cross-site scripting are two types of application attacks that can bring an organization to its knees. Discover the five most prevalent application security threats, and learn how to protect against them.







