
Getty Images
TB vs. GB: Is a terabyte bigger than a gigabyte?
A terabyte comprises more than 1 trillion bytes. Discover how the storage measurement scale was created and where a terabyte stands among other units of measurement today.
In data storage, capacities have grown exponentially from the early days in the late 1970s and early 1980s when a megabyte of storage could cost upward of $100,000. Today, thanks to advances in storage technology, devices with much larger capacity -- for example, one terabyte -- are available for less than $100.
Measuring data capacity has evolved into a variety of terms -- for example, a terabyte (TB) is about 1,000 times larger than a gigabyte (GB), which is about 1,000 times bigger than a megabyte (MB). The humble byte -- which started it all -- is now attached to several prefixes denoting vast amounts of data.
A terabyte is equal to 1012 bytes. Hitachi released the first terabyte-level hard drive in 2007, and today, HDDs such as the Seagate Exos M can hold up to 36 TB of data. The largest SSDs -- for example, the Kioxia LC9 -- offer up to 246 TB capacity. Meanwhile, some LTO-10 tape cartridge systems -- the most recent LTO edition -- feature a compressed capacity of 90 TB.
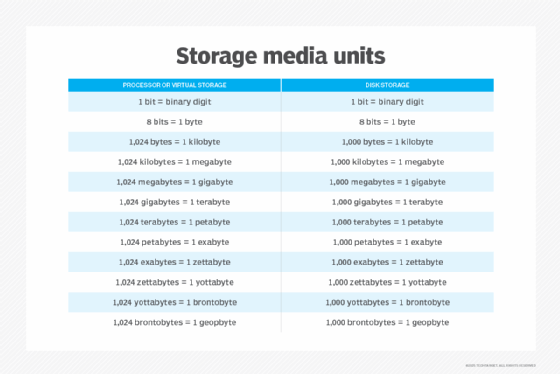
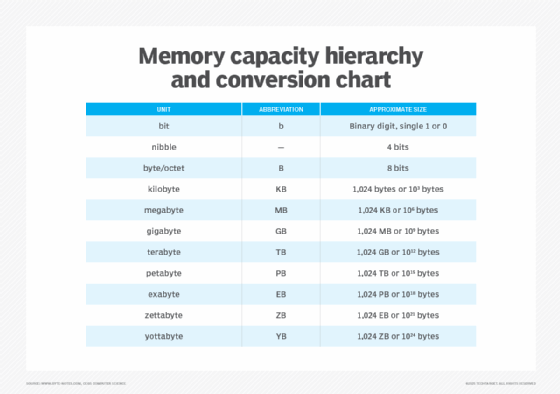
Specifically, a terabyte is equal to 1,024 GB, which itself is equal to 1,024 MB, while a megabyte is equivalent to 1,024 kilobytes (KB). All current storage measuring units -- kilobyte, megabyte, terabyte, gigabyte, petabyte (PB), exabyte (EB) and so on -- are multiples of a byte.
What is larger than a terabyte?
A terabyte is one of the largest units of storage media that products on the market use today, but it is not the biggest unit of measurement in data storage. Units larger than a terabyte include a petabyte, exabyte, zettabyte (ZB), yottabyte (YB) and brontobyte (BB). A geopbyte (GPB) is also larger than a terabyte and refers to 1,024 BB.
Additional units of measurement become necessary as the amount of data in the world increases. And it's not going to slow down any time soon. Drive capacity may not currently go beyond the terabyte scale, but this will undoubtedly change as storage media technology evolves. Storage capacities in the petabyte and exabyte ranges are possible by configuring multiple-terabyte drive arrays or using cloud storage, which can offer virtually unlimited capacity.
How much data is in a terabyte?
A terabyte has a storage drive capacity of about 1 trillion bytes or, more specifically, 1,099,511,627,776 bytes; 1,073,741,824 KB; or 1,048,576 MB.
In practical terms, a terabyte of data is equivalent to the following:
- 728,177 floppy disks.
- 1,498 CD-ROM discs.
- 212 DVD discs.
- 40 single-layer Blu-ray discs.
- 85,899,345 pages of Word documents.
- 132,150 650-page books.
- 500 hours of movies.
- 1,000 hours of video.
- 310,000 photos.
- 17,000 hours of music.
How the size scale was created
Bytes hold a string of bits, typically eight for most computer systems. A bit, short for binary digit, has a single binary value of either 0 or 1 and is the smallest unit of data in a computer system. Memory or storage devices typically store the value of a bit above or below a designated level of electrical charge in a single capacitor. A byte holds its string of bits so they can be used in a larger unit for application or OS purposes.
Werner Buchholz is credited by Fred Brooks -- author of the classic software engineering tome The Mythical Man-Month: Essays on Software Engineering and an early IBM hardware architect and IBM System/360 OS project manager -- as the originator of the term byte. According to Brooks, Buchholz came up with byte while helping to design IBM's first transistorized supercomputer, the 7030 Stretch, in 1956.
Kilobytes date to early PCs and disk storage devices, mostly in the early 1980s. Megabytes emerged for larger disk storage devices in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Gigabytes first appeared in the early 2000s as device capacities grew. Further device capacity resulted in the term terabyte in the 2010s. Still more prefixes emerged as capacities continued their rapid growth in the late 2010s and early 2020s.
Paul Kirvan, FBCI, CISA, is an independent consultant and technical writer with more than 35 years of experience in business continuity, disaster recovery, resilience, cybersecurity, GRC, telecom and technical writing.
Erin Sullivan is senior site editor for Informa TechTarget's SearchDataBackup and SearchDisasterRecovery sites.
James Alan Miller is senior executive editor who leads Informa TechTarget's remediation and optimization efforts.







