
Henrik Dolle - Fotolia
The top 5 enterprise advanced analytics use cases
Advanced analytics adoption has been growing across industries. The technology has many growing use cases in enterprises, but these are the top five.
The use of advanced analytics has been growing fast over the past few years as the technology keeps getting better, cheaper and easier to use. And demand will surge exponentially over the next five years, according to a report from Frost & Sullivan.
Deviki Gupta, senior industry analyst at Frost & Sullivan, said in the report that advanced analytics is expected to grow dramatically in the future as customers become more comfortable with analytics as a whole and use cases for the technology increase.
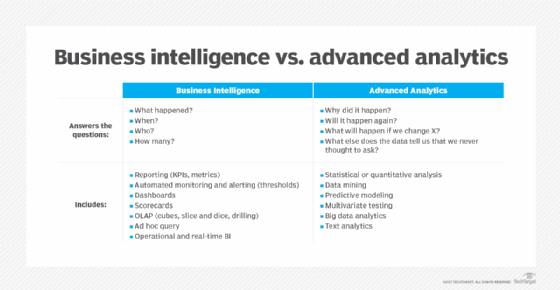
What is advanced analytics?
Advanced analytics is a category of analytical tools that use sophisticated techniques and tools to analyze data beyond those of traditional business intelligence platforms.
Advanced analytics uses machine learning, pattern matching, semantic analysis, network and cluster analysis, sentiment analysis and neural networks for tasks such as making predictions, identifying patterns, generating recommendations and discovering deep insights in data. Predictive and prescriptive analytics are a large part of the advanced analytics market.
Here are some of the top advanced analytics use cases for enterprises.
1. Customer service
Advanced analytics are being used in a wide variety of ways to improve customer service, and companies are feeling the benefits.
According to an insurance industry survey released earlier this year by Willis Towers Watson, the world's third-largest insurance brokerage and advisory firm, about 77% of insurance companies want to use advanced analytics on customer data and 54% are already analyzing that data.
And what is the top reason to apply advanced analytics? To speed up customer service.
And the positive results are already in. According to the survey, 68% of respondents are already seeing a positive impact on top-line performance due to their advanced analytics use -- and 86% are seeing a positive impact on bottom-line performance.
And the insurance industry is not alone.
According to a recent Forrester Research survey of analytics professionals, 47% of respondents used analytics to get new customers, 31% used it to improve customer retention, 28% used it to increase the lifetime value of customers and 23% used it to improve the customer experience.
The percent of companies that use advanced analytics for customer acquisition was up 14% from last year, Forrester analyst Brandon Purcell said.
"But many companies actually start with customer retention as [an advanced analytics] use case because companies typically have better data on their own customers," he added.
Analysts look at the historical data of customers who have left, feed it into a supervised machine learning model, then use the model to calculate risk scores for existing customers.
"You can optimize your retention efforts," he said. "Telcos are really good at this -- Verizon has a churn rate of less than 1% due to this. Their churn models are very robust. Banks too."
Nonsubscription businesses such as retail companies are also looking to use advanced analytics to improve retention by looking at historical data on customers who haven't shopped there in a certain period of time.
2. Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is the single largest industrial advanced analytics use case estimated to have made up over 24% of the total market in 2019, according to a report released last December by IoT Analytics. According to Deloitte Analytics Institute, predictive maintenance based on advanced analytics can increase productivity, reduce breakdowns and lower overall maintenance costs.
Royal Dutch Shell, for example, develops and maintains thousands of models to support predictive maintenance applications across thousands of pumps and valves on offshore oil rigs, said Doug Henschen, vice president and principal analyst at Constellation Research.
"That's a high-value use case because an outage on an oil rig could mean millions of dollars lost or, worse, environmental damage," he said.
3. Recommendations
Another high-value use case for advanced analytics is recommending products or services to customers. Amazon is the 900-pound gorilla here, but many other companies are putting recommendations to use to improve sales.
There are also startups that specialize in narrow applications of this technology.
The Climate Corporation, for example, is a digital agriculture company that helps farmers figure out what to plant and where and when to plant it, Henschen said. The company's seed advisor service collects historical data such as past crop yields and soil samples and combines it with other data sources -- including weather data -- and then runs it through thousands of different models, he said.
"It provides recommendations on what seeds to plant and when, how deep to plant the seeds, and how far apart to space the rows," Henschen said.
He said farmers who used this information were able to increase their yields by more than nine bushels per acre.
4. System optimization
Companies are using advanced analytics to optimize everything from supply chains to drug research to data center operations.
According to Dan Simion, VP of AI and analytics at Capgemini, one of the top advanced analytics use cases in enterprises is using pattern recognition to analyze trends in the use of IT resources, such as servers and networks and forecasting application usage and bandwidth requirements.
"The goal here is to not have customers who are unhappy because their applications don't work," he said. "One client of ours used AI-infused models to predict the number of licenses needed for different applications."
This use case was especially useful when the COVID-19 pandemic hit, he said.
"When they moved to working from home, it led to a surge of requests for video collaboration," Simion said. "With the AI-infused models, they were able to ensure they had the bandwidth and licenses to use the tools."
The healthcare sector has been the most impacted by COVID-19, and many organizations are using advanced analytics to address new challenges.
"We're seeing them use advanced analytics to analyze patient and hospital data, and visualize COVID-19 data from inside the organization, as well as research from outside sources," said Vijay Raman, VP of product management at Ibi, an analytics vendor that is currently in the process of being acquired by Tibco.
Ibi has recently worked with St. Luke's University Health Network in Pennsylvania to help them develop more than a hundred self-service applications that use advanced analytics. Raman said analytics are used on a global scale to track the impact of the virus and locally to support high-risk patients.
5. Product development
Advanced analytics is also being used to help create new products and services. Purcell said this is the most exciting emerging advanced analytics use case.
"Using the results of customer analytics to create a new phone or whatever customers may need," he said.
Analytics also can be part of the actual product or service, he added.
"In the world of IoT and connected devices, for example, how do we create products that can better track customers and improve engagement through the products themselves?" he said.
The future of advanced analytics
As advanced analytics continues to get easier and less expensive, we can expect to see many more use cases as the technology becomes more economically feasible.
"Fifteen years ago, the predictive analytics and data mining methods associated with advanced analytics typically showed up in high-value use cases," Henschen said.
Those high-value use cases include lending; fraud and risk analysis; insurance claims processing; and high-volume, high-value marketing use cases -- such as direct mail targeting and customer churn-risk analysis for mobile phone and cable companies.
"The model-development methods of the day were slow and manual and the required infrastructure costs were high," Henschen said. "As a result, it was not easy to spread the advantages of these techniques far and wide."
Today, data science platforms and cloud computing have reduced the costs and effort involved in creating and using models, he said. Advanced analytics are now being applied much more broadly across industry verticals, and for many new use cases within those industries.





