IBM IMS (Information Management System)
What is IBM IMS (Information Management System)?
IBM IMS (Information Management System) is a database and transaction management system that was first introduced by IBM in 1968. Since then, IMS has adapted to new programming tools and environments. IMS offers a low-cost way to manage and distribute data.
IMS is a major legacy database and transaction manager subsystem from IBM that runs on the z/OS mainframe operating system.
IMS systems facilitate storage, organization and retrieval of data. Today, IMS is used in numerous vertical markets, including banking, finance, healthcare, government, retail and manufacturing.
Java programs can access IMS databases and services. IMS applications and databases can also integrate with the Customer Information Control System (CICS) online transaction processing system and Db2 databases.
What components make up IMS?
IMS has two major components: IMS Database Manager (IMS DB) and IMS Transaction Manager (IMS TM). IMS DB data is organized into a hierarchy, where data in each level is dependent on the data in the next, higher level. The data is arranged so that its integrity is ensured and the storage and retrieval process is optimized. IMS DB Value Unit Edition (VUE) is a one-time-charge pricing option for eligible workloads that are used for virtualization and management in IMS and IBM Z.
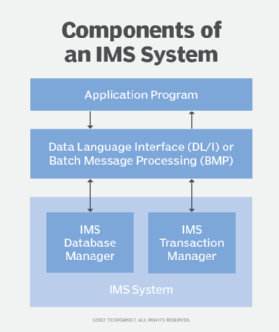
IMS TM controls input/output processing and provides formatting, logging and recovery of messages. It maintains communications security and oversees the scheduling and execution of programs. TM uses a messaging mechanism for queuing requests. IMS TM VUE, like IMS DB VUE, offers a one-time-charge pricing option. TM VUE manages new applications and workloads, as well as business growth on IBM Z. It offers application management, data storage and data access.
IBM IMS also has three forms:
- Full-function databases are used to store and access database fields. They have primary and secondary indexes and store data using Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM). Databases are accessed using Data Language Interface calls from an application program.
- Fast path databases are designed to optimize databases with high transaction rates. Data entry databases are an example of a fast path database, which is built on VSAM.
- High availability large databases are used to handle large data volumes to provide reliable data availability.
What are the benefits and features of IMS?
Even though IMS is an older tool, it is still updated and used today. Features and potential benefits of IMS include the following:
- provides different storage options for databases, depending on the database needed and amount of data;
- offers a value pricing option for IMS DB and TM;
- encrypts IMS and Db2 data;
- identifies different IMS workload performance anomalies;
- enhances data privacy during diagnostics; and
- provides Java Virtual Machine 64-bit support.
What current editions of IMS are available?
IMS version 15.2 is the most current edition. Along with updates to IMS DB VUE and TM VUE, IMS 15.2 introduces new features to aid in making digital transformations to the cloud.
Updates to IMS 15.2 include the following:
- support for more modern DevOps tools and programming languages, which adds flexibility for using IMS in the cloud;
- open access to IMS DB through Java Database Connectivity;
- two-way communication with external applications, enabled by IBM z/OS Connect Enterprise Edition;
- security features that enable management of customer data privacy, encryption of IMS data and the addition of overflow sequential access method (OSAM) encryption -- OSAM data is automatically encrypted;
- the option to remove identifiable information when sending diagnostic data to IBM;
- additional support for VSAM linear data sets and OSAM databases;
- the ability to import by NAME or NOCHECK, which enables database administrators and application and systems programmers to selectively import database descriptors;
- data privacy for diagnostics that is now supported for IMS 64-bit storage; and
- support to redact data in client data dumps, which helps protect data privacy during diagnostics.
History of IMS
IMS was developed in the 1960s to help support the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Apollo space program. IMS, which was initially released in 1966, was developed by IBM, Caterpillar Inc. and Rockwell International. Early versions of IMS served as a precursor to IBM's hierarchical database management system. Initially, IMS was used to inventory the bill of materials for the Saturn V moon rocket and Apollo space vehicle. But, by the 1970s, companies in many different industries -- including manufacturing, insurance and retail -- started using IMS. In the 1980s and 1990s, IMS was being used by the majority of banks and financial institutions. In the early 2000s, IBM stated that 90% of the top worldwide companies used IMS. Today, IMS is still widely used in Fortune 1000 and global companies.
Learn more about IBM z/OS, such as how it integrates with hybrid clouds.







