call tree
What is a call tree?
A call tree is a layered hierarchical communication model used to notify specific individuals of an event and coordinate recovery if necessary. A call tree is also known as a phone tree, call list, phone chain or text chain. Call trees play an important role in disaster recovery plans.
A call tree is a notification model, procedure or chain that shows how people will be contacted in case of an emergency or unusual incident as well as who will contact them. The call tree is distributed to all involved parties and stored in a location where it can be viewed or accessed by them.
A call tree is an important element of an emergency communications plan, which itself may be part of a disaster recovery plan. The communications plan might include both an automated emergency notification system and a traditional landline tree in case internet or cellular service is disrupted.
Call tree benefits include human interaction, the ability to relay important information and the creation of a comprehensive list of employee contact information.
In terms of format, the call tree may be as simple as a worksheet or word processing file with a tabular structure listing who calls whom. An easy-to-read format provides clarity and ensures that everyone understands the following:
- Who needs to be contacted in the event of an emergency.
- Who will contact whom (communications hierarchy).
- Contact details.
Furthermore, a concise call tree makes communications easier. It ensures all stakeholders can be contacted quickly and other relevant activities for disaster recovery can begin without delay.
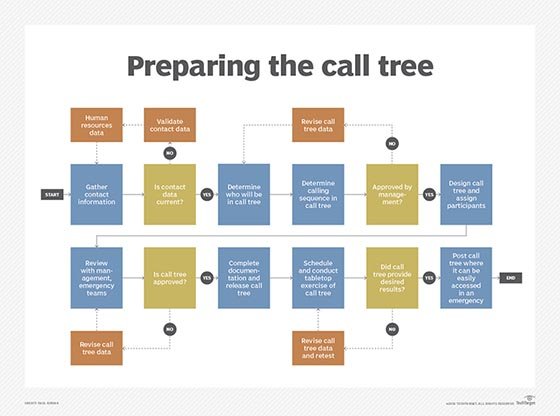
How call trees work
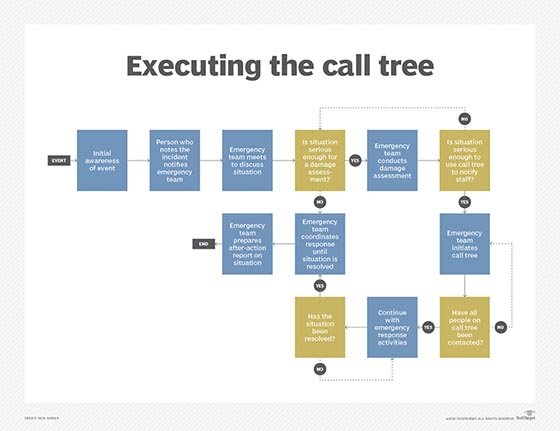
During an incident, the call tree is initiated once the incident response team has completed its assessment and determined that employees must be notified.
One employee or job function is designated to launch the emergency call tree. An organization should have an alternate call tree lead contact in the event the designated lead is not available.
As the call tree progresses, members should make note of the people they can't reach, as that data must be relayed back to the emergency team for follow-up.
To ensure calls were completed as planned, the last person on the list should confirm receipt of the final call to a designated employee. Another designee can serve as the communication list manager to monitor responses and contact backup staff if necessary.
Once the entire call tree has been notified, other business continuity plan procedures can proceed.
How are call trees created and tested?
The team creating the call tree coordinates data gathering with human resources, as contact data typically will be available from that department. Each listed employee may have several contacts, including office, home and cellphone numbers, and an email address.
The list of contacts and sequence of notification is then approved by the emergency management team and company management. The emergency call tree should be available in several locations, such as the company intranet and in hard-copy format, and someone should ensure the information is kept up-to-date.
After creating a call tree, it’s important to test it prior to implementation by doing a conference room tabletop test. Testing provides a critical check of the call tree procedure in the event of an incident. It also ensures everyone knows what to do when the emergency call tree is initiated, confirms the call tree procedure works according to plan and validates that contact information is correct.
A company can complete call tree testing on its own or perform it as part of a full-scale disaster recovery test.
During call tree testing, organizations generally adopt most or all of these guidelines:
- Ask designated callers to have recipients confirm other contact numbers.
- Record the start and end time of the call tree exercise to figure out how long it takes to contact each person and notify all stakeholders in the tree.
- Make the necessary corrections regarding contacts or contact information, such as new contacts, updated numbers and other necessary revisions.
- Create records for audit, employee training and call tree optimization purposes.
In addition to pre-implementation testing, regular testing of the call tree is also important. Regular testing ensures the notification chain is up to date and there are no missing or outdated numbers that may degrade tree performance or notification outcomes.
Automated vs. manual call trees
Smaller organizations will often use a manual call tree in which each person who receives a call contacts the next person on the list until everyone has been contacted. In the event the next person on the list cannot be reached, the caller continues with the next level of the phone tree to ensure the chain does not break.
The manual call tree procedure, while often simple and effective, may not be scalable and could take too long if there are many employees to be contacted. Phone-only methods are also not always sustainable or feasible. For example, cellphone coverage can be lost during an emergency, making it hard to contact everyone or ensure that everyone has been notified.
Most employees also use a variety of devices and media to communicate information. To ensure all of them can be contacted and updated, it’s important to account for their preferences. In some cases, text messaging may provide a more efficient way to reach someone than a phone call.
Automated phone trees provide a way to address these limitations. The automated method lets business continuity managers record a voice message that is then broadcast to employees. The manager can also configure the system to receive input from users in response to instructions, such as, "Press 2 if you need any assistance."
Call trees can be automated with software that contacts individuals using a landline, email, cellphone, text message or another type of communication. Because the automated method places calls simultaneously, this can reduce or eliminate possible breaks in the emergency call tree. The systems can keep track of all calls made and responses received.
Call tree automation software often provides functionalities beyond emergency notification:
- Conference calls.
- Person-to-person communication.
- Message center.
- Customer notification.
- Progress reporting.
- Employee reporting.
- Text-to-speech messaging.
Popular call tree automation software include the following:
- OnSolve.
- CallFire.
- CallMultiplier.
- RingCentral.
- HelpShift.
- AlertMedia.
See how to fortify emergency communications systems with a business plan as well as design and initiate a call tree procedure. Explore key elements of a crisis management plan.





