
A Stockphoto - stock.adobe.com
7 steps to fix a black screen in Windows 11
A black screen can be a symptom of several issues with a Windows 11 desktop. Knowing where to look for the source of the problem can simplify the troubleshooting process.
A black screen is a frustrating issue for Windows 11 users to encounter, and it can create cascading delays for IT support teams responsible for restoring access quickly.
Black screen issues in Windows 11 can be difficult to resolve. It's not because the fixes themselves are particularly complicated, but because of the time it can take to try different troubleshooting methods. Black screen errors, sometimes known as the black screen of death, can occur for many reasons, such as Windows updates, faulty applications, outdated drivers or malware infections.
As an IT administrator or desktop support professional, you'll have to narrow down the possible causes and prioritize fixes based on how and when the black screen appears.
The steps below are not strictly linear. In many enterprise environments, the fastest resolution comes from matching the troubleshooting step to when the black screen occurs -- for example, before login, after login or only when using an external display. Use the steps that best fit the symptoms you're seeing, rather than working through each one sequentially.
What can cause a Windows 11 black screen?
A black screen in Windows 11 can sometimes resolve itself before you ever figure out the cause. It might take many instances of trial and error to resolve the issue. When trying to identify what's behind Windows 11 black screens, you should consider the following possibilities:
- Windows OS. The operating system itself can be the cause of Windows 11 black screens. This is usually the result of faulty Windows updates, but corrupt or missing system files can also play a role.
- Applications and drivers. An outdated or malfunctioning application or driver can lead to black screen errors. Graphics drivers are particularly suspect when it comes to these errors.
- Configurations. Misconfigured settings can sometimes cause black screen issues. For example, the projection settings might be incorrect, or there might be a problem with the boot configuration data (BCD) store.
- Hardware. Internal components and peripheral devices can also cause black screens. For instance, a physical connection such as a monitor's cable might be loose, or the graphics card might not be in the right position.
- Malware. A malware infection might cause a system to behave erratically, and that erratic behavior can include black screens.
At best, black screen errors are an inconvenience that wastes time and causes user frustration. But it seldom stops there. Black screens can lead to lower productivity, the loss of unsaved work and even the permanent loss of data. To prevent these risks, be sure to troubleshoot and solve black screen issues as soon as possible.
How to troubleshoot and fix a Windows 11 black screen
If the system cannot reach the Windows login screen, most advanced troubleshooting steps require access to the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE).
If the black screen prevents you from logging in normally, accessing the system through the WinRE provides advanced recovery options such as Safe Mode and Startup Repair. In fact, many of the black screen troubleshooting steps are easiest to accomplish within WinRE.
The WinRE is a companion OS installed alongside the regular Windows 11 OS. It provides options for accessing, controlling and repairing the Windows 11 environment. However, getting to the WinRE can be difficult when you can't access the PC through the normal means. In this situation, you must use a workaround. Turn the computer off and then on several times. Each time you turn it off, hold the power button for about 10 seconds. After it's off, turn it back on. As soon as Windows launches, turn it off again. After the third restart, the computer should display the WinRE Automatic Repair screen. From there, click Advanced options, which takes you to the Choose an option screen (Figure 1).
The Choose an option screen lets you choose from the various options available for working within WinRE.
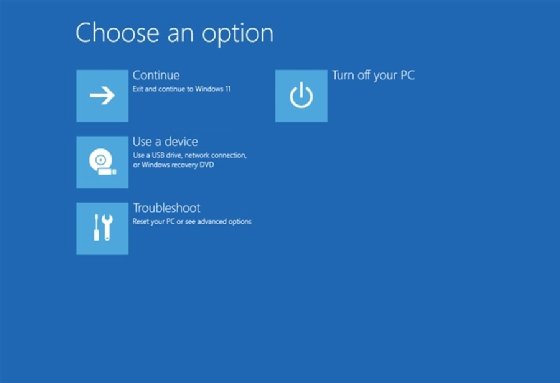
In most cases, you should select Troubleshoot to access the features you need when dealing with Windows 11 black screens. Clicking this option opens the Troubleshoot screen, where you can choose to either reset the PC or access more advanced features.
Next, select Advanced options. At the Advanced options screen, you can access startup settings, open the command prompt, uninstall updates and more (Figure 2).
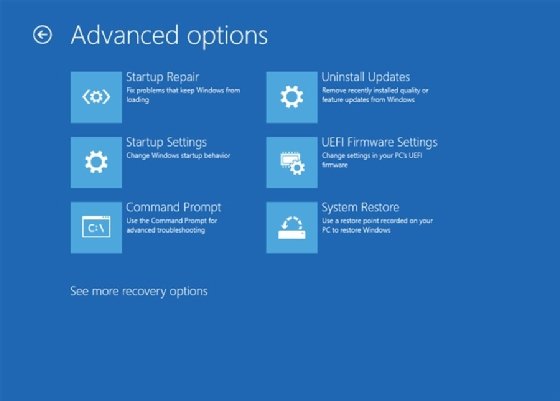
Clicking the Startup Settings option opens the first Startup Settings screen, which includes only one option: Restart.
Clicking Restart launches the second Startup Settings screen (Figure 3). This screen presents the three Safe Mode options, as well as options to enable or disable functions such as debugging and automatic restart.
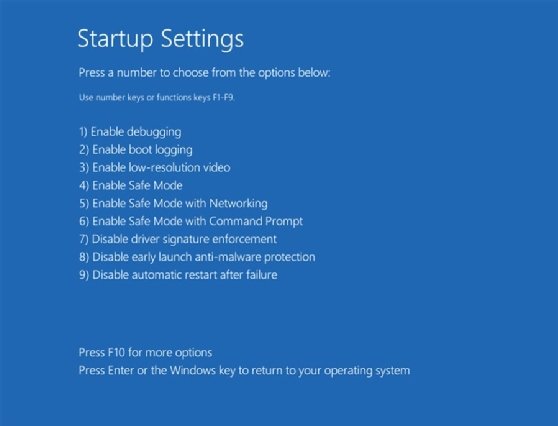
In most cases with black screen errors, you should go to Safe Mode from here. Safe Mode provides a pared-down operating environment for diagnosing and resolving performance issues such as black screens.
WinRE is one of the best tools available for troubleshooting Windows 11 black screen issues and other problems with the underlying computer. When attempting to address black screen errors, you should try these seven steps, performing them in the order that seems most appropriate to your circumstances.
1. Restart the computer
Whether the black screen issue began before or after login, you should first try to restart the computer. Sometimes all it takes is a simple reboot to get the system back on track. This step is most useful when the black screen appears intermittently or immediately after a recent update or restart.
If you can't restart the computer the normal way, try to access the power button by pressing Ctrl + Alt + Delete. This should bring up a mostly blank screen showing a list of options, with the power button in the bottom right corner (Figure 4).
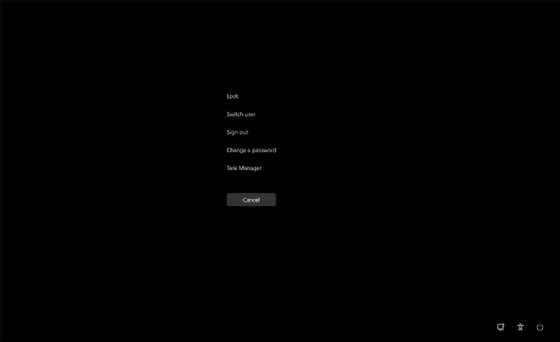
If this approach doesn't work, press and hold the power button until the computer shuts down. After that, try booting the computer normally. If this doesn't resolve the problem, work through the other steps.
2. Update, reset or remove applications
Black screens that occur after login -- especially when a cursor is visible -- often point to File Explorer, a startup application or a recently updated app.
In some cases, an application is the cause of black screen errors. However, it's not always third-party applications. File Explorer in Windows 11 can also cause black screen issues. For this reason, you should try to restart Explorer, especially if the black screen appears after login. For this, you'll need to open Task Manager, which you might be able to access by pressing Ctrl + Alt + Delete.
If you can reach Task Manager, you can restart Explorer by selecting Windows Explorer in the Task Manager window and moving your cursor to click Restart (Figure 5). Another option is to open explorer.exe as a new task in Task Manager.

If restarting Explorer doesn't work or isn't possible, confirm that Explorer is properly included in the Winlogon settings in the registry. You can do this in Safe Mode, if necessary. Open the Registry Editor and navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon. From there, make sure that the Value data for the Shell value under the Winlogon subkey is set to explorer.exe (Figure 6).

If the black screen issue started after the installation of a new app, you might need to uninstall the app in Safe Mode. You should be able to launch Safe Mode even if a faulty application is causing black screen errors. Once in Safe Mode, use the Apps & features option to remove the application.
3. Verify system configurations and settings
On systems that use multiple displays, docking stations or custom boot configurations, it's common for black screen issues to stem from misconfigurations.
Incorrect projection settings are a possible reason for black screen errors. If the black screen doesn't prevent the PC from displaying the projection settings, you can access them with the command Win + P (Figure 7). Correcting any misconfigured settings might fix the black screen problem.

You might also be able to resolve black screen issues by rebuilding the BCD store, which can sometimes become misconfigured or corrupted. The BCD contains information about boot applications and boot application settings. Microsoft provides the bootrec command-line utility to troubleshoot and repair Windows BCD (Figure 8). This includes rebuilding the BCD store. However, you should be familiar with the bootrec utility and how the command options work before rebuilding the BCD.
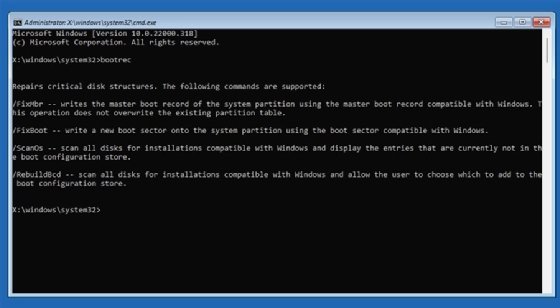
The Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool and the System File Checker (SFC) can also be helpful when troubleshooting Windows 11 black screen issues. You should run the DISM scan first, and then run the SFC scan. Together, these tools can help identify and replace missing or corrupted Windows 11 system files, which can sometimes cause black screen problems.
4. Examine the hardware devices and their connections
In managed Windows environments, problems with hardware or drivers -- display drivers, in particular -- are one of the most common causes of persistent black screen issues.
You should update, disable or uninstall drivers wherever you suspect they might be causing problems. To do this, use Device Manager when in Safe Mode. If you're updating a driver, you'll likely need to use Safe Mode with Networking.
The display driver is often behind black screen errors, so it's usually a good place to start when evaluating hardware drivers. In some cases, you might be able to resolve black screen issues by simply restarting the graphics driver in a normal Windows environment. To do this, press Win + Ctrl + Shift + B.
If you don't think a driver is the cause of the black screen, you should look to the hardware itself. First, unplug any peripherals that aren't necessary and then restart the computer to see if that helps. If that doesn't work, check all physical connections, unplugging them and then reconnecting them as necessary. Make sure that all graphics cards sit firmly in their respective slots and that all internal components are free from dirt and dust. If a spare is available, you can try replacing the monitor as well. It can also be useful to run diagnostics against the memory, storage and other components to verify that they're operating properly.
5. Scan for malware
If the desktop has been exhibiting other unusual behavior besides the black screen, malware is a likely cause.
Computers sometimes experience black screen problems because of a malware infection. For this reason, you should scan the system to ensure that there are no signs of infection. Malware can cause far more damage than just black screens, so you must identify and deal with any possible malware infections as quickly as possible.
6. Add or remove Windows updates
In some cases, you can address black screen issues by applying a Windows update that might have failed or been deferred. If you have direct access to the computer that's experiencing problems, you can use the Windows Update feature in Settings to view the update history and check and install any pending updates (Figure 9).

If you're using Safe Mode for troubleshooting, you won't be able to run Windows Update in that environment. Instead, install the updates after restarting Windows normally.
Black screen errors might be the result of a recent Windows update. If the problems started after an update, you can use the Uninstall Updates option in WinRE to roll back the update.
From WinRE, you can choose to roll back the last quality update or feature update. If you want to do both, you should do only one at a time and restart the computer normally after each one to see whether it fixed the problem.
IT support teams should also be sure to align update installation and rollback with organizational patching and change management policies.
7. Repair, restore or roll back Windows
You can use other WinRE options to try to address black screen issues as well. One of these is Startup Repair, which can help fix problems with the Master Boot Record, partition table or boot sector. It will also remove the most recent update if it immediately preceded a startup failure. When you click the Startup Repair option in WinRE, the repair feature automatically starts diagnosing the system.
You can also use WinRE to roll the computer back to a specific point in time, assuming that there are restore points on the computer. The System Restore utility makes it possible to revert the system to a restore point that was created before the black screen issues started. This won't remove any personal data, but it will remove any updates, drivers or apps that users have installed since the time of the restore point.
If you're unable to resolve black screen issues through other approaches, you might need to reset Windows 11, which returns the OS to its original factory settings. To get started, select Reset this PC in WinRE, which will take you to the Choose an option screen. Here, you can choose to either retain personal files or remove all personal files, settings and applications.
If resetting the OS doesn't work, the last troubleshooting option is to reinstall Windows 11, which means reinstalling all applications and reconfiguring all settings. It might be possible to roll back to Windows 10, but only if the Windows 11 upgrade occurred within the past 10 days. However, you might still be able to install Windows 10 rather than Windows 11 if you determine that reinstallation is the only viable option.
When troubleshooting Windows 11 black screen issues, the goal is to restore user access as quickly as possible while minimizing unnecessary disruption. Matching the troubleshooting approach to the symptoms enables IT teams to prioritize the most effective actions under real-world constraints. This further helps reduce downtime, standardize response and lower the likelihood of recurrence across managed environments.
Editor's note: This article was updated in February 2026 to reflect technology changes and to improve the reader experience.
Robert Sheldon is a freelance technology writer. He has written numerous books, articles and training materials on a wide range of topics, including big data, generative AI, 5D memory crystals, the dark web and the 11th dimension.






