
Tierney - stock.adobe.com
Broadband vs. Wi-Fi: What's the difference?
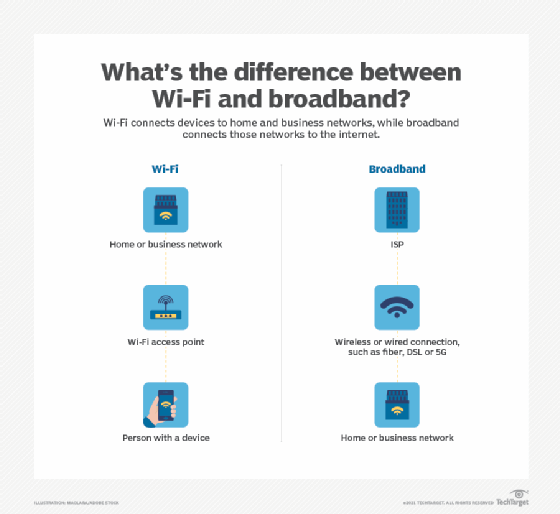
Broadband and Wi-Fi are common technical terms often used interchangeably -- although they shouldn't be. Both provide connectivity, but they do so in different ways.
It's not uncommon for non-network professionals to use the terms broadband and Wi-Fi interchangeably. However, although both are networking technologies, the two words are quite different.
Fortunately, it's easy to grasp key differences with a clear understanding of each term's characteristics.
What is broadband?
Broadband is a connection to the internet. This is also often referred to as internet broadband. ISPs deliver broadband to homes, businesses or broadband-capable devices using multiple different methods. Common examples include copper or fiber Ethernet, cable, DSL, mobile 4G or 5G, and fixed satellite technologies.
An ISP can also deliver broadband over a fixed wireless connection in certain situations. However, ISPs deploy most broadband installations using a wired connection to connect a home or business to the internet.
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi, on the other hand, is the name used to describe a suite of IEEE wireless technology standards within the 802.11 specification. Examples of popular Wi-Fi standards from the past and present include 802.11b, 802.11n, 802.11ac and 802.11ax. More recently, a few of the more popular Wi-Fi standards used at home and in the enterprise adopted the following simplified naming convention:
- Wi-Fi 4 = IEEE 802.11n
- Wi-Fi 5 = IEEE 802.11ac
- Wi-Fi 6 = IEEE 802.11ax
Most businesses deploy Wi-Fi access points (APs) throughout their buildings as a convenient form of wireless network edge connectivity. Nearly all modern laptops, tablets and other smart devices come with a wireless chip and antenna compatible with one or more Wi-Fi specifications. Thus, instead of connecting over a wired connection, such as Ethernet, a user can enable a device's built-in wireless chip to connect to the corporate network over Wi-Fi.
Broadband vs. Wi-Fi: When to use each term
The connection to the corporate network is where many people get confused about when to use the terms broadband vs. Wi-Fi.
Thus, when the internet broadband connection is down or having intermediate connectivity issues, network engineers will often hear comments such as, "The Wi-Fi is down." However, the wireless connection between the endpoint and the corporate AP is likely operational. End users can still access applications, data and services hosted within the corporate network itself, but the broadband connection the end user needs to access may be having problems.
Because many modern businesses rely on public cloud infrastructure to deliver business applications and data, some users conflate broadband and Wi-Fi, as both can affect access to business applications and data. However, one path -- Wi-Fi -- connects users to the corporate network, while the other, broadband, connects the corporate network to the internet.








