What is a cloud radio access network (C-RAN)?
A cloud radio access network (C-RAN) is a centralized, cloud computing-based architecture for radio access networks. The C can also stand for centralized or collaborative.
A C-RAN is an evolution of the current wireless communication system and enables large-scale deployment, collaborative radio technology support and real-time virtualization capabilities. It uses the latest Common Public Radio Interface standard, coarse or dense wavelength-division multiplexing technology, and millimeter wave (mmWave) transmission for long-distance signals.
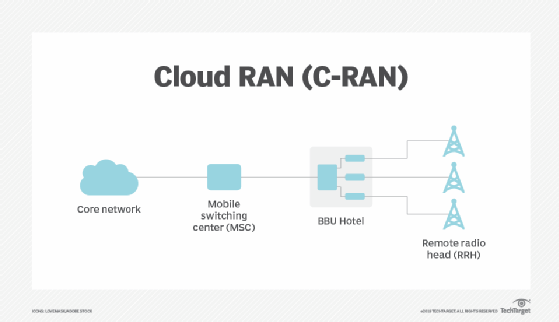
A RAN establishes a connection or communication between base stations and end users. In C-RAN architecture, baseband units relocate from individual base stations to a centralized control and processing station, known as a BBU hotel.
The BBU hotel connects to the network with high-speed optical fiber and maximizes the distance between cells. This type of cloud computing environment operates on open hardware and network interface cards that dynamically handle fiber links and interconnections within the station.
C-RANs are significant for the progression of wireless technology, such as 5G and the internet of things. The transition from LTE to 5G networks relies heavily on C-RAN development. It also provides a cost-effective, manageable approach to support more users.
C-RAN components
C-RAN networks comprise the following primary components:
- BBU hotel. This is a centralized site that functions as a data or processing center. Individual units can stack together without direct linkage or interconnect for dynamic resource allocation based on network needs. Communication between units has high bandwidth and low latency.
- Remote radio head network. Also known as a remote radio unit, RRH is a traditional network that connects wireless devices to access points.
- Fronthaul or transport network. Also known as a mobile switching center, a fronthaul or transport network is the connection layer between a BBU and a set of RRHs that use optical fiber, cellular or mmWave communication.
Advantages of C-RAN
Benefits of C-RAN include the following:
- Higher spectrum efficiency.
- Less hardware, which makes networks more cost- and footprint-effective.
- Lower heating, cooling and power requirements.
- A more simplified, scalable and flexible network.
- Support for more mobile users and wireless standards.
- Efficient network upgrades, enhancements, testing, monitoring and maintenance.
- Pooled resources and reusable infrastructure.
- Faster speeds than distributed RANs.
- Cloud computing open platforms and real-time virtualization dynamically allocate shared resources between BBUs.








