logical network
What is a logical network?
A logical network is a software-defined network topology or routing that is often different than the physical network. It appears to the user as a single, separate entity, although it might, in fact, be either an entity created from multiple networks or just a part of a larger network.
Logical network is a broad term that can be used for many different technologies and protocols. As a shorthand way to understand logical networks, think that the word logical means "the way the devices on the network see it."
Physical networks consist of discrete components, such as interfaces, cables and switches. These are usually relatively simple and easy to visualize and explain. As networks and networking equipment became faster and more complicated, it became possible to change how data moved through a physical network with software changes. The term logical network is used to refer to any situation where the network as seen by the computers and data flow is different than the physical network.
As an example of a logical network, imagine an organization wants to have a computer and a network voice over IP (VoIP) phone on each user's desk. Both the computers and VoIP phones use Ethernet for data transfer, but they need access to different resources and services.
One option would be to use two completely different physical networks with separate cables and switches for computers and VoIP phones. This would be costly and difficult to maintain. The better option is to use two different logical networks, separated by virtual local area networks (VLANs), that use the same underlying physical network. The network can be configured so that all the computers go on VLAN 1, and all the IP phones go on VLAN 2. The network routers manage the traffic so that, as far as the devices can tell, they are on separate networks.
Modern networks are complicated and can be different than the physical network. The use of virtual private networks (VPNs), software-defined networking (SDN) and virtual networks makes it so that understanding the logical design of a network is more important than the physical design. This is documented on a logical network diagram.
What are uses for logical networks?
Logical networks have several different uses, including the following.
Network segregation
Network administrators may want to separate one type of traffic from another. This can be separating trusted traffic from public -- for example, corporate Wi-Fi from public guest Wi-Fi. These separate networks may have different access, routing or priority rules assigned -- perhaps, giving the VoIP traffic higher quality of service (QoS) priority than data traffic.
Server or storage area network traffic may exist on a separate logical network than regular data traffic.
Logical network segregation is not infallible, though. It can be misconfigured or attacked to allow data between the logical networks improperly, such as in VLAN hopping. Therefore, some life safety or extremely sensitive networks are air-gapped using separate physical networks.
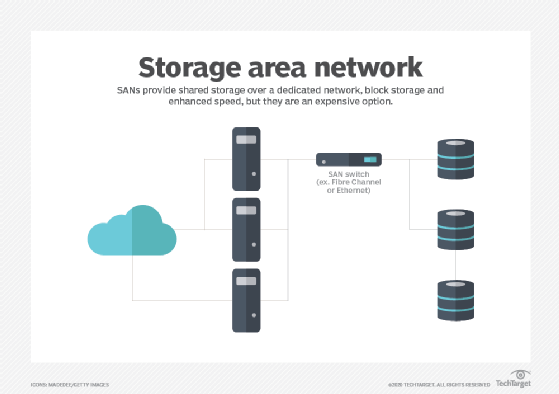
Network combination
One large logical network can be made by combining smaller networks with software. An organization may have two offices in different cities, each with a physical network. A VPN link can be set up over the internet to connect the two networks.
To any clients on these networks, it would appear to be one large logical network, even though there is no single physical connection between the physical networks. Next Hop Resolution Protocol can be used by routers to automatically route traffic in an organization to combine smaller networks into one large logical network.
The internet itself can be thought of as one large logical network, even though it is composed of many different smaller networks. Protocols like Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) provide the logic that keeps them working together and directs the data traffic.
Virtual networking
Virtual machines (VMs), container services and cloud services may have entirely virtualized networking.
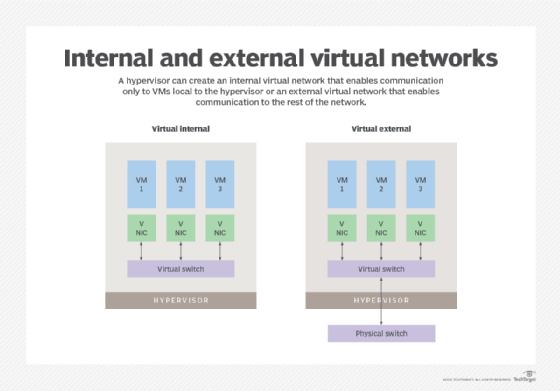
One single physical server may have dozens or even hundreds of VMs or containers running on it. It would be impossible to give each VM its own physical network connection. Also, if one VM wanted to send data to another over the physical network, it could be slow.
Virtual logical networks can be set up to enable these VMs and containers to communicate. A single physical network connection can also be split into many logical network connections for each device to use.
Read about the 12 most used network protocols, as well as their purposes and use cases. Learn from experts discussing stretched VLAN use cases, and see how to set up a VLAN for enterprise networks. Explore the differences between VPN vs. VLAN, and learn about network virtualization benefits in the LAN, wide area network and data center.








