HDD form factor (hard disk drive form factor)
What is an HDD form factor (hard disk drive form factor)?
HDD form factor (hard disk drive form factor) is the size or geometry of a data storage device equipped with one or more magnetic-coated spinning platters and one or more moving actuator arms with magnetic heads to read and write information.
The form factor of an HDD refers to its size, measured in inches. HDDs are available in various form factors, such as 2.5-inch, 3.5-inch, 5.25-inch and 8-inch. It's important to note that the HDD size refers to the diameter of the disks and not the size of the external housing or enclosure, which is larger.
The HDD form factor determines the storage device's physical compatibility with the drive bays in a storage array or enclosure, server, desktop or laptop computer, consumer electronics product or any other type of computing system. Industry standards dictate options for the length, width and height of HDDs, as well as the position and orientation of the host interface connector.
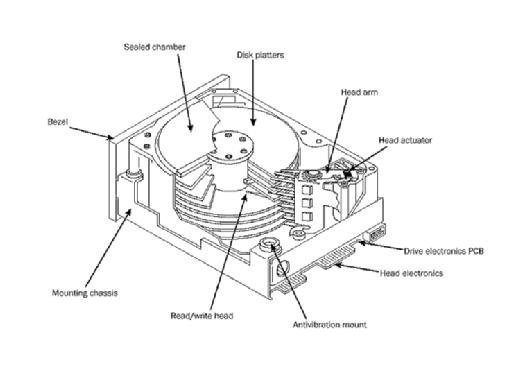
Available HDD form factors
The most common HDD form factors in enterprise systems are 2.5-inch, also known as small form factor, and 3.5-inch, or large form factor. The 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch measurements represent the approximate diameter of the platters within the drive enclosures. Enterprise-class HDD enclosures typically have a standard length and width.
The 3.5-inch desktop HDD form factor offers a range of height options, from 19.9 millimeters to 26.1 mm. The 2.5-inch HDD form factor devices range in height from 5 mm to 15 mm. Two of the most popular mobile form factors are single-platter 7 mm and dual-platter 9.5 mm. The 3.5-inch HDDs for desktop and 2.5-inch HDDs for laptops may have Integrated Device Electronics or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) interfaces.

In the past, HDDs were available with 8-inch form factors, meaning their size was similar to the now-obsolete 8-inch floppy disks. The smaller 5.25-inch HDDs were later developed by companies like Seagate. These drives were standard in most PCs in the 1980s and 1990s until they were superseded by the smaller and quieter 3.5-inch form factor HDD.
HDDs with small form factors, like 1.8-inch and 1-inch, were once available, generally used in specialized implementations. For example, 1.8-inch HDDs were used in some audio players, while 1-inch HDDs were designed to be housed inside a CompactFlash II slot. Optical drives, such as CD or DVD drives, typically used the 5.25-inch HDD form factor.

What is the HDD form factor used in laptops?
Portable devices, like laptops, typically use HDDs with a 2.5-inch form factor. The 2.5-inch form factor is also used to package solid-state drives (SSDs). The 2.5-inch HDDs are smaller and quieter than drives in larger form factors (3.5-inch and up). But 2.5-inch HDDs tend to have lower capacities and smaller memory caches, although they consume less power than larger HDDs.
Modern 2.5-inch HDDs for laptops are also built to be vibration- and drop-resistant. Many come with built-in accelerometers that detect drops and other potentially damaging actions in order to safely park the drive head and protect the drive from damage. Accelerometers and other systems are rarer in larger HDDs because these HDDs are designed for computing systems that are not meant to be portable -- e.g., desktop computers and servers -- and, therefore, unlikely to suffer damage from extreme vibrations or drops.
HDDs with 2.5-inch form factors may also be used in desktop PCs since they perform at levels comparable to 3.5-inch HDDs. However, a dedicated mount is advisable to protect the system from vibrations and damage.

What is an SSD form factor?
SSDs use flash memory, which is a type of semiconductor-based memory. SSDs are non-volatile, meaning they retain stored data even when power is removed and they are turned off. Compared to HDDs, SSDs are smaller and lighter.
Unlike traditional mechanical HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts and store data inside an integrated circuit. The lack of moving parts means that SSDs are quieter and cooler than HDDs and offer lower latency and time to access stored data. Most modern desktop PCs and laptops now come with SSD storage.
SSDs are now available in many form factors. The two main form factors are the following:
- Mini SATA III (mSATA III) and SATA III. These legacy SSDs provide a lower throughput than Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) and non-volatile memory express (NVMe) SSDs.
- PCIe and NVMe SSDs. These newer SSDs deliver high data transfer speeds and lower latency and include controls to prevent the computer system from overheating.
Many SSDs are designed for the HDD form factor. SSDs that fit into the same slots as HDDs generally use the SATA or Serial-Attached Small Computer System Interface (SAS) to transfer data to and from the host computing system.
Compare SATA vs. SAS HDD specifications, and explore the meaning of mean time to failure, annual failure rate and unrecoverable error rate for different classes of drives.






