What is an mSATA SSD (mSATA solid-state drive)?
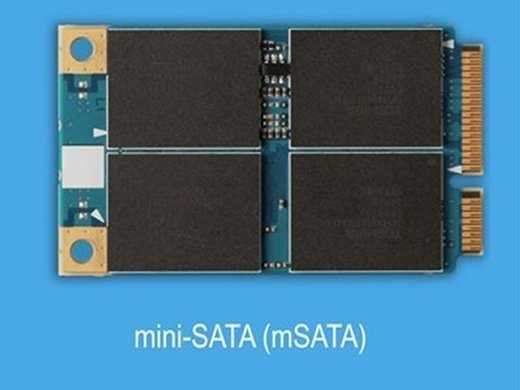
An mSATA SSD is a solid-state drive that conforms to the Mini Serial Advanced Technology Attachment interface specification developed by the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO). It has a smaller form factor than a standard SSD and is designed for use with portable, power-constrained devices, such as laptops and tablets.
Advantages of mSATA SSDs include a small form factor, lower power consumption than a standard SSD, shock and vibration resistance, and fast boot and shutdown capabilities. The maximum bandwidth of an mSATA SSD is 6 gigabits per second (Gbps), which is equivalent to the SATA 3 standard.
How is mSATA used?
The SATA interface is a standardized and low-cost way to attach storage devices to a computer's system bus. SATA supports device hot plugging, and SATA drives can be directly controlled from the system BIOS or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface.
These drives can easily fit into most desktops and even laptops and notebooks. However, they cannot fit in slimmer or smaller devices, such as ultrathin laptops and tablets. Because those devices require compact drives with a smaller form factor than standard SATA drives, the mSATA SSD form factor was developed. MSATA SSDs offer the same data transfer rates as SATA. Additionally, these devices can act as cache drives, speeding up access to frequently used data and applications.
An mSATA SSD flash storage device is commonly used in commercial products, such as digital signs, point-of-sale devices, retail kiosks and multifunctional printers. It can also be found in older laptops and devices. However, mSATA SSDs are increasingly being replaced by M.2 SSDs.
Examples of mSATA devices
Although often replaced by M.2 SSDs as noted, mSATA SSDs can still be found in the following devices:
- Notebooks.
- Tablets.
- Phone conference systems.
- Global Positioning System devices.
- Automated care devices.
- Electronic patient records systems.
- Drive caches.
- Electronic smartboards.
What are mSATA features?
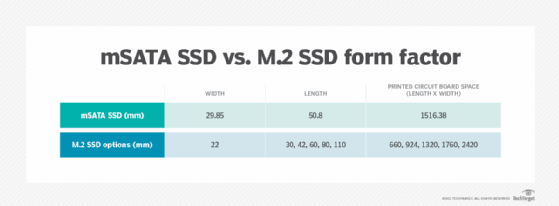
As an internal solid-state drive designed with lightweight construction in mind, an mSATA SSD is 50.8 mm x 29.85 mm x 4.85 mm. It is roughly the size of a business card. These SSDs support all three revisions to the SATA interface specification. They are also characterized by these features:
- Speed. Read/write speeds can reach up to around 550 megabits per second and 520 Mbps, respectively. MSATA SSDs have a maximum bandwidth of 6 Gbps.
- Capacity. Storage capacity options typically range from 8 gigabytes to 512 GB, but mSATA SSDs can also range up to 1 terabyte or 2 TB, which is comparable to some newer solid-state storage devices.
- Reliability. MSATA SSDs provide reliable data storage and can last from 1.5 to 2 million hours. They can also be made resistant to external shocks and vibrations by adding a protective coating or case.
Some mSATA drives can also include end-to-end data protection to maintain data integrity and availability. Others may include error correction codes and cyclic redundancy checks to detect errors in transmitted data.
How do you test mSATA?
Users can test mSATA SSDs with software tools. These tools can determine if an SSD is faulty, providing either a pass or fail result. Most health check tools can examine both sequential and random read/write speeds, power consumption, file transfer speeds and general performance.
But not every test tool has these features, and not every test tool can test every SSD. So, it is best to check the testing software's description before downloading. For example, Samsung Magician can be used to test all Samsung memory products, including SSDs, memory cards and USB flash drives. However, it may not work well with SSDs from other manufacturers.
Samsung Magician -- the latest version, as of April 2025, is v8.3 -- works with many different operating systems. It provides an intuitive interface, drive status indicators and numerous customization features to help users test their Samsung mSATA SSDs and find opportunities to improve drive performance.
Other tools are also available for testing and monitoring SSDs, including mSATA SSDs. One popular tool is the free and open source CrystalDiskInfo app.
What is the difference between SATA vs. mSATA?
SATA-IO started developing the mini interface connector in 2009. The mSATA specification emerged in 2011 as part of SATA revision 3.1. SATA itself has been around since 2000. Vendors that contributed to the mSATA specification include Dell EMC, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Lenovo, Samsung, Sandisk, Toshiba and sTec Inc., which was acquired in 2013 by HGST, a Western Digital company.
SATA-IO initially referred to the specification as mini-SATA, later changing its name to mSATA. The mSATA specification describes how to map SATA signals onto a Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) mini card connector to enable use with a wide range of applications. All SATA and mSATA connectors adhere to the same SATA-IO requirements, minimizing compatibility issues.
Like SATA, mSATA uses the ATA command set to transfer data between a host computer and a target storage device. The main differences between an mSATA SSD and a SATA SSD are physical size and the connector. With a bulky, 2.5-inch casing, SATA drives are thicker than mSATA drives. For this reason, SATA SSDs can only be used in bigger devices.
On the other hand, the smaller form factor of mSATA SSDs can be both an advantage and a limitation. Smaller devices benefit from mSATA drives. However, their small size also means that these SSDs typically offer less storage capacity than a SATA SSD. That said, they offer similar read/write speeds to SATA drives.
What is the difference between M.2 SSDs vs. mSATA SSDs?
Like mSATA SSDs, M.2 SSDs are also small form factor, high-performance storage devices for use with small devices, such as notebooks and tablet computers. In fact, M.2 drives are even smaller than mSATA, making them suitable for especially thin devices. M.2 SSDs are also used in client devices and, to a lesser degree, in enterprise storage systems. Many modern gaming laptops also use M.2 SSDs due to their small size.
The M.2 form factor emerged in 2013, a few years after mSATA, with the goal of superseding the mSATA format. The PCI Special Interest Group consortium of technology vendors defined the M.2 specification.
Some of the differences between M.2 and mSATA SSDs are the following:
- MSATA SSDs only use the SATA interface. M.2 SSDs also support SATA Express (SATAe), which enables SATA or PCIe connectors. The SATAe-based M.2 drive tells the host if it is PCIe or SATA.
- M.2 SSDs support non-volatile memory express, which can boost performance and reduce latency over devices that use the ATA or Small Computer System Interface command set.
- The M.2 form factor offers many different sizes, compared to mSATA SSDs, which ship in only two sizes. Half-size mSATA SSDs are 30.1 mm x 26.8 mm and provide higher read/write times than mSATA.
- An M.2 SSD is faster, as it can extend the data rate beyond the 6 Gbps limitation of an mSATA SSD. A PCIe-based M.2 SSD can support up to four lanes of PCIe, with a theoretical transfer rate of up to 20 Gbps.
- M.2 drives typically have higher storage capacities than mSATA drives.
What is the difference between mSATA vs. mini PCIe?
An mSATA SSD is similar in size and appearance to a mini PCIe card, and both can physically fit into the same mPCIe slot on the motherboard. But their similar size and form factor can cause some confusion.
MPCIe cards can be used to connect wireless adapters, solid-state device storage and other performance boosters for laptops and mobile devices. PCIe is a point-to-point technology in which each serial link has a full-duplex pair of differential signals, known as a lane. PCIe supports up to 32 lanes, but mPCIe supports only one.
MPCIe uses PCIe signals for desktop expansion cards, while mSATA uses the SATA storage interface for SSDs. MSATA SSDs also use the SATA storage bus interface and must have a direct connection to the SATA host controller. Meanwhile, mPCIe cards support PCIe and USB signals.

Even though an mSATA card can be slotted into an mPCIe slot, they are not compatible devices. They do not work properly if switched because of each use's different connection protocols. But using a SATA host controller can make some mSATA cards compatible with mPCIe slots.
Explore our flash memory guide to architecture, types and products. Check out this primer on SSD response time and other performance benchmarks.







