solid-state
What is solid-state?
Solid-state is a common descriptor used to refer to electronic components, devices and systems based entirely on semiconductor materials such as silicon, germanium or gallium arsenide. The term solid-state was especially prevalent in the late 1950s and early 1960s, during the transition from vacuum tube technology to the diode and transistor.
Solid-state systems rely heavily on diodes and transistors, which are two of the most common types of solid-state devices. Diodes and transistors come in multiple forms and support various types of switching functions. Diodes can also serve as rectifiers, which means they can convert currents from AC to DC.
Transistors can also serve as rectifiers, but more importantly, they can provide amplification, something diodes can't do. To implement amplification, the transistor uses an external power source that magnifies the signal.
NOR and NAND (see video above) are two common types of memory based on solid-state technology.
A diode, which has two terminals, allows current to flow in only one direction, while blocking the flow from the other direction. Common examples include laser diodes, P-N junction diodes and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). A transistor has three terminals and can pass current between resistance regions, providing more versatility than diodes. Common examples include bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs).
Solid-state and integrated circuits
Transistors and diodes are often combined with resistors, capacitors and other components to create the integrated circuit (IC). Also referred to as a chip or microchip, the IC is a solid-state device that binds the individual components to a thin substrate of semiconductor material. The IC then connects them all together and packages everything into a miniaturized electronic circuit. Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including cars, airplanes, microwaves, televisions, smartphones and, of course, computers.
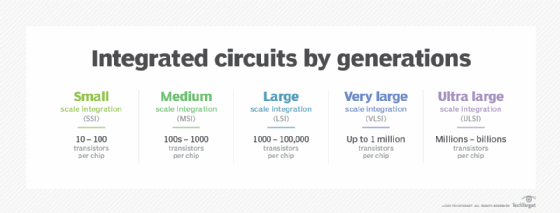
In a solid-state component, the current is confined to solid elements and compounds engineered specifically to switch and amplify the current, which can flow in one of two ways: as negatively charged electrons or as positively charged electron deficiencies called holes. In some semiconductors, the current consists mostly of electrons; in other semiconductors, it consists mostly of holes. Both the electron and the hole are called charge carriers.
Solid-state storage
Solid-state systems have no moving parts, making them more portable, efficient and durable than their mechanical counterparts. For example, today's solid-state drives (SSDs) typically use NAND chips to provide flash-based storage.
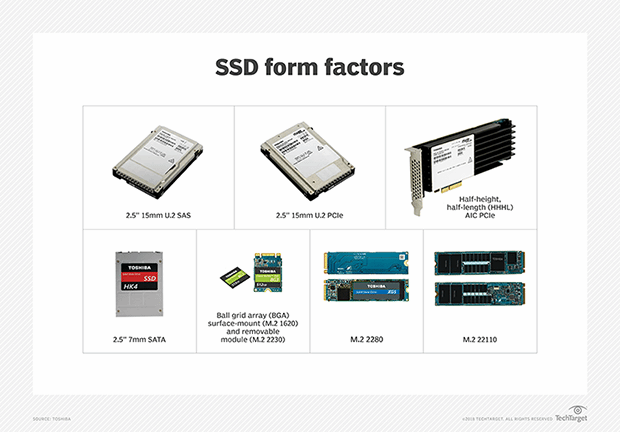
Data is stored on ICs, rather than on mechanical components. This is much different from the hard-disk drive (HDD), which relies on spinning disks and other moving components to read and write data.
Read this guide on flash memory architecture, types and products, and learn how to choose between NOR and NAND flash memory.
