byte
What is a byte?
In most computer systems, a byte is a unit of data that is eight binary digits long. A byte is the unit most computers use to represent a character such as a letter, number or typographic symbol.
Each byte can hold a string of bits that need to be used in a larger unit for application purposes. As an example, a stream of bits can constitute a visual image for a program that displays images. Another example is a string of bits that constitute the machine code of a computer program.
Byte is abbreviated with an uppercase B.
Bytes in computer processing and programming
In some computer systems, four bytes constitute a word, a unit that a computer processor can handle efficiently as it reads and processes each instruction. Depending on the capabilities, some computer processors can handle two-byte or single-byte instructions. Language scripts can sometimes require two bytes to represent a character. These are called double-byte character sets.
How many bits in a byte?
A bit is represented by a lowercase b. While a byte can hold a letter or symbol, a bit is the smallest unit of storage, storing just one binary digit. The standard number of bits in a byte is eight, but that number can vary from system to system, depending on the hardware.
Fred Brooks, an early hardware architect at IBM, project manager for IBM's OS/360 operating system and author of The Mythical Man-Month, credits Werner Buchholz for originating the term byte in 1956 when working on IBM's Stretch computer. Initially, there could be one to six bits in a byte because the equipment at the time used 6-bit pieces of information. The change to eight bits in a byte occurred later in the same year with OS/360 circulating the new standard.
Another unit of data representing eight bits is an octet. Unlike a byte, an octet always consists of eight bits, no matter the architecture. Octets, as a measurement, can help avoid possible ambiguity associated with bytes, particularly with legacy systems, but the terms are often used synonymously.
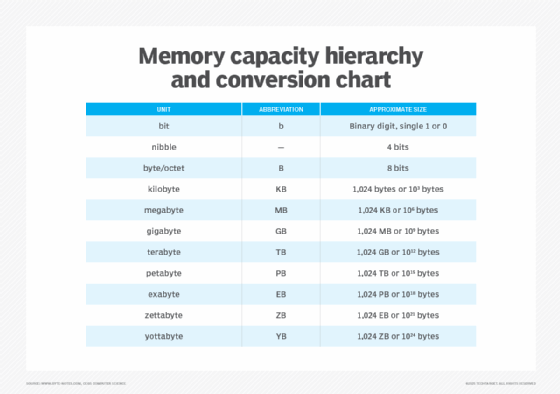
A nibble, or quadbit, refers to four bits, or half of a standard byte/octet.
Types of bytes
While bytes are measured in bit multiples, computer storage is typically measured in byte multiples. In many computer architectures, a byte is the smallest addressable unit of memory. For example, an 820 megabyte (MB) hard drive holds a nominal 820 million bytes of data.
Due to massive increases in storage capacity over time, there are now eight additional units of measurement following the byte. The eight different types of bytes currently used in computer architectures range from kilobytes (1,024 bytes) to yottabytes (1,024 zettabytes).
Byte multiples can be measured using two systems: base-2 or base-10. A base-2, or binary, system is commonly expressed as a rounded off decimal number. One megabyte (1 million bytes) is actually made up of 1,048,576 bytes by the base-2 definition.
A base-10 system states that bytes for computer storage should be calculated as powers of 10. In that system, 1 MB would be 1 million decimal bytes. This system is now most common among manufacturers and consumers. While the difference between the base-2 and base-10 systems was once fairly insignificant, as capacity has increased, the discrepancy has widened considerably.
Prefixes
Understanding the prefixes used with bytes can help further identify the size of a byte. Commonly used prefixes include kilo-, mega-, giga- and tera-.
A kilobyte (KB) is equal to 1,024 bytes. A small email could be considered around 2 KB and a three-page paper around 25 KB.
Megabytes (MB) are equal to 1,048,576 bytes. For normal quality audio, a song is about 3-4 MB -- about 1 MB per minute. A high-quality photo may be about 2-5 MB.
A gigabyte (GB) is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes. As a frame of reference, a computer may have up to 4 GB of RAM; a single layer DVD can hold up to 4.7 GB of data; a hard drive could be used to hold 750 GB; or a video game could have 30-60 GB of data.
A terabyte (TB) is 1,000,000,000,000 bytes, or 1,000 GB. External hard drives may commonly be found at around 1-8 TB.