
Getty Images
How to choose between scale-up vs. scale-out storage
Scaling up and scaling out are both approaches to increase storage capacity. To decide which approach to take, consider short- and long-term requirements.
Organizations that need to accommodate rising data volumes have several options available to them. These options include scaling their storage using either scale-up or scale-out storage architectures.
Both approaches increase the capacity of an existing storage infrastructure. To decide between scale-up or scale-out for storage, consider factors such as data growth expectations, budget, criticality of systems and existing hardware.
Generally, organizations will scale up when they face performance issues and need a short-term fix; by contrast, they will scale out when flexibility and capacity are important. There are advantages, disadvantages and other considerations for each approach.
What is scale-up storage (vertical scaling)?
In some cases, organizations might need to add capacity to existing storage devices. This could be due to rapid expansion or complexity of one or more applications running on a storage device. In this type of situation, organizations can increase the storage of the specific device. This is referred to as scaling up, an approach where the primary equipment does not change, it only increases its storage capacity.
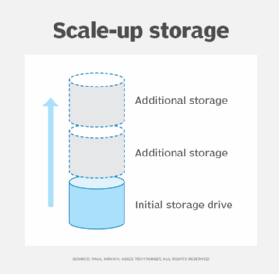
In a scale-up approach, organizations add to existing infrastructure, such as with more disks or drives. If it is important to retain the same device rather than splitting up critical applications and data across multiple storage devices, use a scale-up storage approach. This is also known as vertical scaling.
Benefits of scale-up storage
Scale-up storage is a simple and generally cost-effective way to increase storage capacity to achieve short-term goals. Other advantages of a scale-up storage approach include the following:
- Since the underlying hardware is a single device, storage management is simplified.
- There are lower costs associated with licensing and additional equipment, such as networking components.
- Organizations don't need to change the system architecture.
- It is easy to scale up when using cloud-based storage systems.
- A scale-up strategy can boost the performance of existing storage resources.
Challenges of scale-up storage
Over a longer term, the scale-up approach is constrained by the maximum amount of storage a single storage server can accommodate. This must be carefully considered, along with these other challenges:
- Scale-up storage can make it difficult to take advantage of newer storage technologies if the organization does not integrate new devices.
- A scale-up approach is usually a short- to medium-term fix and is not always good for longer-term requirements.
- Upgrading options might be costly and limited by the vendor or legacy storage systems.
- Scaling up a specific device can potentially create a single point of failure.
What is scale-out storage (horizontal scaling)?
Longer-term storage growth plans might require more storage capacity than is possible using a scale-up strategy. Adding storage capacity using more physical storage devices, such as SSDs, HDDs and NAS, defines a scale-out approach.
In practice, it might be necessary to add additional equipment racks close to the original storage equipment. In such situations, it makes more sense to boost storage by configuring a variety of devices that support those requirements. This is referred to as scaling out from the initial storage equipment, or what is also known as horizontal scaling.

Benefits of scale-out storage
Scale-out storage offers long-term flexibility, as well as these additional advantages:
- Scale-out storage benefits from improvements in storage monitoring, as well as fault identification and tolerance.
- Virtually unlimited storage capacity is possible.
- There is greater fault tolerance if a device fails.
- Organizations can implement newer storage and server technologies.
- Storage resources can be located virtually anywhere.
Challenges of scale-out storage
Despite its benefits, scaling out might not be the most suitable approach in the short term. Other disadvantages of scale-out storage include the following obstacles:
- Storage management can be complex due to a variety of devices and requirements.
- Costs can be higher for more equipment racks, power, physical space, networking and physical security.
- Scaling out can increase the burden on HVAC systems.
How to choose between a scale-up vs. scale-out storage approach
While both strategies are effective ways to increase storage, one approach might be more suitable than the other depending on the storage architecture. The following lists describe situations that are the most appropriate for each option.
Examples of when to scale up storage
Choose a scale-up approach for the following scenarios:
- When there are size increases in files or databases and breaking up large files into smaller pieces should be avoided.
- When longer-term storage capacity needs are minimal.
- When the organization's existing storage requirements are relatively small.
- When the organization wants to add to existing storage but not add new storage.
- When existing production activities are increasing.
Examples of when to scale out storage
Scaling out, on the other hand, is a better fit in the following instances:
- When organizations require additional performance and capacity needs that scaling up cannot facilitate.
- When backup data storage requirements are significant and growing.
- When medium- to long-term growth of data and storage requirements is significant, and multiple distributed nodes must handle multiple workloads.
Data storage administrators must carefully monitor current storage usage levels while keeping in touch with business units to identify any trends where adjustments -- especially increases -- in storage might be needed.
Additional considerations when changing storage architecture
Depending on the storage architecture being used, be sure to consider the following issues that go beyond simply selecting the storage device. Three options are presented: scale-up storage only, scale-out storage only and transitioning from scale-up to scale-out storage.
Using scale-up storage
- Adding capacity to existing devices can cause changes in power usage.
- Cloud storage can help add more storage without increasing the physical footprint.
- Storage as a service (SaaS) might be a viable option.
- Additional storage resources can add to HVAC requirements.
Using scale-out storage
- Adding new storage devices can increase power usage.
- Additional storage devices can necessitate more rack or floor space.
- New devices will require finding space in the data center or outside the center to house them.
- Added devices will need networking resources to connect them.
- Cloud storage and SaaS can be viable options for a new scale-out storage array.
- Additional devices can add to HVAC requirements.
Transitioning from scale-up to scale-out
- Determine if a complete switch from a scale-up to scale-out approach is needed.
- Consider if a hybrid approach -- combining scale-up with added scale-out storage -- can address the new requirements.
- Determine if a cloud storage array will deliver the scale-out requirements.
- Evaluate if SaaS is a viable option.
- Analyze how storage scheduling will change with an expanded arrangement.
- Examine how such a transition will impact disaster recovery activities.
- Determine how the expanded arrangement will affect recovery time and recovery point objective metrics.
- Evaluate the costs of a scale-up to scale-out transition.
Cloud storage services provide an easily available and flexible way to handle both scale-up and scale-out requirements. As with any storage architecture, current and longer-term storage requirements must be carefully determined.
Paul Kirvan, FBCI, CISA, is an independent consultant and technical writer with more than 35 years of experience in business continuity, disaster recovery, resilience, cybersecurity, GRC, telecom and technical writing.






