load balancing
What is load balancing?
Load balancing is a technique used to distribute network traffic across a pool of servers known as a server farm. It optimizes network performance, reliability and capacity, reducing latency as the demand is equally distributed among multiple servers and compute resources.
Load balancing uses an appliance -- either physical or virtual – to identify in real time which server in a pool can best meet a given client request, while ensuring heavy network traffic doesn't unduly overwhelm a single server.
In addition to maximizing network capacity and ensuring high performance, load balancing provides failover. If one server fails, a load balancer immediately redirects its workloads to a backup server, thus mitigating the effect on end users.
Load balancing is usually categorized as supporting either Layer 4 Layer 7 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) communication model. Layer 4 load balancers distribute traffic based on transport data, such as IP addresses and TCP port numbers. Layer 7 load-balancing devices make routing decisions based on application-level characteristics, which include Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) header information and the actual contents of the message, such as URLs and cookies. Layer 7 load balancers are more common, but Layer 4 load balancers remain popular, particularly in edge deployments.
How load balancing works
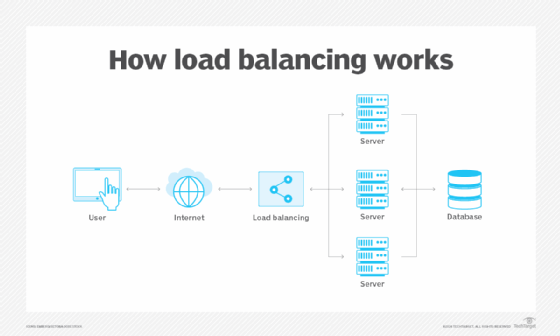
Load balancers handle incoming requests from users for information and other services. They sit between the servers that handle those requests and the internet. Once a request is received, the load balancer first determines which server in a pool is available and online and then routes the request to that server. During times of heavy loads, a load balancer acts promptly and can dynamically add servers in response to spikes in traffic. Conversely, load balancers can drop servers if demand is low.
Types of load balancers
Load balancing is a key component of highly available infrastructures. Depending on a network's needs, various types of load balancers can be deployed with different storage capabilities, functionalities and complexities.
A load balancer can be a physical appliance, a software instance or a combination of both. The following are two types of load balancers:
- Hardware load balancer. A hardware load balancer is a hardware device with specialized and proprietary built-in software that's designed to handle massive amounts of application traffic. These load balancers have a built-in virtualization capability and enable multiple instances of a virtual load balancer to be used on a single device.
Traditionally, vendors loaded proprietary software onto dedicated hardware and sold it to users as standalone appliances -- usually in pairs to provide failover if one system goes down. Growing networks require an organization to purchase additional or larger appliances. - Software load balancer. Software load balancing runs on virtual machines (VMs) or white box servers, most likely as an application delivery controller (ADC) function. ADCs typically offer additional features, including caching, compression and traffic shaping. Popular in cloud environments, virtual load balancing can offer a high degree of flexibility. For example, it enables users to automatically scale up or down to mirror traffic spikes or decreased network activity.
Cloud-based load balancing
Cloud load balancing uses the cloud as its underlying infrastructure to balance cloud computing environments.
The following are examples of cloud-based load-balancing models:
- Network load balancing. This is the fastest load-balancing option available. It operates on Layer 4 of the OSI model and uses network layer information to transport network traffic.
- HTTP Secure load balancing. This enables network administrators to distribute traffic based on information coming from the HTTP address. It's based on Layer 7 and is one of the most flexible load-balancing options.
- Internal load balancing. This is similar to network load balancing, but it can also balance traffic distribution across the internal infrastructure.
Load-balancing algorithms
Load-balancing algorithms determine which servers receive specific incoming client requests. There are two main types of load balancing algorithms: static and dynamic.
1. Static load-balancing algorithms
- The IP hash-based approach calculates a given client's preferred server based on designated keys, such as HTTP headers or IP address information. This method supports session persistence, or stickiness, which benefits applications that rely on user-specific stored state information, such as checkout carts on e-commerce sites.
- The round-robin method goes through all the available servers in sequential order and distributes traffic to a list of servers in rotation using the domain name system (DNS). An authoritative nameserver carries a list of different "A" records and provides one in response to each DNS query.
- The weighted round-robin approach enables admins to assign varying weights to each server. This way, the servers that can handle more traffic receive slightly more traffic based on their weight. Weighting is configured within DNS records.
2. Dynamic load-balancing algorithms
- The least-connections method favors servers with the fewest ongoing transactions and checks and sends traffic to those servers that have the fewest open connections. This algorithm assumes that all connections require almost equal processing power.
- The weighted least connection method assumes that some servers can handle more traffic compared to others. Thus, it enables admins to assign different weights to each server.
- The weighted response time approach uses the response time averages of each server and combines them with the number of connections each server has open to find the best destination for sending traffic. This algorithm ensures faster service, as it sends traffic to the servers with the quickest response time.
- The resource-based algorithm distributes loads based on the availability of resources on each server at the time. Before traffic distribution, it queries a specialized software called an agent that runs on each server to measure the availability of the central processing unit and memory.
Benefits of load balancing
Organizations that manage multiple servers can benefit greatly from load-balancing their network traffic. The following are the main advantages of using load balancers:
- Improved scalability. Load balancers can scale the server infrastructure on demand, depending on the network requirements, without affecting services. For example, if a website starts attracting a large number of visitors, it can cause a sudden spike in traffic. If the web server isn't able to manage this sudden influx of traffic, the website might crash. Load balancing can spread the extra traffic across multiple servers, preventing this from happening.
- Improved efficiency. Due to the reduced burden of traffic on each server, the network traffic flows better and improves response times. This ultimately provides a better experience for site visitors.
- Reduced downtime. Companies with a global presence and multiple locations in different time zones can benefit from load balancing, especially when it comes to server maintenance. For example, a company can shut down the server that needs maintenance and route traffic to the other available load balancers without causing service interruptions or downtime.
- Predictive analysis. Load balancing can provide early detection of failures and help manage them without affecting other resources. For example, software-based load balancers can predict traffic bottlenecks before they happen.
- Efficient failure management. In the event of a failure, load balancers can automatically redirect traffic to functional resources and backup options. For example, if a failure is detected on a network resource, such as a mail server, load balancers can redistribute resources to other unaffected areas to prevent service disruption.
- Improved security. Load balancers add an extra layer of security without requiring additional changes or resources. As more computing moves to the cloud, load balancers are being outfitted with security features, such as the offloading function. This defends an organization against distributed denial-of-service attacks by transferring attack traffic from the corporate server to a public cloud provider.
Hardware vs. software load balancers
Both hardware and software load balancers have specific use cases. Hardware load balancers require rack-and-stack appliances, while software load balancers are installed on standard X86 servers, VMs or cloud instances. Hardware load balancers are sized to handle peak traffic loads. Software products are typically licensed based on bandwidth consumption.
The following are some pros and cons of hardware- and software-based load balancers.
Hardware load balancers
Pros
- They provide fast throughput, as the software is run on specialized processors.
- These load balancers offer better security, as they're handled only by the organization and not by any third party.
- They come with a fixed cost at the time of purchase.
Cons
- Hardware load balancers require extra staff and expertise to configure and program them.
- They can't scale when a set limit on several connections has been reached. When this happens, connections are either refused, dropped or degraded, and the only option is to purchase and install additional machines.
- They're more expensive, as the cost of their purchase and maintenance is higher. Owning a hardware load balancer might require hiring consultants to manage it.
Software load balancers
Pros
- They offer the flexibility to adjust to the changing needs and requirements of a network.
- By adding more software instances, they can scale beyond the initial capacity.
- They offer cloud-based load balancing, which provides off-site options that can operate on an elastic network of servers. Cloud computing also offers options with various combinations, such as hybrid with in-house locations. For example, a company could have the main load balancer on premises, and the backup load balancer could be in the cloud.
Cons
- When scaling beyond capacity, software load balancers might cause an initial delay. This usually happens when the load-balancer software is being configured.
- Since they don't come with a fixed upfront cost, software load balancers can add ongoing costs for upgrades.
Learn how cloud load balancing differs from traditional network traffic distribution. Also, explore cloud load-balancing services offered by various vendors.






