What is an entrepreneur (entrepreneurship)?
An entrepreneur is an individual who identifies a need in the marketplace and works to fulfill it. The term, historically, has been applied to an individual who starts a business, seeing the ability to fulfill that identified need as an economic opportunity.
The textbook definition of entrepreneur speaks to that classic perception. Consider, for example, Merriam-Webster's definition, which explains entrepreneur as "one who organizes, manages and assumes the risks of a business or enterprise."
Harvard Business School professor Howard Stevenson, whose research and teaching focused on the field of entrepreneurship, said, "Entrepreneurship is the pursuit of opportunity beyond resources currently controlled."
Why are entrepreneurs important?
They tend to be innovators and people with new ideas or new approaches. They come up with new products, new methods of doing things, new ways of creating things. They advance production, and in so doing, they invigorate the economy. Entrepreneurs are commonly the source of new business ideas and new business models, spurring business competition and broadly boosting economic vitality.
Steve Jobs, with his introduction of Apple's many first-ever products, is an example. Jeff Bezos, courtesy of Amazon, changed the way people buy things. Mark Zuckerberg, via Facebook and its parent company Meta, altered the nature of social discourse.
What are different types of entrepreneurships?
The terms entrepreneur, entrepreneurial and entrepreneurship have expanded meanings. They're sometimes used to describe individuals who can identify unmet needs in a variety of settings, including in existing companies, and seek to find ways to meet those needs. As such, those terms are also applied to a way of thinking and a way of organizing or managing, rather than simply a way of developing a new business.
For example, people describe innovative individuals in nonbusiness settings such as nonprofits and social movements as social entrepreneurs. Innovative individuals working in existing companies are sometimes called intrapreneurs. Other terms used in the corporate setting are corporate entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship.
Additionally, the terms entrepreneur, entrepreneurial and entrepreneurship are sometimes applied to individuals who identify and pursue new ways of working or new processes and procedures, regardless of their positions or settings. Entrepreneur is occasionally used as a synonym for a go-getter, a person who could also be described as having an entrepreneurial spirit.
In pursuing any of these, an entrepreneur might initiate a new venture at any one of many levels, depending on the nature of the venture and available resources. A tiered representation of those entrepreneurial levels includes the following:
- Startup. A startup is a from-scratch operation -- not an outgrowth or a spin-off of an existing corporate entity but one grown from the ground up. Often, but not always, entrepreneurs finance startups themselves. When the entrepreneur doesn't have the resources to launch, crowdfunding is often an option -- putting out a call for contributions from those who have an interest in seeing the product or service made real or from those who want to become customers. Crowdfunding is most often achieved via social media. An important consideration with a startup is that it be scalable -- easily expanded to reach a greater audience and facilitate greater production with few, if any, barriers to growth.
- Small business. An entrepreneurial small business is generally one that represents a first iteration of a new business idea or business model that's new and different, but later expandable to, for instance, a chain, with the idea being that the initial small business be a proving ground for the expanded business to follow. When the idea is proven and a customer base exists, the entrepreneur might seek venture capital to finance expansion.
- Corporate. A corporate entrepreneur is typically someone already in place in an existing large company who has the skills, inclination and mandate to create new products or processes for the organization and has the prospect of reward for growing the organization by producing market-strategic innovations. Beyond this, a corporate entrepreneur might be a corporate enterprise entity who uses their position and resources to launch entirely new entrepreneurial ventures. Elon Musk is a prominent example.
What does an entrepreneur do?
In the classic sense of the term, an entrepreneur starts a new business venture, building the organization by fulfilling what they see as an unmet market need.
In this regard, an entrepreneur also meets the definition of both a business founder and a small business owner. However, not every business founder or small business owner is an entrepreneur. Businesses that were started to provide existing products or services in ways similar to others already in the market aren't considered entrepreneurial, even if they provide superior products or services.
To meet the definition of entrepreneurship, the business venture requires a new or unique element or process.
For example, the four co-founders of Whole Foods Markets are considered entrepreneurs because when they founded the store in 1980, they saw an opportunity to provide natural food products to fill an unmet need for such items in an established grocery store market that focused more on delivering commercial and processed products.
Common traits of entrepreneurs
Although every entrepreneurial endeavor follows its own path, entrepreneurs share many common traits as they establish their businesses.
They often build their organizations from the ground up, developing business plans that articulate not only the market need they plan to fulfill but also how they intend to produce and deliver their products or services. In this way, entrepreneurs are following recommended standard business practices.
Entrepreneurs typically operate on a limited budget. Many start by financing their operations with their own money or soliciting funds from friends and family members -- a financial scenario commonly called bootstrapping.
Entrepreneurs, like other business leaders, can take different paths as they try to grow their organizations. They can opt to produce minimally viable products to test the market, or they might decide to partner with another company to improve their chances of success. They might obtain financing from new sources such as angel investors and venture capitalists, who seek out early-stage companies that have demonstrated promise and potential for future success.
As their companies grow, entrepreneurs can opt to continue running their business, sell their businesses or merge with others. Some remain as presidents and chief executive officers. Some hand over operational leadership to others, preferring to handle other roles, including serving as the visionaries that keep their businesses growing and on the cutting edge of new opportunities.
Personality types and characteristics
Entrepreneurs are often characterized as visionaries. Case in point is Steve Jobs, who is credited with developing and bringing to market numerous revolutionary computer products.
They're also risk-takers, but successful entrepreneurs are calculated in their risks. They're also adaptable and agile, so they can adjust their objectives as markets and their businesses evolve.
Self-discipline is also crucial to becoming an entrepreneur. According to a survey conducted by National Business Capital, approximately 38% of entrepreneurs consider self-discipline an essential part of launching and sustaining their businesses.
Other characteristics commonly seen among successful entrepreneurs include perseverance, passion, creativity, courage, vision, resourcefulness, confidence and decisiveness.
Examples of famous entrepreneurs span not only centuries, but industries. Commonly recognized entrepreneurs include the following:
- Virgin Group founder Richard Branson.
- French fashion designer Coco Chanel.
- Entertainment mogul Walt Disney.
- Prolific inventor Thomas Edison.
- CNN founder Ted Turner.
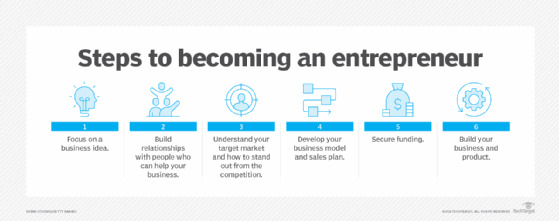
How to become an entrepreneur
Becoming an entrepreneur isn't like becoming a developer or a manager. It's not about identifying a profession that sounds interesting, getting training and education, and applying for jobs. It's about leveraging traits already in place and applying them in new ways -- finding a landscape that's appealing and putting energy, initiative and creativity into remaking that landscape.
As mentioned above, there are several entrepreneurial roads. But most of them include some, if not all, of the following steps:
- Start with what you know and add to it. Build a knowledge base in the niche in which you choose to work. If you have a great new approach to social media, learn everything you can about social media. It will advance your insights and save missteps.
- Make connections. Networking is essential to learning a new business terrain, breaking new ground and building the relationships that you will need to bring a new business into being.
- Lock in on the big goal. Study the target market in which your new idea will live, and define the idea in that context. Understanding that market fully provides context for fully clarifying how your new product, service or method will change things and what you must do to achieve this. It will also define the customer base you're hoping to attract.
- Design the thing you're creating. Whether it's a product, service or process, the details of how it must be designed and implemented will be clear once you've studied your market. Business ideas only have meaning in a market context, so now the idea can become real through development.
- Find the means. As mentioned above, a new business needs funding. The entrepreneur's options include self-funding, crowdfunding and seeking venture capital. Which of these is best depends on the nature of the idea, the size of the venture and the business model that works best.
- Get to work. Whether the new entrepreneurial venture will live in brick and mortar or online, it needs infrastructure. Building out that infrastructure as well as the structure of the organization that facilitates the selected business model and means of implementation and production is the final essential step to launching the venture.
History and origins
The term entrepreneur comes from the Old French word entreprendre, meaning to undertake. It's the same French word that gives English its word enterprise.
Both terms date back hundreds of years in the English language, according to Merriam-Webster. However, scholars say entrepreneurship dates back hundreds, if not thousands, of years, as medieval and even ancient explorers and merchants established ventures to bring products to market.
Developing a product, service or process often involves first creating a proof of concept. Learn how entrepreneurs can create a proof of concept using our free templates.