How to set business goals, step by step
Setting business goals that are detailed and come with deadlines motivates employees and keeps your company on track. Learn how to do it.
What are business goals?
Business goals articulate the specific accomplishments that an organization will work to achieve over a defined period of time.
For business goals to be effective, they should be specific and have a deadline. The specificity and the timeline enable organizations to measure if they've met their stated goals -- and, if not, to know how far they've fallen short.
"Business goals are the way that businesses keep their activities aligned," said George Westerman, senior lecturer at the MIT Sloan School of Management, founder of the Global Opportunity Initiative and co-chair of the MIT Sloan CIO Leadership Awards.
Importance of a mission statement
When business goals are done right, a business first establishes its mission or vision -- typically a statement of the value it will deliver to customers and the market.
"A vision is the future state that the business wants to achieve," explained Irving Tyler, a distinguished vice president analyst with Gartner, a tech research and advisory firm.
The organization's senior-most executives create and communicate the vision, Tyler said. Then leaders throughout the enterprise determine which business goals must be accomplished to fulfill the organization's vision of itself.
 Niranjan Ramsunder
Niranjan Ramsunder
"With business goals, you're talking specifics. Business goals are close to the ground," said Niranjan Ramsunder, CTO and head of data services at UST, a digital transformation solutions company.
Think of business goals as part of the multi-tiered structure businesses adopt to set their direction, said Atif Zaim, a principal and U.S. consulting leader at professional services firm KPMG.
"Once the business identifies what it is and what it is out to do, then the business leaders have to make it more real by setting business goals and determining how to measure progress," Zaim said.
Specificity is key
An organization can set as many goals as it chooses, and it can set goals for the enterprise as a whole and for individual units within the organization.
Business goals can also be broken into short-term, midterm and long-term goals.
 Jennifer Jones
Jennifer Jones
However, all business goals must identify a specific target that the business aims to achieve and a specific timeline for reaching that target, emphasized Jennifer Jones, a senior research advisor in the industry practice at Info-Tech Research Group.
"'Grow the production department by 20% over the next three years'" is an example of the specificity of an effective business goal, Jones said.
While business goals identify what the business aims to achieve, they do not state how the organization plans to get them done. The business's strategic plan typically lays out the actions that the organization intends to take to reach its goals.
It's also important to note that many companies do not consider business goals as synonymous with objectives and key results (OKRs). Some organizations differentiate the two by defining objectives as the milestones achieved in support of and along the way to reaching the business goal.
Why is it important to set business goals?
Although the concept of a business goal seems basic, setting business goals is critical for achieving success.
 Irving Tyler
Irving Tyler
"Historical studies -- ours and others -- find that businesses don't succeed in their missions without business goals, with failures sometimes estimated as high as 75%," said Gartner's Tyler.
That's because business goals, when done well, play a significant role in shaping everyday activities and decisions. They help the enterprise, from executives down through to entry-level workers, know and understand the organization's priorities.
Thus, each employee has the ability to prioritize team decisions, as well as individual actions and activities, that will help them support the organization in its quest to achieve its business goals. This then helps the organization stay focused on what matters most: The crew rows together to the same finish line, Jones said, with timelines to motivate them to do what they must to reach the destination on time.
"Without business goals, an organization becomes rudderless and can be led in conflicting directions," Jones said. "Goals that are tied to a larger strategic vision provide direction to the entire organization. Well-crafted goals provide clear focus, motivate and set tangible targets for your business to work towards."
And they help an organization's business departments know if they are successful, she added.
For example, the IT organization must support the business goals by identifying the people, processes and technologies that enable business success.
"IT can do this by participating in their own strategic planning exercises and by clearly documenting what business processes they currently participate in and what processes they need to develop," she explained.
Nor is it ever enough to simply communicate the company's vision or mission to departments and leave it to them to figure out how to fulfill it, underscored Tyler.
"They're left wondering, 'What does that mission mean to me? How do I connect to that?'" Tyler said. "Without goals, people either come up with something to do that may not support [the mission] or they don't do anything because they don't see how their work supports it. Goals, though, create the linkage to that vision."
Benefits of having business goals
Setting business goals -- and measuring progress against them -- provides businesses with the following advantages:
- A clear, concise and shared understanding of what success is, particularly when OKRs are developed to support achieving business goals.
- A way to communicate priorities and align workers, teams and business units who might not otherwise know how their roles and responsibilities fit with achieving the business goals.
- A framework for better measuring accountability, as the contributions of workers, teams and business units can be assessed on how they met the established OKRs.
- A way to motivate and engage all employees.
 Stephen Courtright
Stephen Courtright
Stephen Courtright, the Henry B. Tippie Research Professor of Management and Entrepreneurship and director of executive education at University of Iowa's Tippie College of Business, summed up the benefits of setting business goals as threefold: Goals connect employees to the company mission, they establish targets for people to aim for and are motivating.
"People are more engaged and are more motivated when they know they're contributing to something bigger than themselves," Courtright added.
10 steps to setting business goals
Here are 10 steps for effectively setting business goals:
1. Assess your current state with SWOT
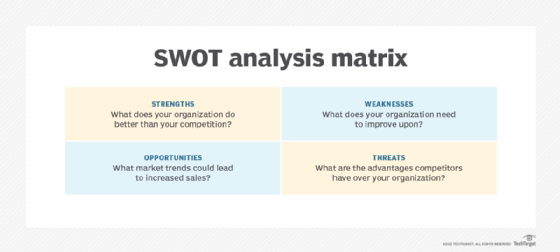
Assess the current state of your business, as well as the industry, market, economy, demographic influences and other trends. Although there are multiple methods for analyzing and measuring an organization's status, the SWOT analysis is one of the most commonly used and recommended approaches. The SWOT framework guides business owners through a process to identify their company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats -- hence the name. Specifically, it helps business leaders identify what's working and what needs to be improved; which new or expanding markets, products or services could provide growth for the company; and the barriers, challenges, competition and other factors that threaten growth and even survival. Benchmarking and market analysis provide further insights into these areas.
2. Seek internal and external input
Executives should engage their managers and other stakeholders, who by being on the front lines of the work are well-positioned to help articulate the goals that contribute to and align with the organization's strategic vision as well as to identify which ones are ambitious yet achievable, Courtright said. "Every goal should align with the why of the organization, provide clarity on what people should be doing and motivate," he added.
Soliciting input from employees at all levels of the organization also helps uncover new opportunities and increase buy-in.
Seeking external voices brings further valuable insight to the process. "Interview key customers and accounts, which allow you to get direct feedback and input and can drive your strategic plan," Jones said.
3. Be specific
Establish specific goals for the business to achieve based on the analysis of the business and both the opportunities for growth and the threats that pose challenges to it. "The goals should answer: What does the business need to do to win in the market?" Ramsunder said.
4. Set clear timelines
Assign a target achievement date to each goal.
Many business owners and executives set short-, mid- and long-term goals and then articulate a specific time frame for each category or each individual goal.
Consider industry and market factors when determining deadlines. For example, startups and companies in fast-paced industries should have shorter, tighter timelines, while well-established companies might be able to opt for goals with longer timelines.
5. Use SMART framework and other available resources
SMART is among the most common frameworks used for setting goals. The framework lays out five attributes of well-set goals: specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time-bound.
Although SMART is highly regarded, other frameworks can be useful, too.
Jones pointed to PESTLE, which stands for political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental factors, as a particularly helpful framework. She also noted that the use of the Business Model Canvas, a management template, can help companies uncover potential business goals.
 Atif Zaim
Atif Zaim
6. Establish and use metrics to measure progress toward reaching goals
When setting business goals, enterprise leaders should determine how they will measure progress, Zaim said, noting that -- like other areas of business -- measuring is essential for good management and oversight of efforts.
Organizations can leverage existing metrics or create new ones, depending on the goals they set and business processes required to fulfill them.
One way to help measure progress is by establishing OKRs to support the business goals and then reporting on them, Courtright added.
7. Communicate and incorporate business goals across the organization
Integrate business goals into the organization's business plan, and develop a strategy to drive the business toward its goals by identifying milestones that mark progress. "The goals are established at the top, but then they should trickle down so that every business unit can translate how they apply to their unit," Westerman said.
 George Westerman
George Westerman
Additionally, communicate the business goals to the entire organization, and align the roles, responsibilities and deliverables assigned to business departments, teams and individual employees with the stated business goals.
"Every person in the organization should understand the goals they're aiming to meet," Westerman said.
8. Choose tools and software to help manage goals
There are a multitude of goal-setting and goal-tracking technologies, with different business management software systems and tools offering features such as visualization and varying levels of integration capabilities. Many enterprise software systems also have modules devoted to business planning that support goal-related activities.
9. Track progress of goals on a consistent basis
"Goals enable a business to take its vision and make it accountable; goals help a business think about its destination," Tyler said.
To reach their destinations, businesses need to regularly check that they're still on the right track and are making the expected progress toward their desired outcomes.
However, experts also said business leaders must recognize that they sometimes will need to adjust business goals or pivot to new ones if progress reports indicate trouble or if an unexpected event -- such as a transformative technology or a pandemic -- hits their company, their industry or society.
10. Recognize milestones
Recognizing progress along the way to reaching business goals helps sustain both alignment and motivation; it also communicates that every employee's contribution to reaching the business goals is critical to overall business success.
Mary K. Pratt is an award-winning freelance journalist with a focus on covering enterprise IT, cybersecurity management and strategy.





