Task Manager
What is Task Manager?
Task Manager, which was previously known as Microsoft Windows Task Manager, is a component of the Windows operating system (OS) that helps administrators and end users monitor, manage and troubleshoot tasks. A task is a basic unit of programming that an OS controls. In the context of Task Manager, a task might be an application, a Windows process or a background process.
Task Manager provides information about hardware resource usage and performance as it relates to the system's individual apps and processes, including services. The information includes usage details about the system's CPU, memory, disk, network and, in some cases, graphics processing unit (GPU) resources.
IT professionals can use Task Manager to quickly identify system bottlenecks that might be responsible for performance or stability problems before they deploy more comprehensive or intrusive troubleshooting tools. Task Manager can help them spot unusual or unexpected behavior that could indicate malware or other unauthorized software.
Task Manager also lets administrators terminate applications and processes, adjust processing priorities and set processor affinity for best computer performance. In addition, they can view information about the users currently logged onto a system, as well as disconnect any of those users when troubleshooting logon or connectivity issues.
How do I use Task Manager?
Task Manager has been included with the Windows OS since the release of Windows NT. Over the years, Microsoft has continuously updated and improved the product, steadily adding more features. As a result, administrators and power users can now do much more with the tool than they could with the original version.
Windows includes a variety of methods for launching Task Manager, including the following:
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del, and then click Task Manager on the Windows Security screen.
- Right-click the Windows taskbar and then click Task Manager.
- Right-click the Start button and then click Task Manager.
- Type task manager in the Window search box and then click the Task Manager app in the results.
When users first launch Task Manager, they might be presented with a compact version that lists only the currently running applications. This version doesn't list any Windows or background processes. Figure 1 shows the compact version with four open apps: Calculator, Clock, Notepad and Paint. If no applications are open, the screen displays only a brief message stating that there are no running apps.
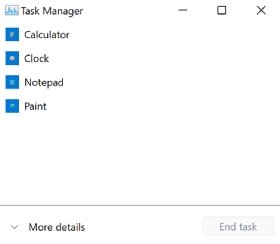
For each listed app, a user can perform operations such as closing the app, going to the app's file location, opening its properties or searching online for information about the app. To access these functions, the user right-clicks the app and chooses the appropriate option from the context menu. Not all the menu options are available to all apps, however. For example, the Calculator app doesn't let the user go to the app's file location or open its properties.
When Task Manager is in compact view, users can click the More details option at the bottom of the window to expand the interface. The expanded view provides access to all the available functionality in Task Manager. Power users and administrators will likely spend the majority of their time here when using Task Manager. Figure 2 shows Task Manager when it's first opened in the expanded view.
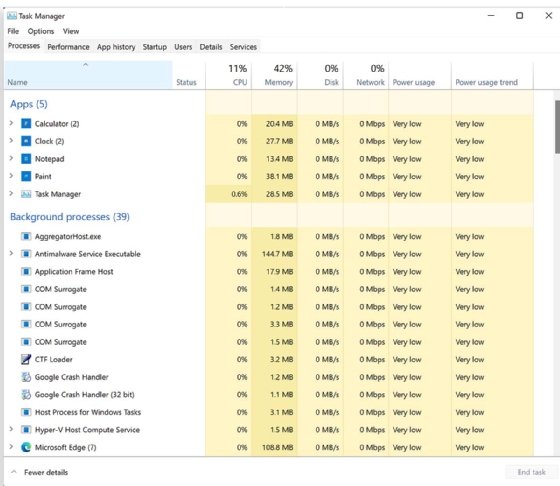
Here the Processes tab is active, which is automatically set as the default tab. However, a user can set a different tab as the default. Once a user has expanded the interface, the expanded view persists whenever they relaunch Task Manager, unless they return to the compact view before closing Task Manager. To return to the compact view, the user can click the Fewer details option at the bottom of the window.
Each tab in the expanded view shows different information about the system's applications, Windows processes and background processes. However, the tabs can vary depending on the OS. Figure 2 shows Task Manager on a Windows 11 system, although the utility works much the same in a Windows 10 environment. On either system, the user interface (UI) includes the following seven tabs:
- Processes. This tab lists all live processes currently running on the system and the resources they're using. By default, the processes are grouped into three categories: Apps, Background processes and Windows processes. Users can also display the processes as a single list. In either case, they can also carry out operations such as ending tasks, going to file locations, opening properties, running debuggers or viewing processes on the Details tab.
- Performance. This tab monitors hardware resources in real time, using visualizations to display performance data about each resource. To view information about a specific resource, the user must select the resource in the left sidebar. The sidebar usually includes CPU and memory resources, one or more disk resources and one or more network resources such as Ethernet or Wi-Fi. In some cases, the sidebar also includes a GPU resource. From the Performance tab, users can also launch Resource Monitor.
- App history. This tab displays the CPU and network resources that individual processes use. The information is specific to the current user account and system accounts. By default, the tab displays only Universal Windows Platform apps, but a user can instead choose to display information about all processes. The data listed on this tab is for a specific range of time, starting on the date listed at the top of the tab. Users can delete the usage history and restart the data collection process.
- Startup. This tab lists the processes that automatically load when the computer boots up. Users can either enable or disable a startup process.
- Users. This tab lists resource utilization information for each user currently connected to the computer. The tab also lists utilization information about the processes associated with each user. This tab is similar to the Processes tab, except that the data is grouped by individual user rather than process type. On this tab, a user can end a process, open its properties, go to its file location or carry out other operations. The user can also disconnect any of the listed users from the system.
- Details. This tab displays all current processes, similar to the Processes tab. However, the Details tab lets users display a lot more information about each process, such as session ID, CPU time, memory working set, base priority, handles, threads and I/O reads and writes.
- Services. This tab, which is a pared-down version of the Services utility, lists all actively running services. Users can start, stop or restart services. They can also launch the Services utility.
Most of the tabs present data in a tabular format, much like the Processes tab shown in Figure 2. On any of these tabs, users can sort the data by a specific column in either ascending or descending order. In addition, many of these tabs provide extra columns of information that users can choose to display. They can also access options related to each listed process.
One tab that stands out from the others is the Performance tab. This tab provides real-time visualizations that show the performance of different hardware resources. For example, Figure 3 shows performance information about the system's CPU.
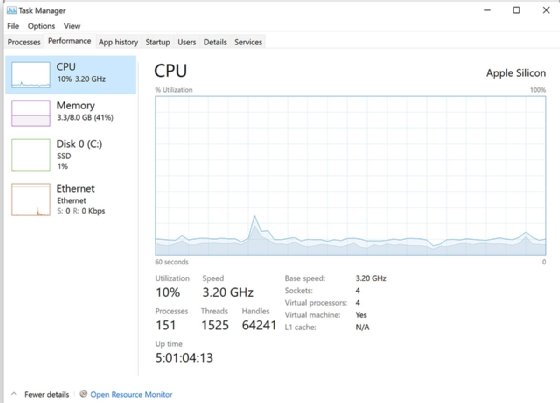
Like Figure 2, this figure is also specific to Task Manager in Windows 11. However, the Task Manager UI in Windows Server is similar to both Windows 10 and Windows 11 except that it doesn't include the App history tab or Startup tab.
Although Task Manager has been improved over the years, it's still only a basic tool. It doesn't include advanced monitoring or management capabilities, such as alerting or comprehensive reporting. For these types of features, IT teams should choose more in-depth tools, such as Microsoft Process Explorer, which is part of the Sysinternals Process Utilities suite. Process Explorer provides more detailed information about running processes and offers more comprehensive visualizations and in-depth reports.
Learn which troubleshooting tips Windows 11 administrators use to resolve desktop issues that don't have a clear fix.





