What is network availability?
Network availability is how long a network system is in uptime over a specific time interval. Uptime refers to how long a network is fully operational.
Network professionals measure availability as a percentage and proactively monitor and record it to ensure the network runs consistently for end users. They do this with real-time network performance monitoring tools. This approach helps networking professionals catch pauses in availability as soon as they occur. Most networks provide users with reactive availability tools to submit support tickets when the network becomes unavailable.
Network uptime and availability are important key performance indicators for network service providers to measure, especially those using multiple data centers. Maintaining a certain level of availability helps organizations create network disaster planning, recognize when issues arise and provide users with a standard quality of service.
How to measure network availability
Network availability is the percentage of time a system stays fully operational over a set period, usually over a year. Service providers typically include a specified level of network availability in service-level agreements.
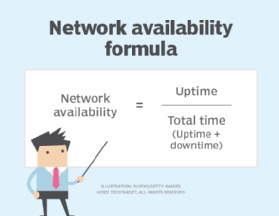
To calculate availability, network professionals divide uptime by the total time. The total time is uptime plus downtime. Downtime includes all times when the network system is down, including the following:
- Maintenance.
- Unplanned failures.
- System recovery time.
Network professionals aim for 100% availability. This is when a network system is fully operational and available for its entire runtime. High availability typically strives for 99.999%, also known as five-nines availability.
Network availability vs. network reliability
Network reliability is similar to availability but measures the likelihood of a system failure instead of the amount of uptime. Reliability tracks how long a network's infrastructure will remain functional without interruption.
Like network availability, network reliability is also measured in percentages. A fully reliable system has 100% availability. Network professionals calculate reliability in two ways:
- The mean time between failures is the total service time divided by the number of failures.
- The failure rate is the number of failures divided by the total service time.





