baseband
What is baseband?
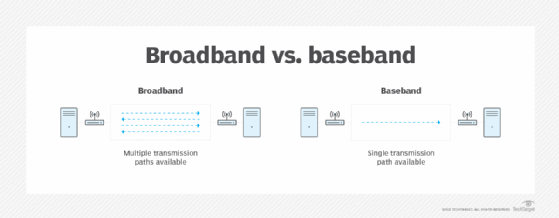
Baseband in the transmission of communications signals means only one path is available to send and receive digital signals between devices. Baseband communication systems have been in use for many years and is still used in technologies such as Ethernet and wireless communications.
Baseband technology is used in several ways:
- Information is carried in digital form on a single signal channel that isn't multiplexed and uses a transmission medium, such as copper twisted-pair wires. Baseband network technology is used in various types of networks, including Ethernet and token ring local area networks.
- With multiplexing, a transmission channel derives additional paths over a baseband channel.
- A baseband signal transmits data streams as analog signals using modulation technology.
- With any frequency band on which information is superimposed, baseband can be used whether or not the band is multiplexed and information is sent on subbands. In this application, it's assumed that the carrier frequency band used isn't shifted to a different frequency band but remains at its original place in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Baseband vs. broadband
A broadband transmission and signal processing system supports multiple frequency bands, whereas baseband transmission uses only one transmission band. Both telecommunications technologies support multiple concurrent transmissions, but they use different equipment at each end to accommodate different signal transmission methods.
10BASE-T and its derivatives
Baseband technology is used in Ethernet networks. Ethernet is typically deployed in a star network configuration with the network hub and device connections radiating from the hub. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) defines current Ethernet transmission specifications as follows:
- 10BASE-T. The initial IEEE Ethernet standard, 10BASE-T provides 10 megabits per second (Mbps) of transmission bandwidth over a baseband channel using twisted-pair copper wiring.
- 100BASE-T. This standard supports transmission speeds up to 100 Mbps.
- 1000BASE-T. The 1000BASE-T standard supports transmission speeds up to 1,000 Mbps or 1 gigabit per second (Gbps). It is also referred to as Gigabit Ethernet.
- 10GBASE-T. The 10GBASE-T standard supports transmission speeds up to 10 Gbps.

In addition to twisted-pair copper cable, providers use coaxial cable and fiber optic cable as transmission media. The following are IEEE standards for each of these media:
- 10BASE-2. This standard is for thin-wire coaxial cable with a maximum transmission distance of 607 feet, or 185 meters.
- 10BASE-5. This is the thick-wire coaxial cable standard with a maximum transmission distance of 1,640 feet, or 500 meters.
- 10BASE-F. This is the standard for fiber optic transmission cables.
- 10BASE-36. The standard for broadband coaxial cable that supports transmission of multiple baseband channels over a maximum distance of 11,800 feet, or 3,600 meters.
Strengths and limitations of baseband
Baseband is a cost-effective technology that's easy to use and inexpensive to install using twisted pair cable. It's also simple to maintain, and its simple structure makes it easy to understand and work with.
However, baseband can only be used for voice and data communications. It isn't generally used for video, and it has a limited transmission range.
Learn more about the evolution of Ethernet as the standard has evolved over the last half century.








