What is ingress filtering?
Ingress filtering is a method used by enterprises and internet service providers to prevent suspicious traffic from entering a network. When configured on an edge device, such as a router or firewall, ingress filtering examines all inbound packets and permits or denies entry to the network based on information in the packet header. It is a form of packet filtering.
Ingress traffic filtering is one of the first lines of defense in a network security strategy. It intends to prevent cyberattacks, particularly denial-of-service (DoS) attacks that use Internet Protocol (IP) address spoofing.
IP spoofing and DoS attack prevention
At its core, ingress filtering establishes an access control list (ACL) containing all permitted source IP addresses. Conversely, the ACL can also block prohibited source addresses.
Ingress filtering takes advantage of an edge router's data link layer IP address filtering capability and blocks traffic that is highly likely to be malicious. It determines this based on whether the contents of an IP packet header meet defined criteria.
The packet filter examines several attributes, including the source IP address. If the source address is invalid -- that is, it doesn't match its originating network -- the filter determines it is forged or spoofed and drops the packet.
Switches also feature ingress filtering, which means they can filter traffic on virtual local area networks to prevent malicious activity within a private network, such as VLAN hopping. In VLANs, ingress filtering discards frames whose port is not a member of the VLAN it is trying to access.
How ingress filtering works
Source IP addresses commonly blocked with an ingress filter include the following:
- Internal IP addresses. Prevents attackers from spoofing internal IP addresses to take advantage of a poorly written firewall rule.
- Private IP addresses. Prevents incoming malicious traffic from an improperly configured internet-based host or an attacker's spoofed address.
- Loopback IP addresses. Prevents traffic from an attacker spoofing a loopback address to take advantage of a poorly written firewall rule base.
- Multicast IP addresses. Prevents undesired multicast traffic that is likely spam.
- Service or management IP addresses. Prevents attackers from using the public internet to gain unauthorized access to network services running at the application layer and above.
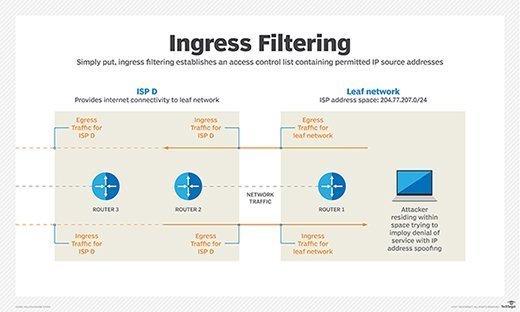
Additionally, network administrators might want to allowlist traffic from specific regions of the world that their organization does business with. They should also blocklist dangerous regions of the world that their company prefers not to have access to its environment. Several free and subscription-based services can create ACLs for network border routers.
Ingress filtering vs. egress filtering
Ingress filtering is one type of packet filtering. Its counterpart is egress filtering, which examines outbound traffic. Egress filtering only enables packets to leave the network if they meet predetermined policies set by an administrator.
Egress filtering can prevent malicious activity, such as the following:
- Infected machines attempting to leak data to remote hosts.
- Blocking legitimate users from accessing prohibited services.








