Secure Sockets Layer certificate (SSL certificate)
What is Secure Sockets Layer certificate (SSL certificate)?
A Secure Sockets Layer certificate (SSL certificate) is a small data file installed on a web server that allows for a secure, encrypted connection between the server and a web browser. This digital certificate allows a website to implement the SSL encryption-based security protocol. It also authenticates the site's identity, secures online transactions performed through it and keeps user information secure and private.
SSL protocol and SSL certificate
SSL is an encryption-based security protocol that helps secure connections between web clients and servers over insecure networks, including the internet. The protocol encrypts the sensitive data traveling between a web client, i.e., a user, and a web server, thereby ensuring that it cannot be read or tampered with by anyone who is not authorized to have access to the data.
One example of sensitive data protected by SSL is financial information, such as credit card numbers. Other examples include:
- User login credentials.
- Personally identifiable information (PII).
- Legal information such as contracts.
- Medical information.
- Business information such as intellectual property.
SSL is the predecessor to the Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption protocol that provides even greater data privacy and security for internet communications, particularly between web apps and the internet.
Websites that have an SSL certificate can implement the SSL protocol to protect data. The certificate is like a badge that authenticates the website and tells users that it is genuine and trustworthy. When a website has an SSL certificate, users see a padlock icon just before the URL in the address bar, indicating that the website and any data they might provide are SSL-protected. Clicking on the padlock will reveal the details of the SSL certificate, including the organization verifying the certificate.
The URLs of websites protected by SSL certificates always start with HTTPS ("s" stands for "secure") instead of HTTP. One example of an HTTPS (SSL-secure) is the TechTarget website; its URL is https://www.techtarget.com. When an SSL certificate is installed on a web server, it activates the HTTPS protocol over port 443.
SSL certificates are used by all reliable websites, particularly those that do the following:
- Encrypt credit card transactions.
- Enable users to make data transfers.
- Process user logins with a set of credentials.
Most SSL certificates today also support the TLS protocol.
SSL certificates and public key cryptography
SSL certificates use -- and contain -- a cryptographic public key to provide validation for a web server. The public key is required to establish secure communications over the internet. This key, by virtue of being "public," is published and can be used by anyone to disguise the data they send over a network. Typically, the "anyone" in SSL refers to web servers and web clients.
A website's SSL certificate is a single data file that includes the public key as well as numerous other details:
- Domain name.
- Subdomains, if any.
- Server name.
- Hostname.
- Company name.
- Location.
- Certificate authority (CA) name and digital signature.
- Certificate expiration date.
SSL also uses a private key that is owned by the website and installed on its origin server. Both the public and private key are required for encrypting and decrypting data sent to and from the website, and thus to ensure its privacy and security. In contrast to the public key, the private key is kept private (it is not included in the SSL certificate) and is used to decrypt the data encrypted by the public key.
How SSL certificates work
A secure website's SSL certificate is hosted on a website's origin server. Every time a web client sends the web server a request to load the website, the server sends the certificate to the client, assuring the latter that all sensitive data is being encrypted to protect the user. Here's how the process works step by step:
- A client -- usually a web browser -- tries to connect to an SSL-secured website.
- The browser requests the web server to identify itself.
- As proof of its identity and authenticity, the server sends a copy of its SSL certificate to the browser.
- The browser determines if the SSL certificate can be trusted and then sends a signal of trust to the server.
- The server starts an SSL-encrypted session.
- When the browser shares sensitive data with the website, the data is encrypted by SSL.
- Identity and authenticity continue until the session ends or the user closes the browser window.
This entire SSL handshake process takes just a few milliseconds so users don't even realize what is happening in the background. However, the process is extremely important to secure user data and show users that the website is genuine.
SSL certificates and certificate authority
SSL certificates are issued by a trusted third party called a certificate authority (CA). To get an SSL certificate from a CA, the website owner creates a certificate signing request (CSR) on their web server. Doing so creates both a public and private key on the server.
The owner also sends the CSR data file to the CA that creates a data structure to match the public key and then issues the SSL certificate. The CA never sees the private key (which is always kept private) but they do sign the issued SSL certificate with their own private key.
After the CA issues the certificate, it is installed on the website's origin server along with an intermediate certificate that helps establish the certificate's credibility. To do so, the intermediate certificate connects the site's server certificate to the CA's root certificate.
After installing the certificate, the website activates it. Once this step is complete, the connection is secure (HTTPS) and all traffic to and from the website is encrypted. From this point on, with the SSL handshake process completed, browsers trust the website's identity and security and assure users that their confidential information is safe from hackers and eavesdroppers.

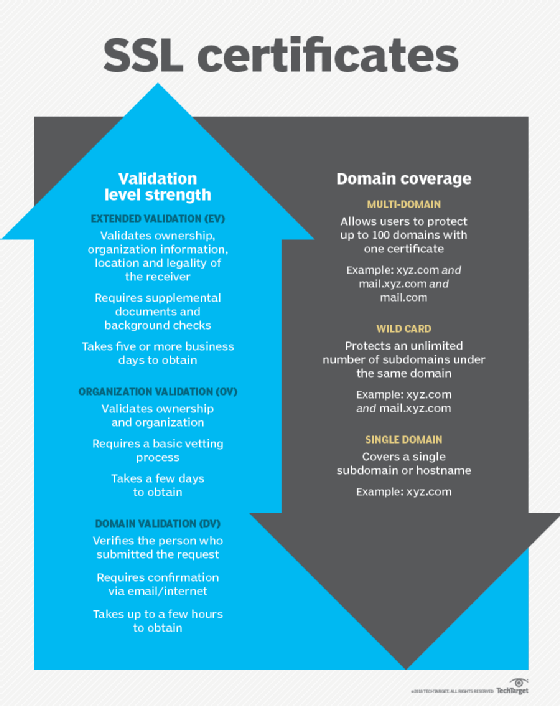
Types of SSL certificates
There are mainly three types of SSL certificates:
- Extended validation (EV) SSL certificates. EV certificates are usually installed on websites that collect or initiate transactions involving sensitive data, like credit card numbers or PII. This type of certificate provides a very high degree of assurance that the website is genuine and the website owner has legal and exclusive rights to the associated domain.
- Organization validation (OV) SSL certificates. OV certificates also provide high assurance about a website's security and reliability. Most commercial websites install OV certificates to encrypt user information. The certificate usually displays the website owner's information in the address bar. It is slightly less expensive than an EV SSL certificate.
- Domain validation (DV) SSL certificates. DV certificates do not provide the same level of data encryption or assurance as EV and OV certificates. As a result, they are not used for websites that collect or process sensitive data. Blogs and informational websites that involve minimal data processing usually install DV SSL certificates. When a site installs a DV certificate, the browser address bar includes HTTPS and displays only the padlock icon. Other details about the business, such as the owner's name, business name, business location, etc. are not displayed in the address bar.
Understand the importance of data encryption and check out some SSL certificate best practices. Learn how to encrypt and secure a website using HTTPS.







