sensitive information
What is sensitive information?
Sensitive information is data that must be protected from unauthorized access to safeguard the privacy or security of an individual or organization. This information, which is also referred to as sensitive data, encompasses the types of data where exposure could lead to detrimental consequences for the welfare and security of individuals and organizations.
Organizations often limit access to sensitive information to users with approved credentials. Sensitive information includes physical as well as digital copies of information.
Why is sensitive information important?
Sensitive information includes personally identifiable information (PII) that's critical to individual privacy, financial security and legal compliance. Social Security, bank account and credit card numbers are examples of PII. When this type of sensitive information falls into the wrong hands, people can become victims of identity theft, financial loss and harassment.
Organizations face similar threats. A cyberattack or breach that exposes an organization's sensitive information is one of the most significant vulnerabilities businesses face. An organization that fails to safeguard sensitive information -- such as customer and employee data and its own trade secrets and intellectual property (IP) -- is vulnerable to negative consequences as well. These can include the loss of trust and reputation, financial loss and penalties for noncompliance with laws and regulations.
Examples of regulations that require protection of sensitive information include the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and General Data Protection Regulation. Regulatory penalties for poor data protection, such as those included in the GDPR, can include fines and legal consequences. Overall, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million dollars.

What are the three main types of sensitive information?
There are three main types of sensitive information, including:
Personal information
Sensitive PII is data that can be traced back to an individual and, if disclosed, could result in harm to that person. Such information includes biometric data, genetic data, medical information, medical records, personally identifiable financial information and unique identifiers, such as passport and Social Security numbers. Sensitive private information also includes names, home addresses, driver's license numbers, phone numbers and dates of birth. Other information, such as race, ethnic origin and sexual orientation, is considered sensitive personal information.
Threats to this type of data include crimes such as identity theft and also disclosure of personal data or information that the individual would prefer remained private. Sensitive PII should be encrypted both in transit and at rest.
Business information
Sensitive business information includes anything that poses a risk to the organization in question if a competitor or the general public has access to it. Such information includes trade secrets, acquisition plans, financial data, supplier and customer information and IP among other possibilities.
With the ever-increasing amount of data generated by businesses, methods of protecting information from unauthorized access are becoming integral to corporate security. These methods include metadata management and document sanitization.
Classified information
Government agencies classify information that might pose a risk to national security or contain protected information on organizations or individuals. Classified information restricts who can access and use it according to level of sensitivity. Data classifications include restricted, confidential, secret and top-secret information. Classifications provide guidance on what sort of information security and access controls should apply to each document or file to protect the data they contain. Once the risk of harm has passed or decreased, classified information may be declassified and possibly made public.
Examples of sensitive information
Sensitive information comes in many forms. Some specific examples include the following:
- Social Security numbers. The U.S. government assigns these unique identifiers to individuals. They can be used to help perpetuate identity theft or fraud.
- Personal health information. PHI includes a person's medical history, healthcare diagnoses and treatment details. It's protected by privacy laws such as HIPAA to safeguard individuals' confidentiality and prevent discrimination.
- Financial account numbers. Banking information, including account numbers and routing numbers, as well as investment and credit card account numbers are sensitive details that can be exploited by cybercriminals for unauthorized access, fraudulent transactions and identity theft.
- Passwords and authentication credentials. Usernames, email addresses and associated passwords grant access to personal accounts. Hackers and other types of threat actors can use this information to gain unauthorized access to accounts and data.
- Intellectual property. IP refers to inventions, designs, logos, trade secrets and proprietary information. Unauthorized disclosure or theft of this type of asset can result in financial loss, competitive disadvantage or legal disputes for organizations and individuals.
How is sensitive information breached?
Sensitive information can be breached through multiple vulnerabilities. Each method poses unique challenges for data security. Some of the most common types of attacks include the following:
- Cyberattacks. Malicious actors can exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks through techniques such as malware, ransomware, phishing, distributed denial of service and SQL injection.
- Physical theft. Bad actors can gain access to sensitive information by physically stealing equipment, such as laptops, smartphones and storage devices.
- Insider threats. Employees, contractors and business partners with access to sensitive information can intentionally or unintentionally misuse or expose it.
- Human error. People making mistakes can cause data breaches, such as sending sensitive information to the wrong recipient, improper disposal of documents and misconfiguring settings.
How to protect sensitive information
There are several ways to protect sensitive information. The most important ones are the following:
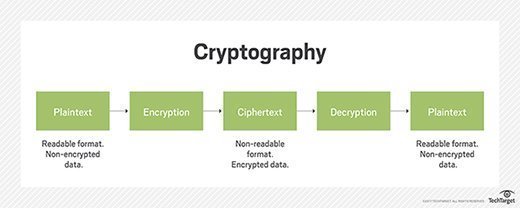
- Encryption. These methods encode sensitive data, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized users, even if intercepted.
- Data classification. Classification of data provides guidance to those using the data and IT professionals protecting it.
- Access controls. Strong access control mechanisms restrict access to sensitive information based on user roles, permissions and authentication factors.
- Employee training. Information is safer when employees and other individuals are educated on cybersecurity best practices, including how to recognize phishing attempts, handle sensitive data securely and report suspicious activities.
- Network security. Secure network environments with firewalls, intrusion detection systems and encrypted communication channels safeguard data in transit.
- Regular updates. Software, operating systems and security should be kept up to date and patched to mitigate vulnerabilities and address known security flaws.
- Monitoring and auditing. Continuous monitoring tools and regular audits and assessments help detect and respond to security incidents promptly.
Sensitive information is often targeted in cyberattacks. Learn the 16 most common types of cyberattacks and how to prevent them.
