6 business benefits of data protection and GDPR compliance
Complying with GDPR and avoiding severe fines is a primary goal of businesses, but the data governing principles and security tools to achieve compliance yield systemic benefits.
Complying with the General Data Protection Regulation isn't just about appeasing regulators and avoiding fines. GDPR compliance also delivers a range of business benefits in areas like data protection, security and beyond.
The GDPR, which took effect in 2018, is a regulation enacted by the European Union to protect data security and privacy. It requires businesses that manage personally identifiable information (PII) to adopt specific measures for protecting and securing that data. Although the GDPR is an EU regulation, it states that any business that stores data about EU citizens or makes its services available to them must comply with the GDPR. So, GDPR compliance impacts organizations around the world, not just those based in the EU.
Consequences of GDPR noncompliance
There were some doubts in the years immediately following the GDPR's introduction about whether its requirements were specific enough to drive strong enforcement. Some observers also wondered whether the GDPR would be enforced inconsistently since its enforcement model relies on individual countries within the EU, not a central enforcement agency, to monitor for compliance and fine violators. Factors like these gave businesses some reason to believe that failure to comply with the GDPR might not result in severe consequences.
That's no longer a plausible position. To date, regulators have issued a number of major fines for GDPR noncompliance. Some of the most notable cases include the following:
- Meta incurred a record-setting 1.2 billion euros ($1.3 billion) fine in 2023 after GDPR regulators concluded the company had transferred PII across borders without adequate data protections. This penalty was on top of earlier fines levied against Meta that totaled in the hundreds of millions of euros.
- Amazon was fined 746 million euros ($805 million) in 2021 for GDPR noncompliance related to using targeted advertising without consumers' consent.
- TikTok was fined 345 million euros ($372 million) in 2023 in response to violations of the GDPR's data processing and transparency requirements.
- Google has been fined multiple times between 2019 and 2022 by GDPR regulators, primarily due to findings that the company lacked sufficient consent and transparency in ad personalization products.
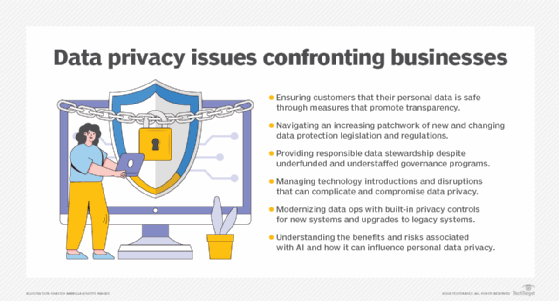
These fines are just some of the GDPR noncompliance penalties involving big-name companies. According to the GDPR Enforcement Tracker, regulators to date have issued more than 2,200 fines for GDPR noncompliance, including many against private individuals or smaller businesses. There's reason to expect noncompliance fines to increase in the coming years due to new rules designed to enhance GDPR enforcement in cases that span national borders.
Data protection's role in complying with the GDPR
Reasons vary for companies failing to comply with the GDPR. The single most common type of violation, however, involves Article 5 of the GDPR, which governs how businesses process and store personal data. To comply with Article 5, enterprises must protect data "against unauthorized or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage" while ensuring they don't retain PII longer than necessary.
Data protection plays such a critical role in GDPR compliance because of Article 5. The primary purpose of data protection is to mitigate the risk of unintended data modification or deletion. By deploying data protection measures, businesses help meet this core GDPR requirement.
In addition, GDPR mandates should inform how companies approach data protection to the extent that storing PII in data backups longer than necessary could potentially trigger a violation of Article 5. To remain compliant, businesses should ensure they are taking steps to avoid including non-anonymized personal data in backups and can justify why they're storing backup data that may contain PII.
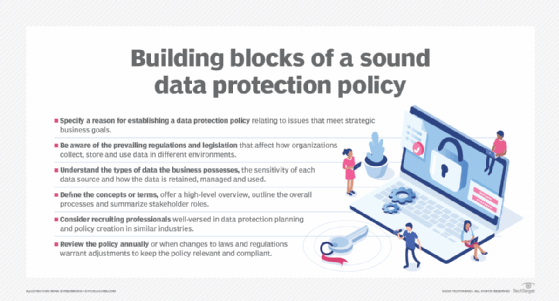
Benefits of GDPR compliance
The key role that data protection plays in achieving GDPR compliance helps to explain why the benefits of complying extend beyond simply avoiding fines. Enterprises in compliance with the GDPR likely achieve several benefits.
1. Enhanced business continuity
Data protection technologies and procedures help companies ensure compliance with GDPR Article 5, which requires businesses to mitigate the risk of accidental loss of PII. But data protection also enhances business continuity in general by increasing the chances that organizations can recover critical systems and restore operations quickly following a data breach.
2. Higher data ROI
In a similar fashion, data that's protected as part of a GDPR compliance strategy is primed to deliver a higher return on investment to the business. Companies hurt themselves financially when they invest heavily in acquiring, processing and storing data only to lose that data permanently because they failed to invest in data protection measures, including backup and recovery. Protecting data will continue to drive ROI even if that data is lost or damaged so long as it's recoverable.
3. Stronger data governance
Data governance, which focuses on managing data availability, usability, security and integrity, helps businesses comply with regulations like the GDPR. GDPR-compliant businesses are likely to have a clear data governance strategy in place, along with controls to enforce that strategy. Companies in turn benefit because of their ability to find, process, protect and secure data in an efficient and scalable way -- not just for the sake of GDPR compliance, but to maximize and monetize data resources in general.
4. Easy data migration
GDPR compliance goes hand-in-hand with the ability to move data easily among systems. When businesses protect their data consistently as part of a GDPR compliance strategy, they implement data backup and recovery methods that can be used to migrate data from one platform to another. Moving a database currently hosted on premises into the cloud, for example, benefits from a reliable snapshot of that database using the tools deployed for data protection.
5. Increased data discoverability and transparency
Determining where PII exists to adequately protect it is an important step toward GDPR compliance. Discoverability and transparency capabilities better position an organization to locate, govern and secure all the data governed by the GDPR. In addition, the ability to find and access other data assets can further maximize monetization of data.
6. Reputation for data stewardship
Companies complying with the GDPR demonstrate to regulators, customers and partners that they take data protection seriously and are responsible stewards of data. GDPR compliance can also increase the trustworthiness of the brand and provide an edge over competitors that might be viewed by customers as less reliable protectors of personal data.
Emerging GDPR compliance challenges
While there are many clear benefits of investing in GDPR compliance strategies, procedures and technologies, be aware that GDPR compliance is becoming more challenging and therefore forcing businesses to modify their compliance techniques.
One emerging challenge is the impact of generative AI technology on GDPR compliance. Since the GDPR was written and enacted well before generative AI became mainstream, it remains unclear how regulators may interpret data processing and protection practices within the context of generative AI tools and technologies.
As a result, vendors like Microsoft have chosen to integrate generative AI into broader platforms to "provide guardrails around the models," wrote IDC research manager Alison Close in her report on the potential of generative AI in customer service. "The choice of OpenAI within Microsoft Azure," she added, as opposed to deploying OpenAI services on their own without compliance guardrails in place, "is to ensure data privacy and GDPR compliance."
Tracking PII across multiple environments is also a key challenge as more and more businesses adopt multiple clouds or IT platforms. In fact, it was the top GDPR compliance challenge in Europe as of 2022, according to IDC research manager Ralf Helkenberg. "Data visibility is essential to building privacy compliance," he wrote in his report on GDPR compliance challenges in Europe, "but keeping track of personal data across different business environments is proving difficult." Meeting this challenge, he reported, will require more extensive use of automated data discovery and classification tools.
Chris Tozzi is an adjunct research adviser at IDC as well as an adviser for Fixate IO and a professor of IT and society at a polytechnic university in upstate New York.







