11 core elements of a successful data protection strategy
Your organization's data protection strategy might not include all 11 core elements and associated activities, but the important thing is to have a comprehensive strategy in place.
Growing concern about protecting information from various risks, threats and potential operational vulnerabilities has necessitated a greater focus on data protection and management. Business and government increasingly depend on the availability of sensitive information and sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information.
Emergence of regulations and legislation that mandate data protection and privacy, such as the EU's GDPR, increases the urgency of addressing data protection as part of an overall data management program. As such, organizations in all sectors must formulate an appropriate data protection strategy to comply with emerging regulations and to assure employees and customers that their personal data is protected.
What is a data protection strategy?
A data protection strategy strives to minimize business losses due to the lack of verifiable data integrity and availability. It's therefore critical to protect data while it is at rest, in use and in motion.
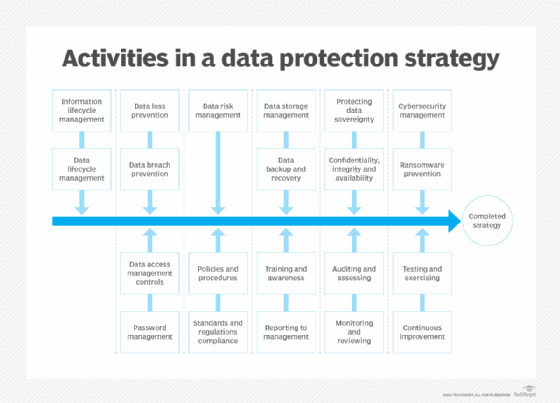
The following 21 attributes of a comprehensive data protection strategy are consistent with the GDPR and many other domestic laws and regulations: information lifecycle management; data lifecycle management; data loss prevention; data breach prevention; data access management controls; password management; data risk management; policies and procedures; standards and regulations compliance; data storage management; data backup and recovery; training and awareness; reporting to management; protecting data sovereignty; confidentiality, integrity and availability; auditing and assessing; monitoring and reviewing; cybersecurity management; ransomware prevention; testing and exercising; and continuous improvement.
Why is a data protection strategy important to enterprises?
When building a strategy of any kind, part of the process is to identify the desired outcome and the actions needed to achieve that goal. In the case of a data protection strategy, the goal is to protect data from damage or destruction by internal and external risks of threats. More importantly, it provides a roadmap for how an organization ensures all data and information is secure, is accessible to those who need it, and retains its integrity without being compromised by cyberattacks or other destructive activities.
A well-thought-out data protection strategy is therefore an essential part of an organization's overall data management and compliance program.
11 elements of a successful data protection strategy
Once data and information have been created, several activities must occur. They include primary storage and backup storage arrangements; choosing the types of storage to use and the appropriate storage devices, whether on-site or located in a cloud, addressing access management and access controls; and establishing data security measures and a comprehensive security strategy to protect the data from unauthorized access and attacks.
Senior management must also approve the creation of the data protection strategy, which should align with the organization's business processes.
The 21 attributes of a comprehensive data protection strategy noted above can be grouped into 11 core elements -- in no particular order or preference -- for ease of understanding and planning. While all the attributes might not be initiated, the endgame is to have as many elements in place and operational as possible to support the enterprise and its operating requirements.
1. Data lifecycle and information lifecycle management
Data lifecycle management creates the framework to manage data -- from creation to storage to archiving to destruction. It's often considered a fundamental component of a data protection strategy and should be regularly reviewed to ensure ongoing and planned data protection activities are in sync with the lifecycle.
Along with data lifecycle management is the process of protecting information and its associated metadata during its lifecycle from creation to destruction. As the amount of information an organization generates increases, this activity becomes increasingly important.
2. Data loss and data breach prevention
Data loss prevention ensures any data created is protected from potential loss or damage using activities such as storing, archiving and securing data with encryption technologies. Two of the key ways to reduce data loss are to encrypt data while at rest and also while in motion.
Data breach prevention stops unauthorized access by a cybersecurity attack or other malicious event using network security and data protection systems to block external access and unauthorized internal data access. Security measures must extend from the network perimeter to storage devices and endpoints, as breaches and attacks can occur at any point on that continuum.
3. Data risk management
Identifying and assessing risks and threats to data is essential when formulating most aspects of a data protection strategy, as the strategy aims to minimize the likelihood of the risks occurring and to mitigate the severity of events that negatively affect data. Performing periodic risk assessments of data and information threat environments ensures the most appropriate prevention, detection, response and mitigation technologies are in place.
4. Data storage management; data backup and recovery
Data storage management encompasses all activities associated with securely moving production data into a secure storage repository -- whether on-site, off-site in a cloud or managed service provider environment, or a hybrid of these options. In situations where the data might be needed at a later date and time, such as for legal purposes, it might be transferred to tape or flash storage for relocation to a secure archive facility.
Once data has been created, unless it's not immediately needed, it must be backed up to a secure and protected location for future use. When the data is needed, a recovery process releases it from its secure storage or archiving, verifies that it's ready for use, and facilitates its retrieval. These activities are key components of business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) initiatives, which help an organization recover and return to operational status in the aftermath of a disruptive event.
5. Protecting data sovereignty; confidentiality, integrity and availability
When addressing risks associated with protecting data gathered and created internationally, it's essential to have a policy to protect data sovereignty so that it remains undamaged by internal or external attacks.
Confidentiality, integrity and availability are the cornerstone attributes of data protection and, specifically, data security. Components of a data protection strategy achieve each of these attributes. Techniques to achieve these criteria range from deploying a secure network perimeter to protecting internal systems and endpoint devices.
6. Cybersecurity management and ransomware protection
Building on the previous initiatives, cybersecurity management covers access management software, perimeter security software and hardware, antivirus software and anti-phishing software, endpoint protection platforms, and endpoint detection and recovery systems.
Gathering numerous headlines in recent years are ransomware attacks, where access to systems and data is blocked unless a fee or other ransom is paid. Anti-ransomware systems prevent and respond to attacks that block access to data and systems, a key component of cybersecurity protection activities.
7. Data access management controls and password management
Achieving one of the cornerstones of data security -- availability -- is the process of securely accessing and using data. Data access controls, such as passwords, and biometric and multifactor authentication, are typically examined by auditors as part of an IT audit. This is one of the most important components of a data protection strategy.
While interest grows for more powerful authentication techniques, passwords are still widely used to prevent unauthorized access. Password management has consistently improved with the use of numerous password creation and management tools.
8. Policies and procedures; standards and regulations compliance
Policies establish the "what" associated with data protection activities, while procedures define the "how" activities. Both are essential in a data management program and are typically examined as part of the audit process. A data protection policy can be a standalone document or be embedded within a larger data management policy.
Good data protection presumes knowledge, use of and compliance with the various regulations and legislation in place that govern how data should be protected. One of the most widely recognized of these is the EU's GDPR. At least 15 U.S. states and several major cities have legislation addressing data protection and privacy. HIPAA and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act include sections addressing data protection, data security and data privacy.
9. Training and awareness; reporting to management
An effective data protection program goes beyond technology issues and educates all employees on how their data is protected and what their responsibilities are to ensure the data is secure. Employees charged with data protection must have sufficient training to perform their work effectively.
Before a data protection strategy and program can be launched, senior management must understand the program and approve it. Regular briefings on all aspects of the data protection program ensure senior leadership is fully aware of how the organization's data and information are being managed and protected.
10. Auditing and assessing; monitoring and reviewing
To ensure data protection strategies are followed and all associated data management programs perform properly, they must be periodically examined, assessed and audited. This is especially true to ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations. Documentation of all policies, procedures, activities and incidents is essential.
A well-organized data management program mandates ongoing monitoring of all aspects of data creation, transmission, storage, archiving and destruction. Data captured from logs and other repositories provides essential evidence for auditors examining data protection and management controls. Such activities are essential to identify events that might indicate flaws in the policies and programs.
11. Testing and exercising; continuous improvement
Regular testing and exercising of data protection program activities -- data backup and recovery, data access management, and cybersecurity prevention activities, for example -- ensures these important programs perform properly and that the employees responsible for performing them know their roles and responsibilities. These activities are also components of BCDR initiatives and provide important evidence to IT auditors.
Data protection and its related activities must be regularly reviewed and continuously improved to be consistent with existing and new regulations, legislation and good practices, and to generate the highest level of confidence among users that their sensitive data and sensitive information are protected.
Paul Kirvan is an independent consultant, IT auditor, technical writer, editor and educator. He has more than 25 years of experience in business continuity, disaster recovery, security, enterprise risk management, telecom and IT auditing.







