What is data migration? Definition, strategy and best practices
Data migration is the process of transferring data between data storage systems, data formats or computer systems. An organization can undertake a data migration project for numerous reasons, including when it's doing the following:
- Replacing or upgrading servers or storage equipment.
- Moving data between third-party cloud providers.
- Moving on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based services.
- Consolidating websites.
- Performing infrastructure maintenance.
- Migrating applications or databases.
- Installing software upgrades.
- Moving data during a company merger or data center relocation.
The data migration process requires organizations to prepare, extract and transform data and to follow a set plan that differs by organization and migration.
Why is data migration important?
Data migration ensures that data is successfully and securely transferred to another application, storage system or cloud. Although moving data from one platform to another can be risky and costly, it also provides an organization with numerous benefits. For example, in addition to upgrading applications and services, organizations can boost their productivity and reduce storage costs.
Data migration has also become a central theme in data science and data quality efforts. From a business and technology perspective, data migration ensures quality data but also gets data to a different location, storage platform or performance tier. Simply stated, the data migrated from one location to another must be good data, accurate, timely and complete.
With the emergence of machine learning and artificial intelligence, the concepts of data migration have extended to merging data sources while maintaining adequate data quality and completeness. In this context, data migration brings together meaningful data sets for machine learning training and optimization.
Types of data migrations and their challenges
Data migration is typically performed using one of the following methods:
- Storage migration. This transfers data from one storage device to another. It involves moving blocks of storage and files from storage systems, whether they're on disk, on tape or in the cloud. Storage migration is an optimal time for organizations to perform data validation and reduction by identifying obsolete or corrupt data to ensure that data can be accessed or recovered properly.
- Database migration. This moves database files to a new device. It's done when an organization changes database vendors, upgrades the database software or moves a database to the cloud. Databases must be backed up before migrating.
- Application migration. This moves an application or program from one environment to another. Application migration typically occurs when an organization switches to another vendor, application or platform. This process is complex because applications interact with other applications, and each one has its own data model. Successful application migration might require using middleware products to bridge technology gaps and ensure complete, accurate and properly formatted data for the new operating environment.
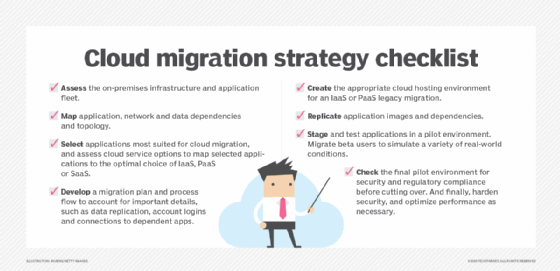
- Cloud migration. This moves data or applications from an on-premises location to the cloud or from one cloud service to another. Cloud migration is a common form of data migration. Cloud environments provide on-demand flexibility and scalability and reduce the capital expenditure for on-premises infrastructures. Public cloud providers offer a variety of services for storage, database and application migrations. Hybrid clouds can migrate data from a private cloud to a public cloud and back.
- Business process migration. This moves business processes and applications, including customer, product and operational data, to a new environment.
- Data center migration. This moves data from one data center environment to another. This can involve a migration from a traditional data center to a newly built facility or a migration from one traditional data center to a hosted environment, such as a colocation data center or a public cloud provider.
During data migrations, teams must pay careful attention to the following challenges:
- Source data. Not preparing the source data being moved might lead to data duplicates, gaps or errors when it's brought into the new system or application. This is a common but increasingly important data quality issue.
- Retention and destruction. Consider how data retention and secure deletion policies might influence data migration planning. Older records and files might be removed from the data set before or during the migration process to ensure migrations comply with retention and deletion policies.
- Wrong data formats. Data must be opened in a format that works with the system. Files might not have access controls on a new system if they aren't properly formatted before migration. This is another common data quality issue.
- Mapping data. When stored in a new database, data should be mapped in a sensible way to minimize confusion.
- Data users. When data migration occurs, it's common for applications and other consumers of that data to update links and configurations to point to the new data location. This can require more data migration planning and preparation than expected.
- Sustainable governance. Having a data governance plan in place can help organizations track and report on data quality. This helps them understand the integrity of their data.
- Security. Maintaining who can access, edit or remove data is a must for security.
Data migration software to use
Data migration is rarely ever a manual process; there are too many nuances and too much potential for human error. Enterprise data migrations almost always involve the use of data migration software that brings automation to the migration process, ensures compliance and continuance requirements are met, and log results for examination and testing. Most data migration tools fall into one of three categories:
- Self-scripted tools. Short and simple data migration tasks can generally be handled through in-house scripts using common tools, such as PowerShell or other scripting platforms. Scripts can be created easily, documented and version-controlled so the script's evolution is tracked.
- On-premises tools. Traditional data migrations, such as from one server or data storage platform to another, can be handled using various third-party, on-premises data migration tools. Examples include Fivetran, Matillion and Talend, among many others.
- Cloud-based tools. Cloud computing has brought an assortment of data migration tools designed to bring on-premises customer data into the public cloud for use with enterprise workloads and services deployed to the cloud. Examples of cloud-based data migration tools include Amazon Web Services Database Migration Service, AWS DataSync and Microsoft Azure Migrate.
There are many data migration tools, and specific tools can be selected based on various criteria, such as the following:
- Size and complexity of the data environment.
- Security and regulatory compliance obligations.
- Tolerable downtime during the migration.
- Risks to the business, such as risk of lost data or downtime.
- Tool costs and maintenance support expenses.
- Tool requirements, such as the operating system.
- IT administrator and team skills.
Data migration strategies
Although implementation differs by migration type, there are two main strategies organizations use: big bang and trickle migrations.
Big bang migration
This approach transfers all associated data within a set time frame. The advantages of using this method are lower cost, faster migration and less complexity. However, the downside is that big bang migrations require the system to be offline for the migration. There's also a risk of losing data if it isn't properly backed up to another location ahead of time.
Trickle migrations
This is a complete data migration in phases. During the migration, both old and new systems run at the same time, so there's no downtime. As a result, there's less risk of losing data. However, trickle migrations are more complicated, and they need more planning and time to implement properly, as well as more effort to test and validate the data once a migration is complete.
How to create a data migration plan
A data migration project can be challenging because administrators must maintain data integrity, time the project so there's minimal effect on the business and keep an eye on costs. Having a data migration plan helps to ensure there's minimal disruption and downtime to business processes.
Factors to consider during a data migration project include how long the migration will take, the amount of downtime required and the risk to the business due to technical compatibility issues, data corruption and application performance.
Data migration planning should include the following phases and considerations:
- Goals. Organizations must consider why the migration is being performed, its business and technical benefits, and intended outcomes.
- Online vs. offline. They also need to evaluate the tradeoffs of migrating data online across a network versus migrating data offline through the transfer of physical storage devices. Offline migration can be particularly attractive when migrating huge data stores from on-premises to cloud storage facilities.
- Discovery. This step should include considerations such as data sources, destinations, security, cost and which migration strategy to use.
- Resource assessment. It's important to identify who will be taking part in the migration. Understanding the available staff involvement and responsibilities is vital for the smooth execution of the migration. It also enables prompt troubleshooting if issues arise.
- Outages. Business impacts of migrations can be serious. It's important to know if the migration will disrupt normal operations and the potential extent of disruption. For example, online migrations can demand considerable network bandwidth that could reduce the performance of business workloads or require complete downtime during the migration.
- Process and rollback. The process or workflow that will be used to execute the migration should be outlined. All staff should be comfortable with their roles, and a rollback or recovery plan should be in place to ensure that data stores and workloads can continue to function in the event of a migration issue.
- Data inspection. Organizations should examine the data being migrated for data quality, anomalies and duplications. Data should also be backed up.
- Data formatting. It's important to evaluate the data format and determine whether the data requires additional formatting before migration. This can be a common issue when migrating data from one kind of database to another.
- Design. Data is organized and mapped out for where it's being moved to.
- Software tools. Any software that will help in the transition must be purchased or created.
- Migration. The migration process is initiated and its outcome tested or validated. This ensures that new data locations and the workloads that use the migrated data are operating as expected.
- Cleanup. Old or legacy systems are shut down and decommissioned. Unneeded equipment can also be repurposed to mitigate additional infrastructure investments. such as repurposing gear for software development testing tasks.
The three categories of data movers are host-based, array-based and network appliances:
- Host-based software. This is best for application-specific migrations, such as platform upgrades, database replication and file copying.
- Array-based software. This is primarily used to migrate data between similar systems.
- Network appliances. These migrate volumes, files or blocks of data depending on their configuration.
Data migration best practices
The following best practices should be used to protect data during a migration:
- Back up data before migrating it. If something goes wrong during migration and the data is lost, it can be restored from the backup.
- Understand what data is being migrated, where it lives, what form it's in and the form it will take at its new destination.
- Extract, transform and deduplicate data before moving it.
- Implement data migration policies so data is moved in an orderly manner.
- Test and validate the migration of data during the planning and design phase to ensure it's accurate.
- Audit and document the entire data migration process.
Data migration vs. data integration vs. data conversion
Migration, integration and conversion are sometimes applied interchangeably, but the three concepts are distinctly different. They should be applied with care in any business or technology setting.
Data migration
This is the process of transferring data between applications, data storage systems and data formats. Migrations can take place locally, with remote facilities or with cloud services, depending on the goals of the migration.
Data integration
This is the process of combining data from multiple source systems to create a unified data set for operations and analysis. The primary goal of data integration is to produce consolidated data sets that are clean, complete and consistent. Integration is a core element of the data management process and requires careful data quality review.
Data conversion
This is the process of changing data from one format to another. If a legacy system and a new system have identical fields, an organization could just migrate the data. However, the data from legacy systems is generally different and needs to be modified before migrating. Data conversion is often a step in the data migration process. For example, if temperature data is recorded in Celsius, but the application processes temperature in Fahrenheit, the temperature data must be converted to Fahrenheit before processing.
Find out more about the methods and tools used for on-premises-to-cloud migration, and weigh the pros and cons of the main approaches.







