What is a threat actor?
A threat actor, also called a malicious actor or bad actor, is an entity that seeks to cause harm to individuals, devices, networks or digital systems. They pose a security risk, often by exploiting vulnerabilities.
Threat actors can be individuals working alone or groups, such as organized cybercriminal gangs. They can also be state-sponsored groups and even malicious insiders.
What does a threat actor do?
Almost all threat actors have a malicious intent related to intentionally damaging an organization. They can also have other motivations, such as financial gain, political influence, espionage or simply disruption.
Once a threat actor infiltrates a system, they typically aim to access sensitive data, compromise company devices, infiltrate computer systems or gain control over an organization's core digital network.
Threat actors use a variety of techniques to achieve their goals, such as the following:
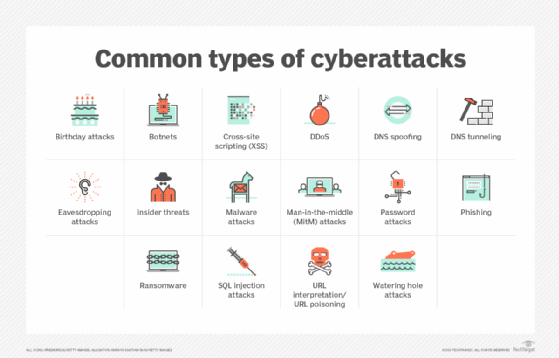
- Installing viruses or malicious software, known as malware.
- Getting victims to click on malicious links or download malicious attachments in email, known as phishing.
- Encrypting enterprise devices and demanding a ransom in exchange for the decryption key, called a ransomware attack.
- Exfiltrating data, known as a data breach.
- Spying on the organization, known as cyberespionage.
- Flooding a network with fake traffic so that it becomes unavailable to users, known as a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack.
- Remaining hidden in an organization's networks with the intention of doing any of the above for a long period of time or undertaking an advanced persistent threat (APT) attack.
- Exploiting insider access through insider threats that use the trusted status of employees or contractors to bypass security measures and access sensitive data and systems.
That said, the purpose of one threat actor might differ from that of another, depending on their motivations.
Types of threat actors
Most threat actors fall into one of the following categories:
- Cybercriminals. Cybercrime is almost always motivated by the lure of financial gain.
- Cyberterrorists. These threat actors aim to hold certain network or systems hostage for a higher purpose, such as to disable a country's critical infrastructure.
- Hacktivists. Hacktivism is usually motivated by political ideology, a social cause, or a desire to embarrass or harm an organization or to take revenge against it.
- Nation-state actors. These threat actors usually work on behalf of a rogue nation-state, either to support that nation-state's ideology or to gain some financial reward.
- Thrill seekers. These are individuals who execute attacks without a monetary or other purpose. Their aim is simply to have fun and to challenge themselves to outwit an organization or government.
- Insider threat actors. These threat actors work from inside the company to spy for another company. Some insider threat actors are motivated by anger or a desire to get revenge.
- Script kiddies. Script kiddies are inexperienced hackers who use prewritten tools to exploit vulnerabilities, often for notoriety or amusement.
Often, different threat actors use the same tools and tactics, such as malware, ransomware, phishing, social engineering attacks and backdoors. For example, hacktivist groups, such as Anonymous, use many of the same tools employed by financially motivated cybercriminals to detect website vulnerabilities, gain unauthorized access or carry out coordinated attacks against their targets. Furthermore, the two groups often have the same motivation: to gain access to sensitive information that will negatively affect the reputation of an individual, brand, company or government.
Threat actors are also classified based on whether they are inside or outside of an organization.
External threat actors
With external threat actors, no trust or privilege previously exists. These threat actors are the primary concern for organizations, not only because they're the most common, but also because they tend to cause more severe negative effects.
External threat actors are sometimes referred to as being commodity or advanced. A commodity threat actor launches a broad-based attack hoping to hit as many targets as possible. An advanced threat actor targets a specific organization, often seeking to implement an APT to gain network access and remain undetected for a long time, stealing data at will.
Internal threat actors
With internal or partner actors, some level of trust or privilege has previously existed. Internal actors are current or former employees, contractors or partners who already have some level of access to the organization's systems.
Internal threat actors generally get less attention from organizations' cybersecurity teams. However, ignoring them can be a mistake because they can also put the company at risk. These threats can be inadvertent -- for example, sending an email to the wrong recipient. They can be the result of carelessness, such as misconfiguring a cloud system. They can also be malicious, such as purposely leaking sensitive information and publishing it on the dark web.
Third-party threat actors
Third parties, such as partners, vendors and suppliers, can also be threat actors. When these parties access an organization's systems or data using insecure means, such as through public Wi-Fi networks or poorly secured accounts, they increase the risk of a real cyberattack or data breach.
Organizations can minimize the risks arising from these threat actors by implementing third-party risk management programs.
Who are threat actors' targets?
Threat actors target any individual or organization they feel could help them achieve their goals, which could be pursuing financial gain, bringing down a network, disrupting company operations or spreading chaos. Common targets of threat actors include the following.
Large enterprise targets
Large organizations are the most common targets of threat actors because they have larger and more complex networks, hold more sensitive data and possess substantial financial resources. In addition, reputational damage and business disruption are often part of the malicious activities attackers undertake against large entities.
These factors combine to make large organizations attractive targets for ransomware, phishing, APTs, social engineering, data breaches and other types of cyberattacks.
Government and infrastructure targets
Government organizations and critical infrastructure are key targets for threat actors. Nation-state actors, in particular, seek intelligence, conduct espionage and aim to disrupt government operations. By attacking and compromising these entities, threat actors can cause damage and chaos that could extend to a city or country.
The Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack is an example of an attack on critical infrastructure that had a major effect on the supply of oil and was deemed a national security threat. Similarly, the SolarWinds supply chain attack compromised the data, networks and systems of many government organizations all over the world.
Healthcare organizations
The healthcare industry is a major target for threat actors because of the high value of protected health information, which can be exploited for identity theft, insurance fraud or ransomware. According to Cybernews, breaches reached an all-time high in 2024, with more than 276 million compromised records.
Cyberattacks can also disrupt medical services, compromising patient care and safety. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare organizations were particularly vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Financial institutions
The financial sector's critical role in the economy makes it a high-value target for threat actors. These attacks commonly involve stealing valuable customer data, perpetrating various forms of fraud or deploying ransomware to extort significant amounts of money.
Small and medium-sized business targets
Cyberthreat actors have started targeting small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). These organizations typically have weaker security systems, usually because of limited cybersecurity budgets, smaller cybersecurity teams and possibly limited knowledge about cybersecurity risks and threats. Attacks on SMBs are more likely to result in a successful outcome, though the payout from these targets is smaller compared with what could be extracted from a larger company.
Individual targets
Individuals and everyday users are prime targets of threat actors, often falling victim to identity theft, financial fraud or espionage. Public officials, executives and other high-profile individuals are particularly at risk due to their access to sensitive information and their potential to influence key decisions.
Threat actors attack individuals and households by hacking into personal devices, eavesdropping on home and public Wi-Fi networks, or stealing personal information, identities or money via phishing attacks. However, they typically don't use methods such as DDoS attacks, supply chain compromises, code injections, man-in-the-middle attacks or credential harvesting against individuals, as those types of attacks are commonly targeted at organizations.
Impact of a successful threat actor
If a threat actor succeeds in executing an attack, the affected organization experiences a security incident that could result in the following serious consequences:
- Operational disruptions. Threat actors can cause significant system downtime and operational disruptions with cyberattacks that render systems or services unavailable. Such attacks can halt business processes, production lines and customer access. The duration of this disruption can range from hours to weeks -- or even months -- depending on the attack's severity and the organization's recovery capabilities.
- Data breaches and identity theft. Threat actors can expose personally identifiable information and sensitive business data, leading to privacy violations, lawsuits and black market sales.
- Financial losses. Organizations can face direct financial losses as a result of ransom payments, fraudulent activities and disruptions to operations caused by threat actors. Indirect costs could include legal fees, regulatory fines and reputational damage.
- Reputational damage. Businesses and governments lose public trust if they fail to protect sensitive information or respond effectively to an attack. This can lead to churn, where customers leave for competitors perceived as more secure.
- Regulatory fines. Organizations might be subject to legal action, regulatory fines and penalties after a breach, especially if they are found to have neglected mandated cybersecurity standards.
- National security risks. Nation-state actors can infiltrate critical infrastructure, steal classified data and spread disinformation. They can conduct cyberespionage, disrupt government functions, or manipulate economic and political systems as part of their attacks.
- Increased insurance premiums. The cost of cyber insurance policies often rises significantly after a breach due to the company's increased risk profile.
- Investigation and remediation costs. Following a security incident, organizations can incur significant expenses for forensic analysis, incident response, system remediation and rebuilding the compromised infrastructure.
Strategies to stay safe from threat actors
The prospect of substantial financial rewards from successful cyberattacks continues to drive the growing number of active threat actors. Furthermore, as organizations' networks expand and become more complex, their attack surfaces also expand, presenting threat actors with more opportunities to attack.
To mitigate the power and impact of threat actors and prevent them from executing security incidents, organizations should consider taking the following steps:
- Multilayered security approach. Organizations should adopt a multilayered security infrastructure that includes a host of technologies, including antivirus, antimalware, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, endpoint detection and response, and network segmentation.
- Multifactor authentication. MFA enhances security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before accessing a system. Organizations should adopt it to strengthen user authentication and minimize the weaknesses inherent in password-only authentication systems.
- Advanced network protection systems. Organizations should implement advanced systems such as security orchestration, automation and response; security information and event management; and extended detection and response to keep up with sophisticated threat actors and mitigate emerging threats.
- Secure coding practices. Organizations should encourage software development teams to adopt secure coding practices and shift-left testing during the software development lifecycle to identify and address vulnerabilities before deployment.
- Security policies. Organizations need to create and distribute clear and comprehensive security policies that outline which employee behaviors are acceptable and which are prohibited when using the organization's IT assets.
- Security awareness training. Organizations should invest in providing security awareness training to improve cyberhygiene and create a more security-aware culture for their employees.
- Access control. Strict access controls, such as role-based access control combined with the principle of least privilege, should be enforced to ensure users only get access to the resources that are essential for their job functions.
- Zero trust. Adopting zero trust as a core security strategy ensures that every user and device is continuously authenticated and authorized based on the never trust, always verify principle. This approach limits lateral movement and minimizes the potential impact of a breach.
In addition to these strategies, staying informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities is crucial. Regularly following cybersecurity news and participating in security forums and webinars help both individuals and organizations enhance their knowledge and strengthen their preparedness against threat actors and potential cyberattacks.
Organizations should know the signs of common security incidents and how to respond to keep systems and data safe. Learn about the types of security incidents and how to prevent them.