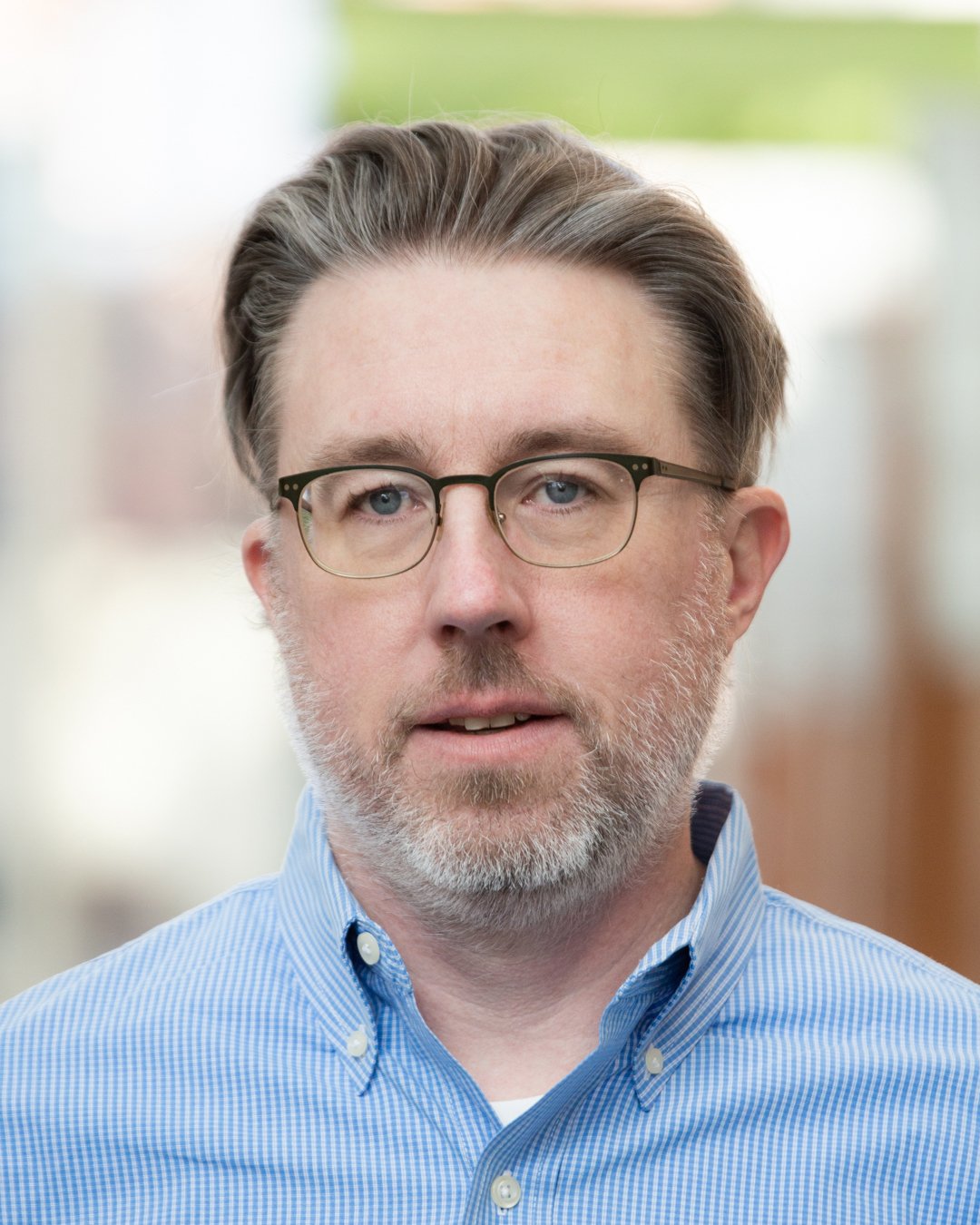
How to build a cybersecurity strategy and plan in 4 steps
A cybersecurity strategy isn't meant to be perfect, but this high-level plan must be proactive, effective, actively supported and evolving. Here are four key steps to get there.
A cybersecurity strategy is a high-level plan for how your organization will secure its assets during the next three to five years. Obviously, because technology and cyberthreats can both change unpredictably, you'll almost certainly have to update your strategy sooner than three years from now. A cybersecurity strategy isn't meant to be perfect; it's a strongly educated guess as to what you should do. Your strategy should evolve as your organization and the world around you evolve.
The intended outcome of developing and implementing a cybersecurity strategy is that your assets are better secured. This generally involves a shift from a reactive to a proactive security approach, where you're more focused on preventing cyberattacks and incidents than reacting to them after the fact.
But solid cybersecurity strategies will also better prepare organizations to respond to those incidents that do occur. By preventing minor incidents from becoming major ones, organizations can preserve their reputations and reduce harm to employees, customers, stockholders, partners and other interested parties.
How do you plan a cybersecurity strategy for your business?
Planning a cybersecurity strategy for your organization takes effort, but it could mean the difference between surpassing your competitors and going out of business. Here are the basic steps to follow in developing an effective security strategy.
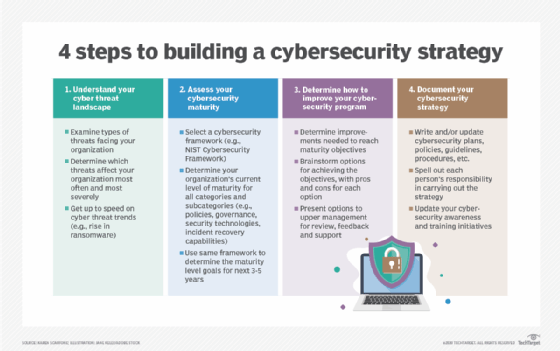
Step 1. Understand your cyberthreat landscape
Before you can understand your cybersecurity threat landscape, you need to examine the types of cyberattacks your organization faces today. Which types of cyberthreats currently affect your organization the most often and most severely: ransomware, other forms of malware, phishing, insider threats or something else? Have your competitors had major incidents recently -- and, if so, what types of threats caused them?
Next, get yourself up to speed with predicted cyberthreat trends that could affect your organization. For example, many security researchers feel that ransomware has become an even bigger threat as ransomware gangs flourish and expand their attacks. There's also increasing concern about supply chain vulnerabilities caused by, for example, purchasing compromised components and either using them within your organization or building them into products you sell to customers. Understanding what cybersecurity threats you'll face in the future and the likely severity of each of them is key to building an effective cybersecurity strategy.
Step 2. Assess your cybersecurity maturity
Once you know what you're up against, you need to do an honest assessment of your organization's cybersecurity maturity. Select a cybersecurity framework, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. Use it first to assess how mature your organization is in dozens of different categories and subcategories, from policies and cybersecurity governance to security technologies and incident recovery capabilities. This assessment should include all of your technologies, from traditional IT to operational technology, IoT and cyber-physical systems.
Next, use the same cybersecurity framework to determine where your organization should be in the next three to five years in terms of maturity for each of those categories and subcategories. For example, if DDoS attacks will be a major threat, you might want your network security capabilities to be particularly mature. If ransomware will be your biggest security issue, ensuring that your backup and recovery capabilities are highly mature could be key. If data breaches due to employee use of external generative AI technologies are a significant concern, emphasizing the maturity of technologies that detect and stop data leakage is prudent. The maturity levels you're targeting are your new strategic objectives.
Step 3. Determine how to improve your cybersecurity program
Now that you've established a baseline and determined where you want to be going forward, you need to figure out the cybersecurity tools and cybersecurity capabilities that will help you reach your destination. In this step, you determine how to improve your cybersecurity program so that you achieve the strategic objectives you've defined. Every improvement will consume resources -- money, staff time, etc. You'll need to think about different options for achieving the objectives and the pros and cons of each option. It could be that you decide to outsource some or all of your security tasks.
Cybersecurity career advice
Looking to further your career in cybersecurity? These five articles provide timely information on how to build the technical and personal skills you'll need to be successful.
Cybersecurity career path: A strategic guide for professionals
Cybersecurity certifications to boost your career
Must-have cybersecurity skills for career success
When you've selected a set of budget options, you'll want to present them to upper management at your organization for their review, feedback and -- hopefully -- support. Changing the cybersecurity program might affect how business is done, and executives need to understand that and accept it as necessary to sufficiently safeguard the enterprise from cyberthreats. Upper management might also be aware of other plans for the coming years that your efforts could take advantage of.
Step 4. Document your cybersecurity strategy
Once you have management approval, you need to ensure your cybersecurity strategy is documented thoroughly. This includes writing or updating risk assessments as well as cybersecurity plans, policies, guidelines, procedures and anything else where you need to define what's required or recommended in order to achieve the strategic objectives. Making it clear what each person's responsibilities are is key.
Be sure that, as you write and update these documents, you're getting active participation and feedback from the people who will be doing the associated work. You also need to take the time to explain to them why these changes are being made and how important the changes are so that, hopefully, people will be more accepting and supportive of them.
Don't forget that your cybersecurity strategy also necessitates updating your cybersecurity awareness and training efforts. Everyone in the organization has a role to play in mitigating security issues and improving your enterprise cybersecurity program. As your risk profile changes, so must your cybersecurity culture.
Cybersecurity strategy pitfalls to avoid
When planning your organization's cybersecurity strategy, look out for common pitfalls to avoid. Here are some examples:
- Insufficient management support. If senior leadership doesn't fully buy into the creation and implementation of the cybersecurity strategy, you're likely to face insurmountable obstacles. For example, the budget and staffing for cybersecurity are likely to be far too low to achieve the plans and to adequately maintain the cybersecurity program over time.
- Weak cybersecurity risk management processes. The cybersecurity strategy must have robust cybersecurity risk management processes throughout the risk lifecycle. This is the foundation the organization will rely on to identify, assess, prioritize and respond to new and changing cybersecurity risks on an ongoing basis. The processes also need to include risks involving third parties, such as supply chain risks for technology products and services. Without strong cybersecurity risk management in place, the organization will often be reacting to incidents after the fact instead of proactively preventing incidents and minimizing damage.
- Overlooking cybersecurity fundamentals. When planning for the coming years, it's natural to be overly optimistic and anticipate that new cybersecurity controls will work much better than what's available today. We've seen over and over that cybersecurity tends to progress slowly. Cybersecurity fundamentals, such as using phishing-resistant authentication methods and having several layers of controls instead of only one (e.g., antivirus software), are just as important as ever in implementing cybersecurity programs. Don't overlook the fundamentals when planning your strategy.
- Shelving the cybersecurity strategy. Implementing a cybersecurity strategy is an ongoing process that necessitates monitoring and reassessment throughout its life. Creating a strategy and never revisiting it is likely to result in implementation gaps that weaken the organization's cybersecurity program; over time, the cybersecurity program will drift further and further from what the organization needs.
Who should be involved in cybersecurity strategy planning?
Organizations should be inclusive when it comes to who participates in cybersecurity strategy planning. The core team should draw mainly from cybersecurity leadership and staff and from technology and risk management professionals. As the strategy develops, input should be sought from other technology groups within the organization as well as technology experts representing the organization's business units. The organization's legal and compliance professionals should also review the strategy and identify any issues that must be addressed before the strategy is finalized. The organization's senior leadership must also review and approve the strategy.
One set of stakeholders that might be overlooked is the organization's users. It's vitally important to take the end users' perspective into consideration when planning the strategy. If the implementation of the strategy negatively impacts the usability of technology, making it more difficult or time-consuming for people to do their jobs, users are more likely to circumvent security controls. And don't forget about remote workers, who likely need their own coverage within the strategy and who will probably have unique usability limitations that must be carefully considered.
Editor's note: This article was updated by the author in June 2025 to reflect the latest best practices in planning, developing and implementing a cybersecurity strategy.
Karen Scarfone is a general cybersecurity expert who helps organizations communicate their technical information through written content. She co-authored the Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 and was formerly a senior computer scientist for NIST.







