cloud storage
What is cloud storage?
Cloud storage is a service model in which data is transmitted and stored on remote storage systems, where it is maintained, managed, backed up and made available to users over a network -- typically, the internet. Users generally pay for their cloud data storage on a per-consumption, monthly rate.
Cloud storage is based on a virtualized storage infrastructure with accessible interfaces, near-instant elasticity and scalability, multi-tenancy, and metered resources. Cloud-based data is stored in logical pools across disparate, commodity storage servers located on premises or in a data center managed by a third-party cloud provider.
Cloud service providers manage and maintain data transferred to the cloud. Storage services are provided on demand in the cloud, with capacity increasing and decreasing as needed. Organizations opting for cloud storage eliminate the need to buy, manage and maintain in-house storage infrastructure. Cloud storage has radically driven down the per-gigabyte cost of storage, but cloud storage providers have added operating expenses that can make the technology considerably more expensive, depending on how it's used.
Types of cloud storage
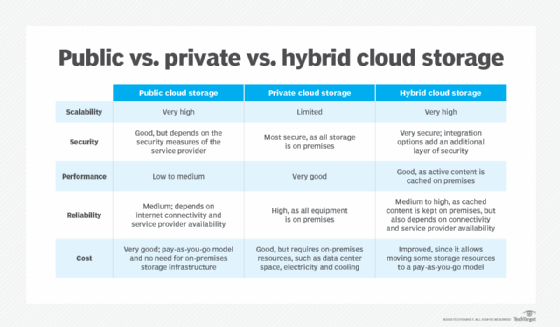
There are three main cloud storage options, based on different access models: public, private and hybrid.
Public cloud. These storage services provide a multi-tenant storage environment that is most suited for unstructured data on a subscription basis. Data is stored in the service provider's data centers with storage data spread across multiple regions or continents. Customers generally pay on a per-use basis, similar to the utility payment model. In many cases, there are also transaction charges based on frequency and the volume of data being accessed. This market sector is dominated by the following services:
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3);
- Amazon Glacier for deep archival or cold storage;
- Google cloud storage;
- Google Cloud Storage Nearline for cold data; and
- Microsoft Azure.
Private cloud. A private cloud storage service is an in-house storage resource deployed as a dedicated environment protected behind a firewall. Internally hosted private cloud storage implementations emulate some of the features of commercial public cloud services, providing easy access and allocation of storage resources for business users, as well as object storage protocols. Private clouds are appropriate for users who need customization and more control over their data or who have stringent data security or regulatory requirements.
Hybrid cloud. This cloud storage option is a mix of private cloud storage and third-party public cloud storage services, with a layer of orchestration management to operationally integrate the two platforms.
The model offers businesses flexibility and more data deployment options. An organization might, for example, store actively used and structured data in an on-premises private cloud and unstructured and archival data in a public cloud. A hybrid environment also makes it easier to handle seasonal or unanticipated spikes in data creation or access by cloud bursting to the external storage service and avoiding having to add in-house storage resources.
Adoption of the hybrid cloud model has increased in recent years. Despite the benefits of hybrid clouds, they present technical, business and management challenges. For example, private workloads must access and interact with public cloud storage providers, so compatibility, and reliable and ample network connectivity are important factors. An enterprise-level cloud storage system should be scalable to suit current and future needs, accessible from anywhere and application-agnostic.
How does cloud storage work?
Cloud service providers maintain large data centers in multiple locations around the world. When customers purchase cloud storage from a provider, they turn over most aspects of the data storage to the vendor, including security, capacity, storage servers and computing resources, data availability and delivery over a network. Customer applications can access the stored cloud data through traditional storage protocols or application programming indicators (APIs), or they can also be moved to the cloud.
How cloud storage works varies depending on the type of storage used. The three main types are block storage, file storage and object storage:
- Block storage divides large volumes of data into smaller units called blocks. Each block is associated with a unique identifier and placed on one of the system's storage drives. Block storage is fast, efficient and provides the low latency required by applications such as databases and high-performance workloads.
- File storage organizes data in a hierarchical system of files and folders; it is commonly used with personal computer storage drives and network-attached storage (NAS). Data in a file storage system is stored in files, and the files are stored in folders. Directories and subdirectories are used to organize the folders and locate files and data. A file storage-based cloud can make data access and retrieval easier, with this hierarchical format being familiar to users and required by some applications.
- Object storage stores data as objects, which consist of three components: data stored in a file, metadata associated with the data file and a unique identifier. Using the RESTful API, an object storage protocol stores a file and its associated metadata as a single object and assigns it an identification (ID) number. To retrieve content, the user presents the ID to the system and the content is assembled with all its metadata, authentication and security. Object-based storage systems allow metadata to be customized, which can streamline data access and analysis. With object storage, data can be stored in its native format with massive scalability.
In recent years, object storage vendors have added file system functions and capabilities to their object storage software and hardware largely because object storage was not being adopted fast enough. For example, a cloud storage gateway can provide a file system emulation front end to its object storage; that arrangement often allows applications to access the data without supporting an object storage protocol. All backup applications use the object storage protocol, which is one of the reasons why online backup to a cloud service was the initial successful application for cloud storage.
Most commercial cloud storage services use vast numbers of hard drive storage systems mounted in servers that are linked by a mesh-like network architecture. Service providers have also added high-performance layers to their virtual storage offerings, typically made up of solid-state drives (SSDs). High-performance clouds storage is generally most effective if the servers and applications accessing the storage are also resident in the cloud environment.
Learn more about the pros and cons of block, file and object storage.
Advantages and disadvantages of cloud storage
Cloud storage provides many benefits that result in cost savings and greater convenience for users, compared with a traditional storage area networks (SAN). There also are shortcomings with cloud storage -- particularly, the public services -- that make organizations hesitant to use these services or limit how they use them.
Advantages
- Pay as you go. With a cloud storage service, customers only pay for the storage they use, eliminating the need for big capital expenses. While cloud storage costs are recurring, rather than a one-time purchase, they are often so low that, even as an ongoing expense, they may still be less than the cost of maintaining an in-house system.
- Utility billing. Because customers only pay for the capacity they use, cloud storage costs can decrease as usage drops. This is in stark contrast to using an in-house storage system, which will likely be over configured to handle anticipated growth. A company will pay for more than it needs initially, and the cost of the storage will never decrease.
- Global availability. Cloud storage is typically available from any system, anywhere and at any time; users do not have to worry about operating system (OS) capability or complex allocation processes.
- Ease of use. Cloud storage is easy to access and use, so developers, software testers and business users can get up and running quickly without having to wait for an IT (information technology) team to allocate and configure storage resources.
- Off-site security. By its very nature, public cloud storage offers a way to move copies of data to a remote site for backup and security purposes. Again, this represents a significant cost savings when compared to a company maintaining its own remote facility.
An in-house cloud storage system can offer some of the above ease-of-use features of a public cloud service, but it will lack much of the storage capacity flexibility of a public service. Some hardware vendors are trying to address this issue by allowing their customers to turn on and off capacity that has already been installed in their arrays.

Disadvantages
- Security. Data security is the most cited factor that may make companies cautious about using public cloud storage. The concern is that once data leaves a company's premises, it no longer has control over how the data is handled and stored. Storing regulated data is also a concern. Service providers have tried to allay those fears by enhancing their security capabilities with data encryption, multifactor authentication (MFA), data storage in multiple locations and improved physical security.
- Data access. Maintaining access to data stored in the cloud can also be an issue and could significantly increase the cost of using cloud storage. A company may need to upgrade its connection to the cloud storage service to handle the volume of data it expects to transmit. For instance, the monthly cost of an optical link can run into the thousands of dollars.
- Performance degradation. A company may run into performance issues if its in-house applications need to access the data it has stored in the cloud. In those cases, it will likely require either moving the servers and applications into the same cloud or bringing the necessary data back in-house.
- Cost. If a company requires a lot of cloud storage capacity and frequently moves its data back and forth between on-premises systems and the cloud, the monthly costs can be high. Compared to deploying the storage in-house, the ongoing costs could eventually surpass the cost of implementing and maintaining the on-premises system.
Cloud storage considerations
To determine whether using cloud storage will result in operational efficiencies and be cost-effective, a company must take these four steps:
- Compare the one-time and recurring costs of purchasing and managing storage capacity in-house versus the ongoing costs of storing and accessing data in the cloud.
- Determine if additional telecommunications expenses will be required for the appropriate access to the service provider.
- Decide if the cloud storage service provides adequate security and data governance.
- Develop an in-house cloud security strategy, with procedures for access and use of cloud storage to maintain effective management of data and control expenses.
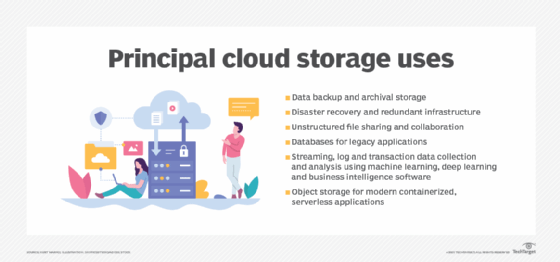
Examples of cloud storage
The most common uses for cloud storage are:
- cloud backup
- disaster recovery (DR)
- archiving infrequently accessed data
An increasing number of companies are using cloud storage services for DevOps as a way to cut capital costs. Developers can spin up the compute and storage resources for the duration of the project development and testing, and then spin them down when it ends.
Increasingly, organizations are moving key applications to the cloud as the service providers have improved performance and tightened security. In addition, companies that experience substantial seasonal fluctuations in the volume of data they create can tap into cloud storage to handle these bursts of data creation activity.
For small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs), some specialized cloud storage services, such as file sync and share, may be useful on an individual server or user basis. The file syncing features of these services ensure the versions of files stored locally on the sync client -- a server or end user's PC -- and in the cloud are consistent. Versioning and file-sharing capabilities also are often included.
Cloud storage service providers
The cloud-based storage market is dominated by Amazon Web Services, Google and Microsoft Azure, but traditional storage vendors like Dell EMC, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Hitachi Data Systems, IBM and NetApp also operate in the space with products for both enterprise and small business owners that include self-service cloud portals to provision and monitor use. Some online file storage services, such as Box and Dropbox, have business-to-consumer (B2C) cloud storage services, as well as business-to-business (B2B) offerings.
Organizations considering the use of cloud storage should be aware of the pros and cons of using cloud computing technologies, in general. If the decision is made to move forward with the cloud, organizations can use topic-based cloud guides to determine which cloud storage types and services best fit their business needs.





