What is a virtual storage area network (VSAN)? How it works, benefits and use cases
A virtual storage area network (VSAN) is a logical partition in a physical storage area network, or SAN. VSAN products enable organizations to create and manage storage for virtual machines (VMs) by logically representing a physical SAN.
A virtual topology is defined on a physical SAN so that a group of hosts can communicate with each other. Network admins can set up multiple SANs with different topologies using VSANs. They can also build a single topology containing switches, links and one or more VSANs, with each VSAN having the same behaviors and properties of a SAN. Without a VSAN, separate switches and links would be needed for separate SANs.
What is the purpose of a VSAN?
Businesses rely on multiple isolated VSANs to make a storage system easier to configure and scale out. Subscribers can be added or relocated without needing to change the physical layout. Using VSAN technology, disk space can be pooled from multiple hypervisor hosts to create a single, distributed storage space. This space or data store is logically partitioned but can be centrally managed as if it were a single SAN.
VSANs enable traffic to be isolated within specific portions of a SAN. So, if a problem occurs in one logical partition, it can be handled with minimal disruption to the rest of the network. Traffic can be isolated based on different requirements, including production or testing in an enterprise network or storing backup traffic on separate VSANs. Also, multiple VSANs can be created on the same physical SAN to provide redundancy protection in case one VSAN fails.
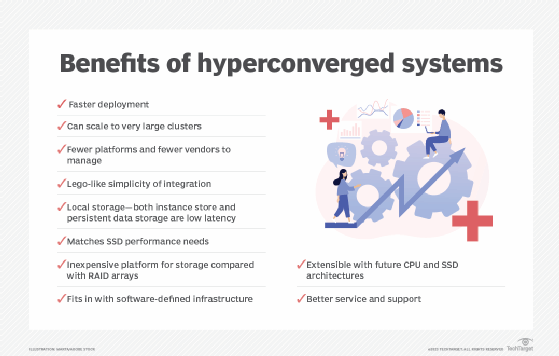
VSAN platforms help achieve hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) by combining an organization's compute and storage resources into a consolidated storage cluster. The HCI approach enables effective management, which is needed to protect critical infrastructure workloads from disruption or failure.
How a VSAN works
A VSAN is a storage virtualization technology that brings the benefits of virtualization to SAN storage. Generally speaking, VSAN refers to a group of storage devices that communicate with each other using a virtual topology. This topology is defined on the physical SAN.
A VSAN appliance enables unused storage capacity on virtual servers to be pooled and accessed by virtual servers as needed. It can pool local storage resources from a cluster of servers within a data center into a single shared storage pool.
This is achieved by virtualizing multiple, disparate physical data storage devices -- such as solid-state drives or hard disk drives -- to form a single data resource. That resource appears to servers as a traditional SAN or network-attached storage (NAS) device without using dedicated SAN or NAS storage devices. Multiple users can share the virtualized storage.
To facilitate the sharing of network storage, the VSAN utilizes various protocols, such as Fibre Channel (FC), Server Message Block, Internet Small Computer System Interface or Network File System. The VSAN also establishes a network that isolates traffic based on different parameters, such as data source or user access level.
A VSAN appliance is often a software program that runs on a VM, but some storage hardware vendors have incorporated VSAN appliances into their firmware. Depending on the vendor, a virtual SAN appliance might also be called a software-defined storage appliance. The software VSAN provides access to storage and unifies disparate storage instances, including cloud storage, on-premises storage, tape drives and hard drives, to ease storage management.
Benefits of virtual storage area networks
VSANs can provide many benefits, including the following:
- Data sharing and performance. With VSANs, more users can access more types of storage, including block and file storage, depending on their requirements.
- High performance. Network admins can create rules to distribute bandwidth and compute capacity depending on the priority of application type or storage access. For example, mission-critical applications are given more resources and prioritized for access, thus ensuring optimal performance. Using caching, data mirroring and distribution further optimizes VSAN performance without requiring specialized hardware.
- Nondisruptive data migration. A VSAN enables adopters to migrate data between storage resources easily and with minimal or no downtime.
- Better information lifecycle management. Storage virtualization makes it easier to ensure data is stored on the appropriate device. Information lifecycle management puts frequently accessed data on high-performance storage and less frequently accessed data on lower-performing, less expensive storage resources.
- Improved manageability. Storage management can become difficult when storage resources involve several vendors or even different models from the same vendor. A VSAN provides a virtualized view of storage resources to simplify storage configuration, provisioning and management. Also, the VSAN software typically provides a single management panel that simplifies VSAN administration, management and troubleshooting.
- Overall simplicity. Compared to the alternatives, a VSAN is easy to provision and manage because it's embedded within the hypervisor. There's no need to change the physical structure of a SAN to add, move or change users among VSANs. Only configuration at the port level is required. This speeds up VSAN installation and configuration.
- Reduced total cost of ownership (TCO). A VSAN can be deployed on inexpensive x86 servers and with generic storage devices. Moreover, it doesn't require physical storage arrays, eliminating the need for upfront investments in expensive physical storage arrays and reducing TCO.
- Scalability. The VSAN approach allows for the creation of multiple logical layers on top of a single physical SAN. The fabric services can be replicated on a per-VSAN basis, making VSAN a highly available and scalable storage option for cloud computing environments.
- Redundancy. Multiple VSANs can be created on the same physical SAN, and each VSAN can be independently configured. These capabilities provide enhanced redundancy and resilience. So, even if one VSAN fails, the backup path between the host and the device includes failure protection.
- Security. VSANs can provide higher security in FC fabrics by isolating devices that are physically connected to the same fabric and separating traffic based on low vs. high security requirements. Also, since independent configurations are allowed, user data access can be controlled on an as-needed basis. Tools such as data replication and snapshots provide even more data security and protection against losses.
Virtual storage area network use cases
A VSAN can prove useful for various real-world use cases, including the following applications:
- Storage virtualization. Virtualization converts local, physical storage devices into virtual storage to consolidate unused storage capacity so it can be managed more efficiently. VSANs also modernize storage infrastructure and enable storage to grow independently to optimize resource utilization.
- Cloud-native applications. With a VSAN, organizations can run and manage storage for containers and VMs on the same platform. They can also easily manage data for both stateless and stateful applications.
- Demilitarized zones and test environments. Vendors provide demilitarized zones, also known as security zones, to further isolate internal infrastructure and applications and provide an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
- Virtual desktop infrastructure. VDI environments let administrators run apps on a host server on-premises or in a cloud data center. They can then deliver those apps to end users' devices over a network. VSANs facilitate VDI setup, improving desktop and app performance and user experiences.
- Support for edge computing sites. VSANs create shared storage environments useful for edge devices operating in remote locations and sometimes austere environments. If an edge server is disrupted, a VSAN can keep it running until the problem is addressed and remedied.
- Remote offices. With a VSAN, enterprises can add as many nodes as needed to support the needs of remote offices and branch offices. Many VSAN vendors offer flexible licensing models to boost IT productivity and control costs.
- Disaster recovery. VSANs provide advanced data security and recovery capabilities that can simplify disaster recovery. These include replication and snapshots, data protection, scalability, flexibility and high availability of critical applications and data. Recovery can be automated with some VSAN solutions, while disaster recovery costs can be reduced by using HCI servers instead of purpose-built storage arrays.
VSAN vendors and features
The acronym for a virtual storage area network is spelled differently by the vendors that offer storage virtualization products with different features.
When represented by all capital letters (VSAN), the acronym is often associated with Cisco Systems and discussed in conjunction with zoning and different topologies. Zoning splits a physical SAN into multiple isolated subnetworks. Multiple zones can be defined within a VSAN. However, a zone can never span multiple VSANs because two VSANs are equivalent to two unconnected SANs with routing, naming and zoning protocols. That's why Zone A on VSAN 1 will be different and separate from Zone A in VSAN 2.
When spelled with a lowercase V (vSAN), the acronym is usually associated with VMware -- the company that introduced vSAN technology in 2014 -- and Microsoft Hyper-V features that allow available storage to be pooled from across clustered hosts.
VMware vSAN is the hyperconverged storage component of VMware Cloud Foundation and vSphere Foundation. It provides integrated storage for private clouds, a consistent infrastructure across environments, unified management tools and disaggregation capability for optimal storage flexibility and scalability.
Today, most storage software or hardware vendors offer some form of VSAN for their own or other vendors' storage and server hardware. Several vendors offer software-only packages that let users assemble their own virtualized storage environments using off-the-shelf servers and storage devices.
Here are some of the most well-known VSAN vendor offerings:
- Dell VxRail.
- HPE SimpliVity.
- Huawei FusionCube.
- Nutanix Cloud Platform.
- Scale Computing Platform.
- StarWind Virtual SAN.
Choosing the right server virtualization management software is critical to meeting your organization's current and future needs. See how to find the best server virtualization management software for your environment. Also, HCI has found a home in data centers since its emergence. However, technology is rapidly changing and evolving. Learn more about what HCI has to offer and explore hyperconvergence trends.