solid-state storage
What is solid-state storage?
Solid-state storage is a type of computer storage media that stores data electronically and has no moving parts.
Solid-state storage is made from silicon microchips. Because there are no moving parts, solid-state drives (SSDs) require less power and produce far less heat than spinning hard disk drives (HDDs) or magnetic tape. In addition to providing faster and more consistent input/output (I/O) times, solid-state storage media offers the same levels of data integrity and endurance as other electronic devices.
Solid-state storage can be found generally in three form factors: SSDs, solid-state cards and solid-state modules. An important advantage of solid-state storage is that it contains no mechanical parts, enabling data transfer to and from storage media to take place at a much higher speed and providing a more predictable life span for the storage media.
How solid-state storage can replace multiple hard drives
Although solid-state storage technology is not new, interest in how the technology can be used to improve enterprise storage has been relatively recent. Part of this trend can be attributed to reductions in price, but hardware performance also plays a role. Since the turn of this century, processor speeds have continued to increase dramatically, while read/write times for mechanical HDDs have not.
Today's central processing units (CPUs) can process data much faster than HDD storage can supply it. The resulting lag time is known as latency.
One way enterprise administrators have traditionally dealt with high storage latency is by short-stroking the HDDs in the storage system. Short-stroking deliberately limits the disk drive capacity to the outer tracks of the drive so the disk drive actuator only has to move its heads across a shorter distance and fewer tracks, which reduces seek time.
Environments that implement short-stroking typically have to make up for the reduced capacity in each disk drive by increasing the number of drives in these configurations. While short-stroking might deliver the required performance, it's an uneconomical solution.
In contrast, solid-state storage devices have zero seek time -- it doesn't matter where the needed data is stored. This considerably reduces their latencies, which makes them faster than HDDs, especially for random read/write operations. Solid-state storage devices have less of a performance advantage when it comes to sequential read/write operations.
Enterprise applications for solid-state storage
Enterprises use solid-state storage technology for primary storage and also as cache in front of traditional spinning disks, introducing a new layer between the processor and storage.
With capacities of dozens of terabytes and a cheaper cost, hard disks may still be the preferred media for archive and other high-capacity/limited-access applications. However, solid-state may soon rival hard disk systems for those applications, too. Solid-state vendors, such as Western Digital, have introduced even higher capacity products.
Advances in solid-state storage haven't been limited to increasing capacities. The non-volatile memory express (NVMe) protocol uses the Peripheral Component Interconnect Express interface to provide more direct and faster communications between the solid-state storage and the server's CPU. NVMe reduces latency and pumps up I/O for more demanding applications.
Types of solid-state storage systems
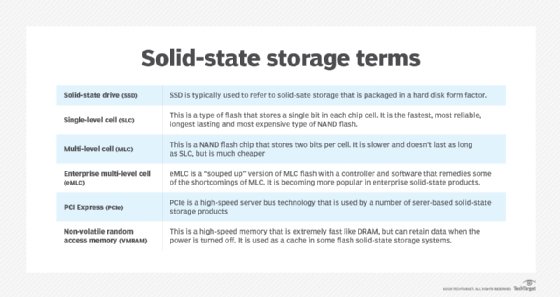
There are two types of solid-state systems: flash memory-based systems and RAM-based systems. There are also two types of flash memory: NAND flash and NOR flash.
NAND flash is generally used in enterprise products because of its higher capacities and faster erase and write times. It is non-volatile, which means the data on the storage media remains in memory after the power is turned off.
In contrast, RAM-based solid-state storage is volatile -- the storage media requires constant power to retain the data it holds. RAM-based systems have the advantage of being relatively insensitive to the number of times data is written to them. However, because of the high cost of RAM and its volatility, it's used almost exclusively as system memory rather than storage.
A new category of solid-state storage called storage class memory (SCM) has emerged that bridges the gap between system RAM and persistent storage. SCM provides greater performance than typical solid-state storage devices but is still slower than RAM. It does, however, mimic RAM in how it addresses and accesses data, so it can work more closely with system memory to further boost performance.
Under the hood of solid-state storage
Flash-based SSDs store data in cells on the NAND chip. Currently, there are four ways data is stored in those cell: single-level stores one bit of data per cell; multi-level puts two bits in a cell; triple-level stores three bits per cell; and quad-level stores four bits of data per cell. Penta-level, storing five bits per cell, was in development as of March 2024. As the number of bits per cell increases, capacity goes up, but performance dips.
Capacity further increases by shifting from a planar to 3D architecture. In a planar design, all the cells are laid out next to each other on one level; 3D NAND layers cells on top of each other, thus making it possible to increase capacity without increasing the chip's footprint.
Flash-based systems have a finite number of writes, and like magnetic tape, the media can wear out. For solid-state storage devices, writing involves a process called the program/erase cycle (P/E cycle) where data that occupies a cell must be deleted before new data is written to that cell. That's why write operations are slower than reads with solid-state storage.
The P/E cycle is the main cause of wear for NAND flash; solid-state storage vendors typically estimate the amount of wear its products can endure before failing in terms of how many device/drive writes per day the device can handle.
Editor's note: This article was revised in 2024 by TechTarget editors to improve the reader experience.







