
What is narrow AI (weak AI)?
Narrow AI, also known as weak AI, is an application of artificial intelligence technologies to enable a high-functioning system that replicates -- and perhaps surpasses -- human intelligence for a dedicated purpose.
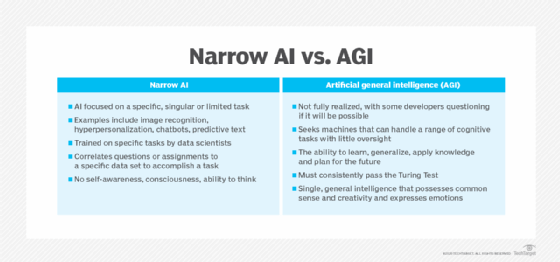
Narrow AI is often contrasted with artificial general intelligence (AGI), sometimes called strong AI; a theoretical AI system that could be applied to any task or problem.
Examples of narrow AI
All forms of modern AI systems can be classified as narrow AI. They are as follows:
- Image and facial recognition systems. These systems, including those used by social media companies like Facebook and Google to automatically identify people in photographs, are forms of weak AI.
- Chatbots and conversational assistants. This includes popular virtual assistants Google Assistant, Siri and Alexa. Also included are simpler, customer-service chatbots, such as a bot that assists customers in returning an item to a retail store.
- Self-driving vehicles. Autonomous or semiautonomous cars, such as some Tesla models and autonomous drones, boats and factory robots, are all applications of narrow AI.
- Predictive maintenance models. These models rely on data from machines, often collected through sensors, to help predict when a machine part may fail and alert users ahead of time.
- Recommendation engines. These systems that predict content a user might like or search for next are forms of weak AI.
Advantages and disadvantages of narrow AI
Advantages. Narrow AI systems can perform single tasks well, often better than humans. A weak AI system designed to identify cancer from X-ray or ultrasound images, for example, might be able to spot a cancerous mass in images faster and more accurately than a trained radiologist.
Meanwhile, a predictive maintenance platform could analyze incoming sensor data in real time, a feat virtually impossible for a person or group of people to do, to predict roughly when a piece of a machine will fail.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
Disadvantages. Still, narrow AI systems can only do what they are designed to do and can only make decisions based on their training data. A retailer's customer-service chatbot, for example, could answer questions regarding store hours, item prices or the store's return policy. Yet, a question about why a certain product is better than a similar product would likely stump the bot, unless its creators took the time to program the bot to respond to such questions specifically.
Meanwhile, AI systems are prone to bias, and can often give incorrect results while being unable to explain them. Complex models are often trained on massive amounts of data -- more data than its human creators can sort through themselves. Large amounts of data often contain biases or incorrect information, so a model trained on that data could inadvertently internalize that incorrect information as true.
The model would make skewed predictions, yet its users, unaware it was trained on biased data, wouldn't know the predictions are off.
Narrow AI vs. general AI, weak AI vs. strong AI
AGI involves a system with comprehensive knowledge and cognitive capabilities such that its performance is indistinguishable from that of a human, although its speed and ability to process data is far greater. Such a system has not yet been developed, and expert opinions differ as if such as system is possible to create.
Some experts believe that an artificial general intelligence system would need to possess human qualities, such as consciousnesses, emotions and critical-thinking.
Systems built on narrow AI, or weak AI, have none of these qualities, although they can often outperform humans when pointed at a particular task. These systems aren't meant to simulate human intelligence fully but rather to automate specific human tasks using machine learning, deep learning and natural language processing (NLP).





