How can AI drive revenue? Here are 10 approaches
Artificial intelligence has captured the imagination of many a boardroom. Now, the emphasis has shifted to capturing revenue through AI-driven use cases.
Enterprise interest in artificial intelligence has ballooned over the past two years, as boardroom discussions focused on how to harness recent developments -- before competitors do.
Generative AI has been a key focus for the C-suite since the arrival of ChatGPT in November 2022 and subsequent product launches such as Amazon's Bedrock, Google's Gemini, Meta's Llama and a host of SaaS offerings all claiming to embed the technology.
But the initial FOMO-inspired rush to explore enterprise AI is subsiding. Indeed, business and technology leaders are shifting their focus from experimentation to practical matters: How can AI drive revenue? That question will become increasingly important as pilot projects head into production and financial expectations rise.
Using AI to increase revenue
AI's ability to boost the top line will influence the rate of adoption and the corporate appetite for additional investment in the technology. Here are 10 ways organizations could increase revenue through AI deployment.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
1. Boost sales
Virtual assistants and chatbots using AI can help organizations generate sales. Furniture retailer Ikea launched a generative AI tool for its customers. Ikea's AI assistant lets users design their living spaces and shop for furniture. In addition, BriteCo, a jewelry insurance company, created a GenAI-based customer service chatbot that has reduced the abandonment rate on chat inquires. A lower abandonment rate reflects more successful customer interactions, which potentially increases sales. Other enterprises are making similar investments. IT leaders responding to TechTarget's spending intentions survey identified generative AI, CRM and chatbots as the top three customer-oriented business applications in their spending plans.
2. Reduce customer churn
AI enables client retention, letting organizations shrink revenue loss and improve their customer lifetime value metrics. In this capacity, AI can profile the attributes of a business's customer base, tapping historical data on customers who have left. Such information lets managers identify at-risk accounts and develop programs for improving customer satisfaction. AI can support that mission as well. The technology offers higher levels of personalization when incorporated into AI-powered chatbots and contact centers. When businesses transform customer experiences, the result is lower churn rates.
3. Bolster recommendation engines
AI algorithms can examine customer data on past purchases to individualize product recommendations with greater fidelity. This greater personalization delivers a top-line AI business benefit: the ability to more readily cross-sell and upsell customers on new products and services. Recommendation engines also encourage users to linger longer on social media platforms, which, in turn, attracts advertisers. Meta earlier this year rolled out an AI-powered recommendation engine that spans its video platforms, citing increased customer engagement. Speaking at Meta's second-quarter 2024 earnings call, CEO Mark Zuckerberg said the company aims to eventually deploy a "single, unified recommendation system" across all its content.
4. Accelerate marketing strategies
Marketing might not directly generate revenue, but effective practices stock the sales funnel. Generative AI's ability to rapidly create content can help organizations churn out marketing material from newsletters to video ads. Marketers can tap AI's personalization benefit to create marketing messages tailored to customers' interests. Gartner predicted that 30% of outbound marketing messages from large businesses will be synthetically generated by 2025. That's up from less than 2% in 2022.
5. Detect fraud
Organizations can use AI to detect suspicious activities and stop payments to fraudsters, thereby preserving revenue growth. Financial services firms deploy AI in this capacity. Capital One, for example, uses machine learning algorithms to flag anomalies and fend off credit card fraud. In addition, e-commerce companies use ML to zero in on fraudulent orders. The technology's ability to identify patterns in user behavior lends itself to such fraud-detection use cases.
6. Reinvent business processes
While using AI to address a specific pain point is a common approach, recasting an entire business process could yield more significant top-line results. Indeed, AI-driven digital transformation can help enterprises unlock new revenue opportunities. A 2024 Accenture report on AI and business reinvention cited an insurance company that anticipates a 10% revenue boost from retooling its end-to-end underwriting workflow with generative AI. In healthcare, generative AI could potentially streamline revenue cycle management. That business process increases revenue, as it determines how quickly providers are reimbursed for their services.
7. Develop new products and services
AI can help organizations create new products and accelerate development cycles. Pharmaceutical companies, for instance, are already pursuing model-driven drug discovery, in which AI identifies the molecules with the greatest potential. The idea is to shrink R&D timelines and increase the likelihood of successful commercialization. AI can also accelerate the delivery of digital products. AI coding assistants have helped companies such as Ally Financial and ServiceNow speed up software development by 20% or more. The upshot: faster time to market for customer-facing, revenue-generating applications.
8. Provide predictive maintenance
Equipment downtime in fields such as manufacturing and fleet management translates into lost revenue. Predictive maintenance, which ranks among the top ML use cases, identifies equipment on the cusp of failure. That insight lets plant managers schedule downtime to make repairs, avoiding outages and missed shipping schedules. Airlines can reduce flight delays, and associated costs, through proactive maintenance scheduling. Predictive maintenance can stem financial losses, but the overall increase in reliability supports uninterrupted operations and revenue growth.
9. Improve forecasting
AI's predictive capabilities can help organizations improve planning and forecasting. The technology can mine historical data and incorporate current trends to shed light on product demand and customer behavior. Forecasting use cases such as inventory management have a direct bearing on revenue. Businesses that can accurately predict demand patterns can tweak inventory levels to ensure product availability for sales-ready customers. Other predictive AI applications include target marketing, budgeting and credit risk assessment.
10. Optimize pricing
Enterprises can tap AI to set prices to take advantage of shifting customer demand and sudden changes in the overall economic environment. Dynamic pricing algorithms react to unit cost, competitor pricing and other factors. AI techniques such as reinforcement learning lend themselves to dynamic pricing. RL technology is geared to optimization problems, using a trial-and-error approach that takes actions and responds to market feedback. The results are optimized prices and the ability to adjust pricing strategies in real time.
Keep ROI in mind when using AI
Many AI use cases have the potential to create new revenue streams, and the temptation to forge ahead can be strong. AI, however, also creates development, infrastructure and operational costs. Some of those expenses might not be immediately evident.
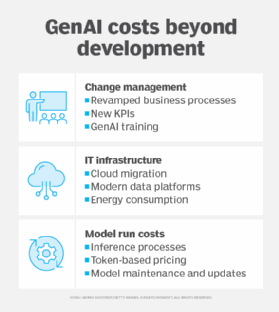
Generative AI, for example, has relatively low startup costs, but research from McKinsey & Company found that GenAI models typically contribute only about 15% of a project's cost. Potentially overlooked costs include change management -- including employee retraining -- and the need for clean and readily available data.
Those cost factors underscore the importance of pursuing AI with a sharp focus on ROI. The revenue outlook for some use cases might simply fail to justify the required investment. An examination of ROI can help organizations prioritize the most promising AI applications -- and defer action on others.
John Moore is a writer for TechTarget Editorial covering the CIO role, economic trends and the IT services industry.








