Linkerd
What is Linkerd?
Linkerd is an Open Source network proxy installed as a service mesh for Kubernetes. Linkerd, originally developed by Buoyant, was one of the first products to be associated with the term service mesh.
In IT, a service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer that controls service-to-service communication and enables separate parts of an application to communicate with each other. Service meshes are typically used in cloud-based applications, containers and microservices.
In a microservices application, managing communications across potentially hundreds of services can quickly become a complex task. Linkerd can serve as a cloud orchestration tool to secure communications among these services by providing features such as load balancing, service discovery, proxy integration and transparency, adaptive routing, failure recovery, circuit breaking, and instrumentation.
How does Linkerd work?
Linkerd runs as a standalone proxy. It does not rely on specific languages or libraries, and it can be used in containers or microservices.
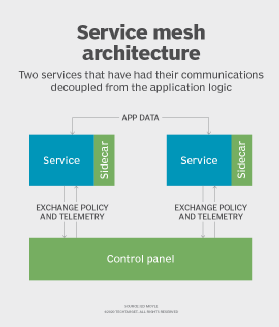
The two most common deployment models for Linkerd are per host and as a sidecar. With per-host deployment, a Linkerd instance is attached to a physical or virtual host that routes all host traffic from each application service instance through the Linkerd instance. In a sidecar deployment, one Linkerd instance is installed per instance of every application service, a useful feature for containerized applications.
Linkerd can communicate with application services using one of three configurations:
- Service-to-linker. Each service instance routes traffic through its corresponding Linkerd instance, which then handles further traffic rules.
- Linker-to-service. Linkerd sidecars take and route traffic to the corresponding service instance, as opposed to service instances receiving traffic directly.
- Linker-to-linker. Combining the service-to-linker and linker-to-service configurations, the linker-to-linker configuration serves incoming traffic with the Linkerd instance, which then routes traffic to the corresponding service instance. The service instance then routes outgoing traffic back through the Linkerd instance.
Benefits of Linkerd
Linkerd was designed to solve issues related to operating and managing large applications and systems.
Interaction among services is a critical component of an application's runtime behavior. By providing a layer of abstraction to control these communications, Linkerd provides developers with more visibility and reliability in their applications. Without this dedicated layer of control, it can be difficult to measure and diagnose application problems and failures.
The potential benefits of Linkerd include the following:
- Simplifies communication among services in both microservices and containers.
- Makes it easier to document how parts of an application interact.
- Offers greater visibility and control by decoupling communication from the main application code.
- Lets application managers address communication and mechanics problems without changing the application itself.
- Provides common service mesh features, such as latency-aware load balancing, service discovery, tracing and instrumentation.
- Enables providers to choose the coding language that is most appropriate for their service.
- Makes application code more efficient and easier to scale.
Linkerd vs. Istio
Istio is an open source service mesh provided by Google, IBM and Lyft that is designed as a universal control plane. Although Istio was first developed for use with Kubernetes, it has since expanded to support multiple platforms.
Istio's features include load balancing, identity and key management, fault injection, hybrid deployment, service-to-service authentication, monitoring, and logging. Additionally, Istio provides automatic sidecar injection, a feature that adds a sidecar proxy to user-created pods.
Both Linkerd and Istio are suitable options for a basic service mesh. Istio has a larger feature set than Linkerd, an advantage for more complicated configurations. However, it also has a steep learning curve and is less user friendly. For example, the Istio control plane is complicated to configure. However, sticking to Istio's default options and settings can make the user experience less daunting.







