log file
What is a log file?
A log file, or simply a log, in a computing context is the automatically produced and timestamped documentation of events relevant to a particular system. Virtually all software applications and systems produce log files.
In computing devices, resources such as operating systems, servers, applications and connected devices all generate a specific type of data file, called a log file. The file includes historical information about that particular resource's operations, activities and usage patterns. This information allows users, such as system admins or hardware developers, to assess the system's health and determine if it is operating properly.
Log files are always autogenerated and contain a wide range of data points about a system, such as the following:
- Processes.
- Events.
- Messages.
- Timestamps.
Timestamps are a particularly important data point in a log file because they provide a detailed record of not only what happened in a system, but also when it happened. This information is crucial for pinpointing an incident's timeline and determining an appropriate remediation strategy.
Log files are useful to many different teams in an organization, including IT operations, DevOps, DevSecOps and IT analysts. Ethical hackers and penetration testers also use different types of log files to conduct security testing.
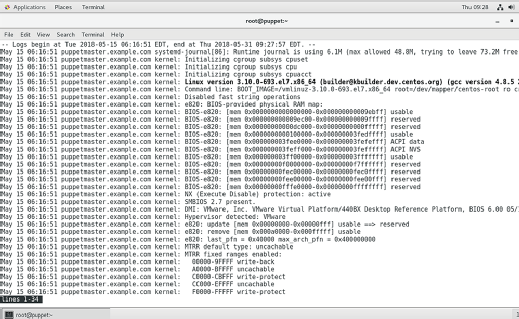
Why are log files important?
A detailed log file provides valuable insights that allow users to identify, diagnose and troubleshoot problems. Simply put, log files are crucial to increase the observability of and visibility into an organization's IT ecosystem. Together, observability and visibility enable IT admins to optimize the IT infrastructure, improve system reliability and usability, and ensure each system properly supports the organization's business objectives.
Since a log file is system-generated, it saves users from having to manually collate data about a system's processes and performance. They can use the log file to quickly resolve issues that could otherwise lead to performance degradation, business downtime and even cybersecurity incidents including data breaches.
Log files are also useful to perform the following functions:
- Identify and analyze usage trends.
- Simplify infrastructure management and maintenance.
- Find ways to improve the operational efficiency of servers and applications.
- Optimize application performance and minimize downtime.
- Identify and address security gaps such as unpatched software or overly permissive firewall rules to reduce risk.
- Analyze user behaviors -- an approach known as user and entity behavior analytics -- to detect and curtail anomalous or suspicious behaviors, and also to enhance user experiences.
Types of log files
Many types of log files are available to improve observability and help with troubleshooting and system optimizations. Each log serves a different purpose, so the different logs are not interchangeable.
The most commonly used log files include the following:
- System logs. System logs typically capture events and activities from the operating system. These include system changes, unexpected shutdowns and shutdown messages, hardware failures and other errors, system resource utilization, and warnings.
- Application logs. Application logs document information about a specific application. While different applications generate their own application logs, most include information like errors, warnings and user actions. Some application logs also include performance metrics.
- Performance logs. System admins often need to track the performance of a system or application. This can be done with the help of performance metrics such as response times, central processor usage or network traffic that are captured in a performance log. By measuring and tracking information, admins can implement measures to identify problems and optimize system performance.
- Security logs. Security logs document security-related events, such as failed login attempts, authentication failures and intrusion detection system alerts. Depending on the setup, they can also capture information related to access control changes and authentication successes.
- Access logs. Access logs record information about attempts to access organizational resources, including individual files. This information can include a list of accessed files, user authentication details, time of access, login/logout timestamps, permissions and network connections.
- Audit logs. An audit log tracks the activities performed in a system. It is usually used for auditing the system's performance, to monitor user actions and to assess system compliance with applicable regulatory requirements.
- Server logs. All servers automatically create log files that document all the activities they perform, including client IP addresses and the number and types of page requests.
- Event logs. An event log records system activity data. It is especially useful to understand system behaviors for troubleshooting and optimization purposes.
- Change logs. System changes are inevitable, but it's important to maintain visibility into these changes, along with version control to ensure user accountability. A change log records the changes made to a system in chronological order. In the case of software, a change log will typically document the changes between different versions as well as any system configuration changes. Change logs are also instrumental in maintaining the effectiveness of firewall hardware and software.
- Error logs. Error logs are useful for troubleshooting since they provide information about errors, exceptions and warnings generated by software and systems.
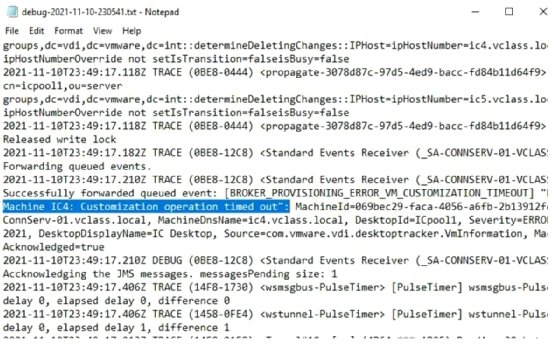
Other types of log files include the following:
- Network logs.
- Container logs.
- Transaction logs.
- Availability logs.
- Resource logs.
- Threat logs.
Examples of log files
On a web server, an access log lists all the individual files that users have requested from a website. These files will include the Hypertext Markup Language files, their embedded graphic images and any other associated files that get transmitted. From the server's log files, an administrator can identify the number of visitors, the domains from which they're visiting, the number of requests for each page, and usage patterns according to variables such as time of day, week, month or year.
In Microsoft Exchange, a transaction log records all changes made to an Exchange database. Information to be added to a mailbox database is first written to an Exchange transaction log. Afterward, the contents of the transaction log are written to the Exchange Server database.
An audit log, also known as an audit trail, is a chronological documentation of any activities that could have affected a particular operation or event. Details typically include the resources that were accessed, destination and source addresses, a timestamp and user login information for the person who accessed the resources.
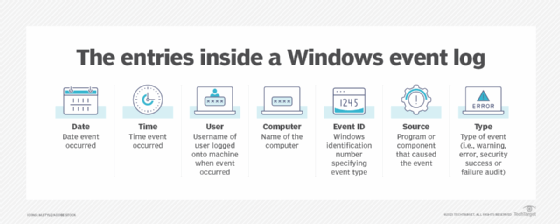
Log file management challenges and solutions
As noted, log files are very helpful in many different ways. However, depending on the size and complexity of an organization's IT infrastructure, the number of log files generated can be very large. It might not be possible for IT teams to manually review every file, limiting their practical use and constraining the potential benefits.
In addition to high volumes, differences in file formats among the various log files can also hinder admins from making full use of them. Without a standardized format, users need to review and analyze each log file separately, which can be cumbersome and time-consuming.
Finally, slow log processing prevents organizations from taking fast action. By the time the file has been analyzed, its information might already be outdated and less useful.
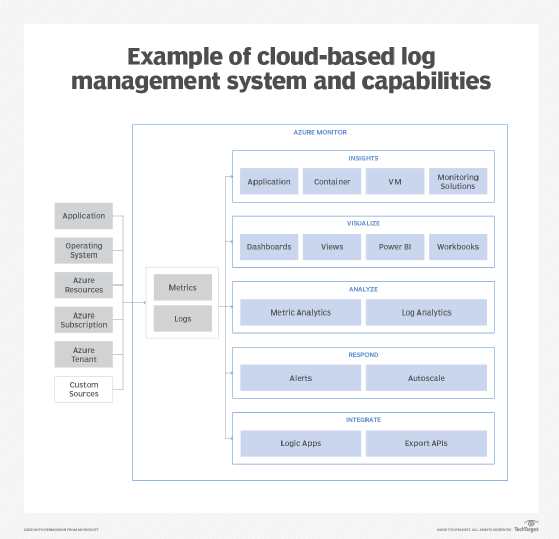
All these log file management challenges can be minimized with cloud-based monitoring and observability services. These include options such as ManageEngine Applications Manager, Azure Monitor, Dynatrace, IBM Instana Observability, APM Insight, SolarWinds AppOptics and Amazon CloudWatch.
CloudWatch, for example, enables organizations to easily monitor their cloud resources to assess performance, gauge operational health, and optimize utilization and costs. Since it provides a unified view of all AWS resources, it eliminates the need to review and analyze different log files.
Use log management and aggregation tools to interpret trends in logs without waste. Learn how to manage application log files with the right tools and guidelines. Also, read about logging best practices that can help with log management and check out the role of Windows log monitoring in the enterprise.