software documentation
What is software documentation?
In the software development process, software documentation is the information that describes the product to the people who develop, deploy and use it.
It includes the technical manuals and online material, such as online versions of manuals and help capabilities. The term is sometimes used to refer to source information about the product discussed in design documentation, code comments, white papers and session notes.
Software documentation is a way for engineers and programmers to describe their product and the process they used in creating it in formal writing. Early computer users were sometimes simply given the engineers' or programmers' notes. As software development became more complicated and formalized, technical writers and editors took over the documentation process.
Software documentation shows what the software developers did when creating the software and what IT staff and users must do when deploying and using it. Documentation is often incorporated into the software's user interface and also included as part of help documentation. The information is often divided into task categories, including the following:
- evaluating
- planning
- setting up or installing
- customizing
- administering
- using
- maintaining
Why is software documentation important?
Software documentation provides information about a software program for everyone involved in its creation, deployment and use. Documentation guides and records the development process. It also assists with basic tasks such as installation and troubleshooting.
Effective documentation gets users familiar with the software and makes them aware of its features. It can have a significant role in driving user acceptance. Documentation can also reduce the burden on support teams, because it gives users the power to troubleshoot issues.
Software documentation can be a living document that is updated over the software development lifecycle. Its use and the communication it encourages with users provides developers with information on problems users have with the software and what additional features they need. Developers can respond with software updates, improving customer satisfaction and user experience.
Types of software documentation
The two main types of software documentation are internal and external.
Internal software documentation
Developers and software engineers create internal documentation that is used inside a company. Internal documentation may include the following:
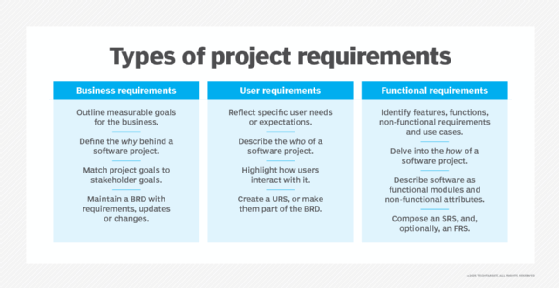
- Administrative documentation. This is the high-level administrative guidelines, roadmaps and product requirements for the software development team and project managers working on the software. It also may include status reports and meeting notes.
- Developer documentation. This provides instructions to developers for building the software and guides them through the development process. It includes requirements documentation, which describes how the software should perform when tested. It also includes architectural documentation that focuses on how all the components and features work together, and details data flows throughout the product.
External software documentation
Software developers create this documentation to provide IT managers and end users with information on how to deploy and use the software. External documentation includes the following:
- End-user documentation. This type gives end users basic instructions on how to use, install and troubleshoot the software. It might provide resources, such as user guides, knowledge bases, tutorials and release notes.
- Enterprise user documentation. Enterprise software often has documentation for IT staff who deploy the software across the enterprise. It may also provide documentation for the end users of the software.
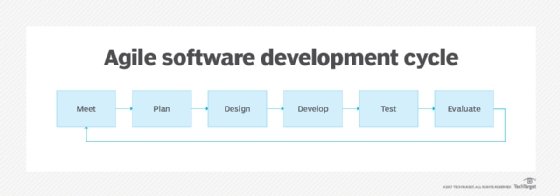
- Just-in-time documentation. This provides end users with support documentation at the exact time they will need it. This allows developers to create a minimal amount of documentation at the release of a software product and add documentation as new features are added. It is based on the Agile software development These can be knowledge bases, FAQ pages and how-to documents.
Best practices for creating software documentation
There are six common best practices for creating software documentation. They are the following:
- Understand user needs. Developers must understand user needs and pain points from the start of the development process. The documentation should address those needs and provide help around pain points.
- Write easily understood documentation. Documentation should be concise, simple and avoid complex jargon. It should use terms and phrases that the intended audience would use.
- Include internal subject matter experts. It can help to have experienced team members and subject matter experts in the software documentation process to ensure that it is accurate.
- Use analytics feedback. Analytics applications provide important feedback that can be incorporated into documentation.
- Ask for user feedback. After a release, ask users what they liked and disliked about a software product and use the input to improve both the product and its documentation.
- Provide continuous maintenance. As software is updated and maintained, the accompanying documentation should also be updated. Teams must constantly improve documentation as IT and user questions reveal additional needs.
Examples of software documentation
Some examples of software documentation include the following:
- System documentation. This includes architectural diagrams that detail the structure of the software and its technical design.
- Application programming interface (API) documentation. This is the reference documentation for calling APIs. It establishes standards for API communication and ensures that different APIs work smoothly together.
- README files. A README file is a high-level representation of software that usually comes with the source code.
- Release notes. Release notes review the new features and bug fixes included in each release of a software program.
- How-to guides. These take IT staff or end users through the steps needed to deploy or use the software.
- Tutorials. Tutorials take users through a series of steps to learn how to use the software or about a specific feature.
- Reference documents. These provide IT and end users with technical documentation of the software.
- Explanations. These clarify a particular element of the software for the user.
Software documentation tools
Various tools help vendors and developers automate the documentation process. Some important features of leading software documentation tools include the following:
- Markdown and HTML support. Markdown and HTML are two programming languages that software documentation is commonly written in. Markdown is an abbreviated form of HTML.
- Feedback. A good documentation tool will have the option to collect and review user feedback. In some cases, users contribute entire code examples. This feature may connect users and developers via email or a comments option. Some tools allow users to look at and make changes to certain code.
- Access control. This feature enables multiple documentation writers to contribute to one piece of documentation. It controls access with roles and permissions.
- Click-button APIs. With this capability, users are able to run APIs from the documentation.
- Table of contents. Documentation tools should enable writers to create a table of contents to simplify navigation.
- Publishing control. Writers can publish and unpublish pages as needed.

Some examples of documentation tools include the following:
- Apiary
- APIMatic
- GitHub Pages
- ReadMe
- Stoplight
- Swagger
Software documentation must keep up with software updates in a given workflow structure. Learn best practices for creating a software update workflow for IoT devices.







