What is IT operations (IT ops)?
The term IT operations (IT ops) describes the many processes and services an IT department manages and maintains within an organization. Traditional IT ops encompasses a range of hardware and software systems, as well as related functions. These can include voice and data networking, physical security and cybersecurity, incident response and disaster recovery (DR), audit support, project management, compliance and environmental management.
The operations team often manages the overall IT environment, quality assurance and system and network infrastructure. The need for IT ops has grown as IT environments have become more complex through the adoption of new technologies, such as cloud computing and software-defined networking, and changes resulting from widespread remote work.
Every organization that uses computers and network technologies has some form of IT operations in place. The work of an operations team is usually separate from IT application development and system administration, though it might support those teams. For example, IT ops in a software development team might include all traditional IT functions in addition to providing technical and planning support for software development and management.
Different organizations define IT operations in various ways. The term is also used to describe the department that manages IT ops, as well as the collection of services, processes and standardized procedures of the department.
Why is IT ops important?
Weak IT operations processes can negatively affect the quality of IT services and other business processes, undermining an organization's competitiveness and reputation. Therefore, IT ops must focus on improving and optimizing business processes and ensuring operational stability. In addition, strong IT operations help a company refine its business processes so that it can quickly adapt to shifting customer needs and competitive activities.
IT ops provides the following benefits:
- Improved network management and support. IT operations is responsible for defining how an organization manages software and hardware. The department provides other IT support, such as network administration, device management, mobile contracting and help desk services.
- Reduced complexity. Transforming a large environment can be costly and complex, but results in long-term benefits, including reduced complexity, which is essential for managing and maintaining an IT infrastructure.
- Optimized performance optimization. IT ops teams strive to maximize the functionality and efficiency of IT applications and systems, ensuring they satisfy user requirements. Performance optimization measures typically entail hardware and software configurations, monitoring performance metrics and troubleshooting performance issues.
- Enhanced visibility across the entire IT infrastructure. IT operations enhance IT visibility across the infrastructure through monitoring tools, alerts, dashboards, reports, capacity planning, compliance measures and incident management systems.
- Maximized efficiency. By utilizing IT ops, organizations can take preemptive and immediate corrective actions that minimize risk. This results in maximized efficiency and productivity for organizations.
- Modernized and adaptable technology. IT ops assists companies in adopting advanced technologies, facilitating rapid adaptation to changing customer needs. Technology trends such as digital transformation, cloud services, artificial intelligence (AI), software automation, cloud infrastructure and advanced cybersecurity all contribute to modernizing IT ops. Adoption of these modern technologies reduces operational costs and increases IT's agility and efficiency.
- Improved security. IT ops play a crucial role in maintaining the security of IT systems and data. This entails using security measures such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls and antivirus software programs in addition to ensuring the organization follows industry standards and best practices.
- Effective cost management. IT ops is responsible for effectively managing IT resources to keep costs down while also fulfilling the business needs of the organization. This includes budgeting, finding ways to cut costs and optimizing resource usage.
- Enhanced business continuity. IT ops ensure business continuity by executing backup and DR strategies. This can include regularly backing up data, testing DR plans and ensuring critical systems can be restored quickly in the event of a disaster.
- Improved IT operations management and IT operations analytics. ITOM and ITOA are roles within IT ops that help an organization refine the way IT approaches tasks such as service provisioning, system deployment, networking and data storage, and maintenance and support of all resources. ITOM and ITOA professionals help ensure consistency, reliability and quality of service.
IT operations processes
IT operations is made up of several different management approaches and processes, including the following:
- Incident management. This refers to the steps a business must take to safeguard itself against events -- such as cyberattacks and unplanned outages -- that aren't part of normal operations and might disrupt operational processes. The objective of the incident management process is to resolve issues and restore IT services as fast as possible.
- Problem management. This is related to incident management, but with a focus on preventing incidents before they happen and minimizing the effects of incidents that can't be stopped. Problem management includes analyzing incident reports and detecting issues using IT service management (ITSM) metrics.
- Service desk management. This provides troubleshooting and technical support to end users by managing service requests through a centralized service desk.
- Access management. A successful access management strategy provides authorized users with the rights to access and use a selected service and prevents unauthorized users from accessing services. Access management is also referred to as identity management and rights management. An organization's information security policies determine who gets access. Role-based access control limits access to data and systems based on an individual's job roles and responsibilities. Multiple types of authentication -- such as biometrics, tokens, proximity cards and passwords -- are used to prevent unauthorized access.
- IT operational control. This involves monitoring and managing a company's IT services and service desk as well as the underlying infrastructure. These controls include routine tasks related to the operation of software applications and infrastructure components. This can include backup and restore activities, patch management, app installation and upgrades, routine maintenance, job scheduling and output management.
- Facilities management. This is all activities and resources involved with maintaining a company's physical environment, including building access control management and power, water, cooling, heating and environmental monitoring. The goal is to protect the physical environment where the IT infrastructure is located through maintenance and support.
- Technical management. This process seeks to deliver technical expertise and service to improve the operations and management of the IT infrastructure.
- Capacity management. Capacity management involves forecasting future resource requirements and ensuring IT infrastructure can meet current and future business needs efficiently.
Some methods used to improve IT operations processes include DevOps, Kanban, ITSM and IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL). The goal of these methods is to prepare employees to prioritize, manage and delegate multiple tasks at any moment.
- DevOps helps IT operations teams adapt to a fast-paced Agile development environment. It also provides a comprehensive approach to project management that improves cross-team collaboration and communication.
- Kanban helps IT ops teams adopt DevOps practices and transition toward a DevOps-oriented approach. Its task scheduling system boosts productivity and tracks the progress of a project, maximizing communication and efficiency. Kanban is often paired with Lean software development to increase collaboration between IT operations and other departments.
- ITSM improves the management of IT systems to maximize the ways businesses use IT resources.
- ITIL provides a set of practices within ITSM that address how IT service delivery happens and is used to empower the daily business operations.
What does an IT operations manager do?
An IT ops manager oversees the daily activities of an organization's IT department and ensures the systems it uses are up to date and are functioning effectively and efficiently. Aspiring IT ops managers should gain experience in a core IT field and obtain IT ops certifications, including basic project management. They should also have strong communication, problem-solving and decision-making skills.
Some areas that an IT operations manager must be knowledgeable in include the following:
- Latest technology trends.
- Industry regulations.
- Security threats and issues.
- Network design.
- System performance and monitoring.
- Software installation and upgrades.
- Working with vendors.
- Overseeing and mentoring IT staff.
An IT operations manager is typically responsible for the following:
- Team management. An IT ops manager leads a team of IT professionals including system administrators, network engineers and support staff. They also hire, train, assign tasks and provide guidance and support to team members.
- Vendor management. An IT ops manager oversees relationships with third-party vendors, including contract negotiations, performance tracking and issue resolution. They also ensure that the provider meets the company's requirements and delivers results while staying within project timelines and budget.
- Ensuring system security. An IT ops manager is responsible for executing cybersecurity best practices such as implementing firewalls, antivirus software and access controls. They also train employees and stakeholders on security policies and procedures, monitor system activity for potential issues and stay updated on security threats.
- Monitoring customer interactions. An IT operations manager oversees and analyzes interactions between the IT operations team and customers -- including phone calls, emails and chats -- to assess service quality and identify areas for improvement within specified time frames. They collaborate with customer service representatives and support technicians to ensure accurate recording and tracking of all communications.
- Facilities management. An IT ops manager maintains and manages the physical environment housing IT hardware, ensuring proper ventilation and cooling in data centers and server rooms to prevent overheating. They also set up backup systems to sustain services during power outages.
To do well in IT operations, a person must possess a combination of technical and soft skills. Having a degree in a related field is essential, as is experience with networks, operating systems, software applications and programming languages. Strong interpersonal skills are required so that an IT ops manager can effectively communicate technical matters to customers and executives who don't have a technical background. Organizational capabilities are necessary for managing multiple projects and allocating resources.
Popular fields in IT operations
There are many different specializations within the field of IT operations, providing a wide range of employment options. Some popular fields in IT operations include the following:
- System management. System management involves administering IT systems within an enterprise network or data center.
- Network management. Network management encompasses the applications, tools and processes for provisioning, operating, securing and maintaining a network infrastructure.
- Cloud computing. Cloud computing enables businesses to transition from on-premises to the cloud.
- Database management. Database management entails controlling and manipulating data to provide secure and efficient access as required by the business.
- Data center management. Data center management involves IT teams fulfilling the daily operational needs of running a data center.
IT ops vs. IT infrastructure
IT operations and IT infrastructure are two key parts of any IT organization that must work in tandem. IT ops ensures the smooth running of IT systems and services. IT infrastructure encompasses the physical and virtual components and software that enable IT systems.
IT infrastructure
IT infrastructure is all the hardware and software that comprise an organization's IT environment. This includes PCs, servers, networks, storage devices, virtual technologies and all the software that makes the hardware run and that runs on the hardware.
Infrastructure management involves oversight of these components, as well as documenting hardware configurations, setting up new configurations and monitoring and measuring the performance of the IT infrastructure.
IT operations
IT operations encompass the design, setup, configuration, deployment and maintenance of the IT infrastructure that supports business operations. It ensures an organization's systems are available when needed and can respond to changing needs. Ops teams use automated processes and comprehensive monitoring tools to respond to technical and security issues as they arise and before they become major problems. IT ops teams also ensure IT systems can scale to meet future and growing needs.
IT operations also facilitates collaboration among other IT teams by providing visibility into complex systems and performance metrics. Comprehensive monitoring tools give stakeholders across departments access to real-time insights into system performance and help them make better decisions. This improves efficiency and ensures everyone is on the same page when it comes to system maintenance and use.
The primary goal of IT operations is to ensure the smooth functioning of IT services and infrastructure, supporting the day-to-day operations of an organization.
IT ops vs. DevOps
IT operations and DevOps overlap in key areas, so it's important to understand what each does and how they differ. IT ops is the management of operations related to the development, maintenance and support of IT systems. This includes activities such as monitoring and management of networks and servers, system upgrades, patches and security updates, user account maintenance and service desk support. The ops team oversees all daily IT tasks with the goal of maintaining existing infrastructure.
DevOps combines both software development and IT operations activities to create an efficient, streamlined product and service delivery process. DevOps uses automation and continuous system monitoring to increase speed, agility and reliability in the product development and delivery process.
DevOps uses Agile methodology for software development to ensure changes can be executed fast without affecting an organization's operational stability or performance. Similar to IT ops, it encourages collaboration among different departments and facilitates better communication among teams. Automation and continuous integration processes simplify product deployment. Both DevOps and IT ops ensure faster resolution of issues through feedback loops that detect problems earlier in the system's lifecycle.
IT operations trends
The following major trends are reshaping the future of IT operations:
- Serverless computing is a cloud computing model that, along with a related capability called function as a service, is designed to simplify cloud application hosting. Serverless computing reduces the need for infrastructure management and provisioning.
- AI and AIOps are optimizing IT operations and automating infrastructure and operations functions, such as failure recognition and predictive analytics.
- Edge computing puts workloads and client data on the network periphery, as close to the customer as possible, reducing latency and improving customer experience.
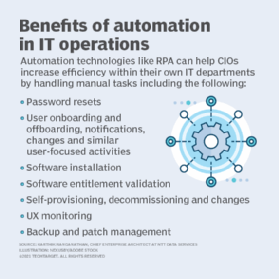
- Automation. Automation is becoming increasingly crucial for IT operations. As digital businesses scale up, demands on IT infrastructure and operations are increasing, prompting a shift in mindset and practices to embrace automation capabilities.
- Platform engineering adoption. As DevOps evolves, platform engineering is becoming more popular. With this method, operations and administration are made more efficient by having a platform team construct and manage infrastructure, services and apps in a repeatable manner.
- Convergence of ITOM and ITSM. There's a growing convergence between ITOM and ITSM processes, as organizations are realizing the benefits of integrating these two areas to address the complexities of modern IT environments. This convergence can streamline processes, improve efficiency, enhance service delivery and meet the evolving needs of businesses.
Other trends influencing IT operations in broader ways include the following:
- Digital diversity management. The modern enterprise is becoming an increasingly diverse and digital environment that, in most cases, stitches together legacy applications and infrastructure with cutting-edge, multi-cloud strategies. Digital diversity management focuses on the need to identify, monitor and manage technologies that affect and support modernization.
- Reducing the role of the traditional data center. A growing number of organizations are expected to shut down their traditional data centers or move to smaller facilities, based on shifting IT operations into cloud-based environments.
- Network agility. Automation and AI are among the advanced technologies contributing to network agility. Over time, AI-enabled networks are expected to show impressive increases in network speeds as networks evolve to meet the needs of 5G wireless technology and edge computing.
- Global infrastructure. An organization's customers and suppliers are more likely to span the globe, requiring operations leaders to make IT resources available everywhere. As a result, IT leaders must look for partnership strategies that provide affordable and accessible capabilities and support.
- Cybersecurity threats. Cyberattacks -- including phishing, distributed denial-of-service attacks, viruses and ransomware -- are becoming more frequent, targeted and destructive. Such attacks can shut down business operations if they aren't quickly found and stopped. This makes security management among the biggest concerns for IT operations managers.
IT ops best practices
By following best practices, organizations can improve the reliability, efficiency and security of their IT operations.
Key IT operations best practices include the following:
- Effectively utilizing IT operations tools. IT ops teams should embrace new tools that are being incorporated into the infrastructure and ensure that all the required skills are in place for growth.
- Setting clear goals. IT ops teams should adopt the SMART framework for setting goals. It's important to clearly define roles within IT teams to increase accountability and ensure that workload and priorities are clearly understood.
- Using a single view of services. By using a single automation tool, organizations can integrate enterprise-class monitoring, event management and operational analytics into a centralized platform, which can provide a comprehensive evaluation of the IT infrastructure.
- Getting leadership on board. IT ops should always gain support from leadership and top executives. A leadership that's on board ensures the alignment of IT initiatives with business goals, provides necessary resources and budget allocation, and fosters a culture of collaboration and accountability. Leadership support can also help overcome resistance to change, aid with decision-making processes and promote the adoption of new technologies and best practices within the organization.
- Building KPIs around business and customer needs. IT operations should tailor key performance indicators (KPIs) to meet business and customer requirements. Metrics should be centered on KPIs, giving the demands of the company and its clients top priority. A focus on KPIs guarantees that all IT ops activities align with the goals of business stakeholders.
- Embracing IT automation. IT ops should set up automation tools and scripts to streamline repetitive tasks, reduce manual errors and increase efficiency.
IT operations vendors
IT ops tools can fall into many different categories, including configuration management, patch management, network management and performance management. The following is just a sampling of the vendors that offer IT operations management platforms and related services:
- CA Technologies.
- Cisco.
- Flexera.
- Google.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise.
- HP.
- IBM.
- Interlink Software.
- Microsoft.
- ServiceNow.
- Splunk.
- VMware.
- Zenoss.
- SolarWinds.
- Zendesk.
- Zluri.
When hiring for roles in cloud and IT operations, soft skills are just as important as technical ones. Discover the top six soft skills that cloud teams need.





