Red Hat
Red Hat is a software company that combines open source Linux operating system components with related programs into a distribution package that customers can order.
The Red Hat business model is based on an open source ecosystem, where collaborative development occurs within a community of professionals focused on providing quality assurance, testing and customer support.
Red Hat offers a variety of open source software that DevOps engineers and businesses use. These include operating system platforms, storage, middleware, management products, as well as training, support and consulting services.
Currently, Dell, IBM and Oracle support the Red Hat platform and open source community of applications.
The history of Red Hat
Red Hat was one of the first companies to realize that free software could be sold as a product.
After examining the successful marketing campaign of Evian water, Red Hat executives concluded that to be successful, the company had to create more Linux users and brand Red Hat as the Linux name that customers preferred.
Today, the "Red Hat Plan" is often discussed in business schools as a model for making customer support a company's primary product.
On October 28, 2018, IBM announced that it was acquiring Red Hat. The $34 billion deal closed in July the next year. Red Hat became a business unit of IBM's Hybrid Cloud team, while continuing to preserve the independence and neutrality of Red Hat's open source development heritage.
Red Hat products
Red Hat Linux Open Source products include, but are not limited to:
- Red Hat Ansible: An open source IT configuration management (CM) developer tool and IT automation platform.
- Red Hat Atomic Host: A variant of Red Hat Enterprise Linux with optimizations for container application platform hosting.
- Red Hat CloudForms: A virtual machine and container management product based on VMware, Red Hat Virtualization, Microsoft Azure, OpenStack, AWS EC2, Google Cloud and Red Hat OpenShift.
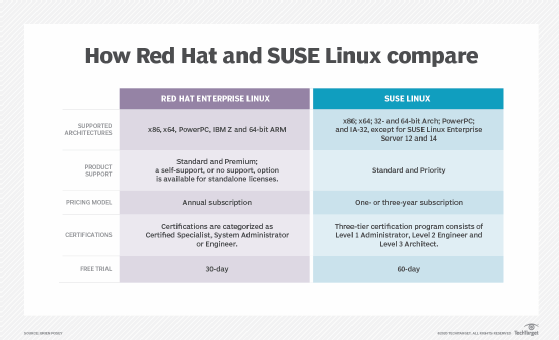
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL): A distribution of the Linux operating system developed for the business market that provides centralized certificate administration and cloud security updates.
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform: A cloud computing, microservices container platform used in conjunction with the Kubernetes to deliver traffic and identity management, telemetry and policy enforcement.
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform: A commercially supported distribution of open source software designed to build and manage large pools of computing, storage and networking resources in a multi-cloud infrastructure.
- Red Hat Package Manager (RPM): A program for installing, uninstalling and managing software packages in Linux.
- Red Hat Satellite: An IT infrastructure management tool primarily used to monitor and manage Red Hat Enterprise Linux environments. Satellite is part of Red Hat's four-piece systems management tool set for enterprise IT, which also includes Ansible, CloudForms and the Red Hat Insights service.
- Red Hat Storage (RHS): A distributed file system that acts as scale-out network-attached storage (NAS) and object storage
- Red Hat Virtualization (RHV): An enterprise-class virtualization platform.
Additional Red Hat products include the following.
Application services
- Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (JBoss EAP)
- Red Hat JBoss Web Server
- Red Hat Data Grid
- Red Hat CodeReady Studio
- Red Hat Fuse
- Red Hat Fuse Online
- Red Hat AMQ
- Red Hat 3scale API Management
- Red Hat Decision Manager
- Red Hat Process Automation Manager
Cloud computing
- Red Hat Certificate System
- Red Hat Directory Server
- Red Hat Quay
Data services
- Red Hat Gluster Storage
- Red Hat Ceph Storage
- Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation
Management
- Red Hat Smart Management
- Red Hat Insights
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes
Services
- Red Hat open innovation labs
- Red Hat training and certification
- Red Hat Consulting
Data services and cloud computing
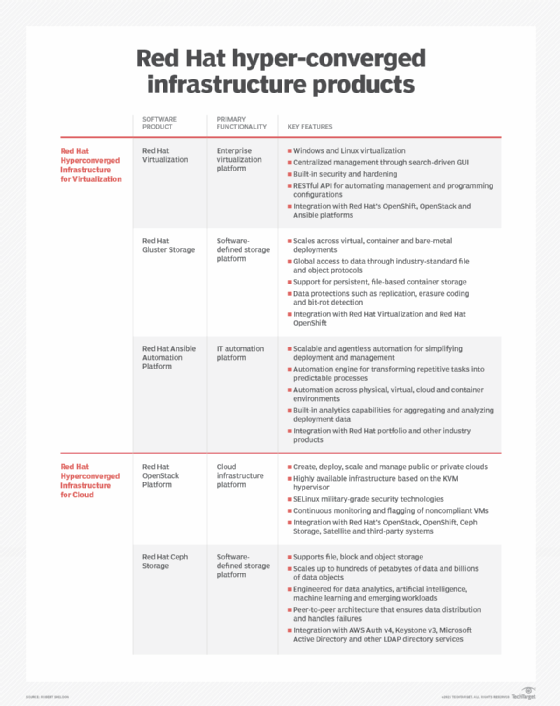
- Red Hat Hyperconverged Infrastructure (RHHI)
Learn how Red Hat OpenShift lays a foundation for hybrid cloud services, how Red Hat Enterprise Linux doubles down on edge computing, and how Red Hat bolstered Ansible-Kubernetes bond via OpenShift ACM. Also, see how Red Hat OpenShift Storage is riding the wave of container momentum.








