Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
What is Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)?
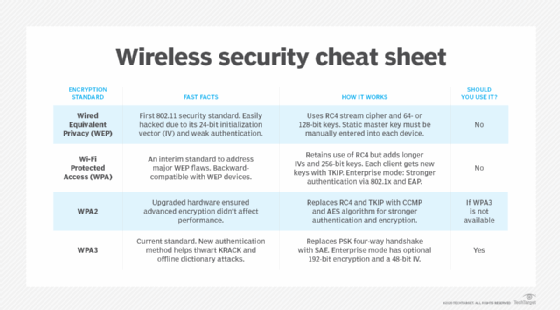
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) is an encryption protocol included in the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11i standard for wireless local area networks (WLANs). It was designed and implemented to provide more secure encryption than the notoriously weak Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), the original WLAN security protocol.
TKIP works on older or legacy WEP hardware. It is also the core component of Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), which replaced WEP in WLAN products.
Anatomy of Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
Like WEP, TKIP uses the Rivest Cipher 4 (RC4) stream encryption algorithm as its basis. However, unlike WEP, TKIP encrypts each data packet with a unique encryption key. Also, TKIP's keys are much stronger than those of its predecessor.
TKIP includes three parts:
- 64-bit message integrity check (MIC).
- Packet sequencing control.
- Per-packet key mixing function.
The mixing function is combined with the initialization vector (IV) or starting variable and sent to the RC4 cipher. The MIC's protocol is called "Michael." It is designed to help with TKIP and provide higher reliability with relatively simple computations. Although Michael is not as cryptographically secure as WPA and WPA2, it is significantly better than WEP's 32-bit Cyclic Redundancy Checksum (CRC-32) and can therefore be used to build fairly secure networks.
The 8-byte MIC is placed at the end of the frame before it is sent for WEP encryption. Since it is based on the entire frame and not just individual fragments and the data of the packet, Michael avoids iterative guessing, bit flipping and some fragmentation attacks to which WEP is vulnerable.
Differences between WEP and TKIP
One difference between WEP and TKIP is that TKIP expands the IV and key ID fields to 8 bytes. It gives a 6-byte IV called the TKIP sequence counter (TSC) that doesn't need to wrap. Even if it gets close to wrapping, the client must renegotiate a new pairwise transient key (PTK), which prevents key reuse.
Another change in TKIP is that its per-frame key uses a new algorithm that takes into account the larger IV and PTK as well as the transmitter's address. There is a brand-new per-frame key for each frame. TKIP also uses an S-box cryptographic device to spread out the per-frame key in a random-looking pattern, which prevents the RC4 from leaking information -- a common issue with weak RC4 per-frame keys.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol algorithms
TKIP is not a single encryption algorithm. Rather, it is a suite of algorithms that works as a "wrapper" to WEP. It thus allows users of legacy WLAN equipment and WEP hardware to upgrade to TKIP without having to replace the hardware. TKIP uses the original WEP programming, but wraps additional code at the beginning and end to encapsulate and modify it.
To increase key strength, TKIP includes four additional algorithms:
- A cryptographic MIC to protect packets.
- An IV sequencing mechanism that includes hashing, as opposed to WEP's plaintext transmission.
- A per-packet key-mixing function to increase cryptographic strength.
- A re-keying mechanism to provide key generation every 10,000 packets.
Development and evolution of TKIP
The Wi-Fi Alliance and the IEEE 802.11i task group developed TKIP between 2002 and 2004 to run on WEP hardware without slowing it down significantly. It was approved as a part of the WPA protocol and adopted as a Wi-Fi security standard to improve confidentiality and integrity.
To prevent slowdowns, TKIP includes a preprocessing step before WEP encryption. It still uses RC4 as the encryption algorithm. However, it adds features into the selection of the per-frame key, and also introduces a new MIC to sit beside the WEP CRC-32 error-detecting function to identify changes between source and target data.
In 2012, TKIP was officially deprecated in the 802.11 standard.
Advantages of TKIP over WEP
WEP is the earliest Wi-Fi security protocol. It is vulnerable to many kinds of cyber attacks, such as replay attacks. TKIP has several security and integrity advantages over WEP. One reason for these advantages is that with TKIP, each data packet is encrypted using a different key, as opposed to simply concatenating the IV and the key. In addition, TKIP uses a sequence counter. If a replay attack is attempted, the counter is different, which results in the failure of the attempt.
In TKIP, the TSC is required to increase by one for each message. During communications, each side keeps the current TSC that it is sending with as well as the last TSC received from the other side. If a frame is received with an old TSC, it is considered to be out of order, so the receiver will drop it. An attacker will not be able to replay valid but old frames. Also, unless the frame is decryptable, the receiver won't update the last good TSC. And the frame won't be decryptable because the attacker does not know the key. In this way, TKIP provides replay protection, which is missing in WEP.
Drawbacks of Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
TKIP is useful for upgrading security on devices originally equipped with WEP. It addresses the key reuse problems common in WEP. However, it does not address all the security issues facing WLANs. It is vulnerable to pre-shared key attacks and attacks originating in the same network, because the session secret doesn't change and remains the same for all users on the network. It is also vulnerable to denial-of-service attacks and attacks where threat actors try to guess at certain parts of a message and make some minor alterations to the packets. Thus, while TKIP is safer than WEP, it is not completely secure or hassle-free. Also, it might not be reliable or efficient enough for sensitive corporate and government data transmission.
The 802.11i standard specifies the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in addition to TKIP. The WPA standard uses TKIP, whereas WPA2 uses AES. AES offers higher security and stronger encryption services than RC4. For these reasons, it is more suitable for government and military use than TKIP. However, AES requires a hardware upgrade for implementation and to provide optimal wireless voice quality. As more organizations replace older wireless equipment, AES is expected to become the accepted encryption standard for WLAN security.
Learn about the differences between WLAN and Wi-Fi and read about wireless network configuration basics.








