Evolved Packet Core (EPC)
What is Evolved Packet Core (EPC)?
Evolved Packet Core (EPC) is a framework for providing converged voice and data services on a 4G Long-Term Evolution (LTE) network. EPC unifies voice and data on an IP service architecture, and both are treated as IP applications. This enables operators to deploy and operate one packet network for 2G, 3G, wireless local area network, WiMax, LTE and fixed access (Ethernet, Digital Subscriber Line, cable or fiber).
Both LTE and EPC are designed to support IP services. The idea behind EPC is to combine voice and data on an IP service architecture by replacing circuit switching with packet switching. As a result, service operators only have to deploy one packet on a 4G LTE network. It provides a high-performance, high-capacity network for both voice and data applications and helps to integrate and simplify networks.
EPC supports access to the packet-switched domain and combines different transfer modes -- e.g., synchronous and asynchronous transfer modes -- in existing systems. Since it can construct many possible networks, it supports simultaneous connections to multiple packet networks and enables service operators to provide valued-added services to their customers, such as voice over IP calls.
EPC is based on an always-on connection. It is essential for end-to-end IP service delivery across an LTE network and is radically different from the Global System for Mobile communication/General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) core network used for GSM, Wideband Code Division Multiple Access and High Speed Packet Access.
Today's 5G networks support EPC, as well as 5G Core network architecture.
Evolution of Evolved Packet Core
The standards for EPC operation were specified by industry trade group 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) in early 2009. When EPC was being developed, many operators using code-division multiple access (CDMA) wanted to join the LTE ecosystem and take advantage of the common packet core being developed under the System Architecture Evolution (SAE). Ultimately, EPC was first introduced in 3GPP Release 8.
EPC is the core component of SAE, 3GPP's flat LTE architecture. SAE was designed to support the evolution of a common type of packet core network -- different from CDMA -- and build a bridge between the two distinct networks that were used previously.
Over the years, EPC has evolved to include the following capabilities:
- It is required for the LTE core to function.
- It authenticates subscribers and determines if they have access to the network.
- It aids mobility management and session management.
Evolved Packet Core architecture and key components
EPC has a flat architecture, so it can efficiently and cost-effectively handle the payload (data traffic) and avoid protocol conversion. Also, it consists only of a few network nodes to handle the traffic and to provide functionalities like session management, mobile management, authentication and quality of service (QoS).
The four main nodes in EPC are the following:
- Mobility management entity (MME). The MME is EPC's control plane node and is located at the edge of LTE EPC. It manages session states and authenticates and tracks users -- and user equipment -- across the network. For authentication, it continuously communicates with the home subscriber service node. It is also responsible for connection and release of bearers to a device and for handling IDLE-to-ACTIVE transitions and security keys. The MME's mobility function enables users to access the network. It also keeps track of every user's location and state.
- Serving gateway (S-GW). The S-GW is the user plane node, meaning it handles user data traffic but not signaling data traffic. It connects EPC to the LTE radio access network (RAN) and routes IP data packets through the access network to the LTE core network. It also routes incoming and outgoing packets to improve system collaboration and collects the information and statistics required for charging back users.
The separation of the control plane (MME) and user plane (S-GW) ensures separation between user data and signaling and enables independent scaling. Such a functional split also enables mobile operators to easily adapt their network as required. - Packet data node gateway (P-GW). The packet data node gateway, also known as the packet data network gateway, acts as the interface between the LTE network and other packet data IP networks. In other words, it connects EPC to external IP networks and routes packets between them. It also manages QoS, provides deep packet inspection of IP user traffic and allocates IP addresses to user equipment.
- Policy and charging rules function (PCRF). The PCRF supports service data flow detection and helps with policy enforcement and flow-based charging. It is also responsible for QoS handling and for defining the charging system. This node is required to ensure that the users receive services and are charged for them according to the contract.
In addition, EPC may also contain other nodes, such as the following:
- Home subscriber service (HSS). HSS is a database containing subscriber information and user authentication details, as well as information for calls and IP session setup. If there are multiple HSS nodes in a mobile network, they must communicate with each other and have their databases updated and synchronized to ensure that the servers can function properly.
- Multimedia broadcast multicast services (MBMS). These nodes enable network resources to send the same multimedia content to everyone (broadcast) or to a group of subscribers (multicast).
All the above nodes in EPC are logical. In actual physical implementations, multiple nodes may well be combined into a single physical node. In addition, the P-GW, S-GW and MME nodes enable packet transmission since they act as the functional interfaces between fixed networks and a public land mobile network, which is a mobile operator's cellular network in a particular country.
Evolved Packet Core vs. 2G/3G: Resource pooling and overload protection
In 2G and 3G systems, the pooling of network systems was added later. But, in EPC, pooling is a foundation of the system, meaning EPC was designed from the beginning to support resource pooling. EPC's pooling mechanism is efficient so a mobile operator can centralize and pool a group of their signaling nodes, thus increasing network efficiency.
Also, the core network in 2G and 3G networks is strictly hierarchical. So, a terminal or user equipment located in a particular cell could only connect to one base station, one BS controller and one serving GPRS support node. As a result, the capacity of the nodes is not perfectly balanced or fully utilized.
To scale the entire pooled capacity to the peak rates of a large region, resource pooling is required. Through that mechanism, a pool of network nodes can be created for an entire region -- e.g., a large city -- instead of splitting the network into multiple smaller regions. In LTE EPC, the pooling mechanism is implemented in the core network architecture.
EPC also provides overload protection. It does this by assigning every MME node a weight factor that indicates its capacity. The MME communicates its weight factor to the eNodeB, which is the BS equipment in charge of handling the radio interfaces with mobile devices. Once the eNodeB knows the weight factor, it can distribute user equipment across the MME pool, thus preventing overload.
Reducing EPC complexity with software-defined networking
EPC complexity increases as the number of subscribers using the core network increases and as more protocols and procedures are used. Also, policy decisions and routing are not scalable. For all these reasons, a new data path is required for the mobile core network.
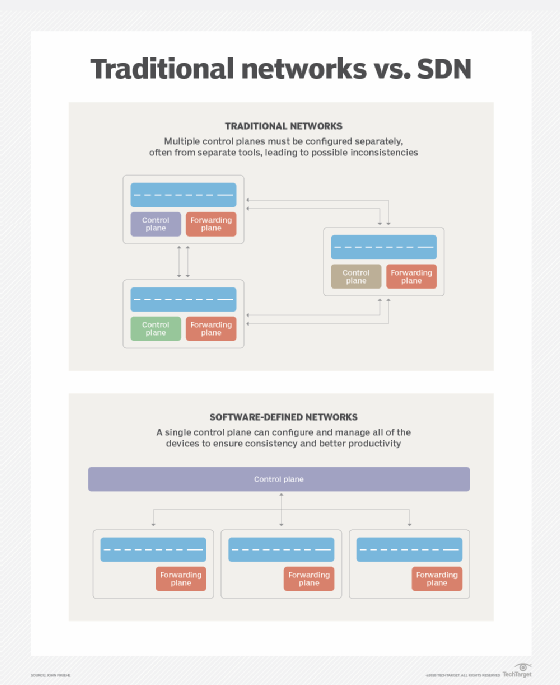
Software-defined networking (SDN) can help eliminate these issues. SDN provides a centralized network controller that separates the control from the data plane. It also schedules applications and controls routing and traffic so operators can implement optimal data paths for specific applications. In addition, distributed user plane forwarding entities in SDN reduce delay by routing the data traffic according to the rules received from the controller.
Learn the key differences between 5G vs. 4G.







