What is network traffic?
Network traffic is the amount of data that moves across a network during any given time. It is also referred to as data traffic, or simply traffic.
Administrators can control network traffic by managing or prioritizing data. They can also monitor network traffic by measuring the amount and types of traffic. Network traffic is encapsulated in packets, which are units of data that provide the load in a network. For example, when a user visits a webpage, they receive a series of packets. A typical packet contains 1,000 bytes to 5,000 bytes.
Types of network traffic
Search engine optimization characterizes traffic to a network in the following ways:
- Direct traffic. Occurs when a user enters a website's URL in a browser.
- Organic traffic. Generates when a user locates content through a search engine.
- Paid traffic. Results when a user clicks on a sponsored advertisement.
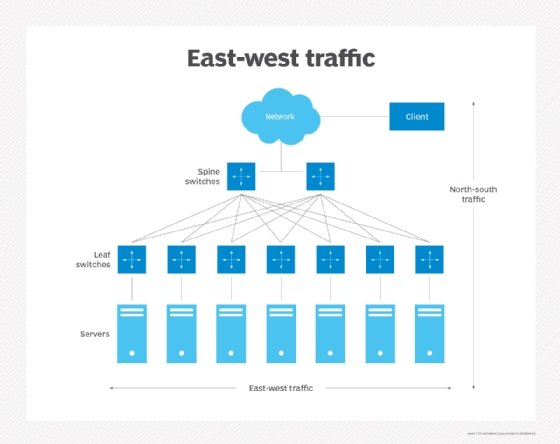
Data center administration characterizes network traffic as being either north-south or east-west. North-south traffic describes client-to-server traffic that moves between the data center and a location outside the network. Network diagrams typically depict north-south traffic vertically to illustrate traffic flowing in and out of the data center. In the early days of the internet, most network traffic was north-south.
By contrast, east-west network traffic characterizes data packets that move from server to server within a data center. The term east-west comes from network diagrams that depict local area network traffic horizontally. Hardware virtualization and the internet of things are two concepts that have driven the growth of east-west network traffic.
Common network traffic problems
Common network traffic issues include the following:
- Component failures in the server, router or firewall.
- Traffic failures, such as bottlenecks and high latency.
Bottlenecks occur when a network has insufficient data handling capacity to process the current traffic volume. Latency -- the delay from input into a system to its outcome -- occurs when data center components relay information to each other and increase network traffic. High latency occurs more frequently with east-west traffic.
Monitoring network traffic
Network administrators should analyze, monitor and secure network traffic to ensure network quality. Network monitoring enables the oversight of a computer network for failures and deficiencies to ensure continued network performance.
Network monitoring tools notify users of significant or troublesome changes to network performance. Network monitoring enables administrators and IT teams to react quickly to any network issues.
Network traffic security
Network and security teams can use network security tools, such as Nagios or Splunk, to secure network traffic. Other best practices, such as enabling firewalls, also support network security.
For east-west traffic, microsegmentation reduces an application's attack surface. Microsegmentation segments a data center into logical units, which enables data center administrators to tailor unique security policies for each unit.







