What is streaming network telemetry?
Streaming network telemetry is a real-time data collection service in which network devices, such as routers, switches and firewalls, continuously push network health data to a centralized location. Telemetry is the science of transmitting measurements from a remote source to a receiving station for storage and analysis.
Data streaming network telemetry is push-based, automatically and continuously transmitting data. The collected data enables the following:
- Setting up network monitors and alerts based on preconfigured thresholds.
- Creating network performance baselines.
- Planning network capacity requirements.
- Troubleshooting connectivity and performance issues.
- Using AI for automated decisions.
How streaming network telemetry works
Data streams with protocols, such as Transmission Control Protocol, User Datagram Protocol, XML-RPC or gRPC, in two ways:
- Cadence-based telemetry. Occurs when data is sent to a collector at regularly configured intervals. Cadence-based telemetry helps build historical baselines.
- Event-based telemetry. Sends data when a specific event occurs. These events include a critical link going down or the throughput on a link passing a specified maximum threshold.
Streaming network telemetry vs. SNMP
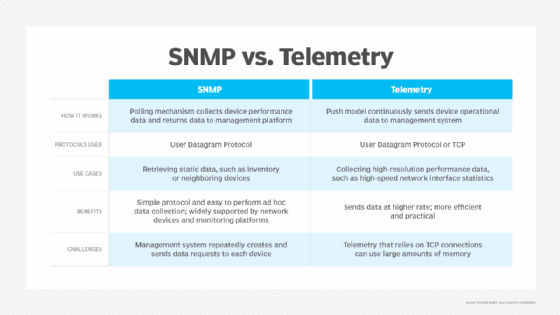
Before streaming network telemetry technologies, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) was the standard method for collecting network telemetry information. However, SNMP uses a pull technology, where an SNMP collector must request telemetry information at regular intervals.
Typical enterprise networks configure collectors to request information every five minutes. In this model, administrators have time gaps in the gathered information. Polling is also fairly resource-intensive and does not scale well.
Streaming network telemetry, however, is a push technology. Instead of the collector requesting data every few minutes, the network device streams health and interface data in near-real time. Ultimately, it can provide more data point granularity with better performance than SNMP.
Streaming network telemetry architecture
Some network components are capable of streaming network telemetry information. Configure these components to point to one or more data collectors. Network devices can subscribe to the collector to establish communications sessions. The reverse -- the collector subscribing to the network device -- yields the same result.
Streaming network telemetry can alert networking professionals to unusually sharp increases or decreases in traffic. Data collected by streaming telemetry is model-driven and ideal for using big data analytics to optimize traffic flow.
During implementation, administrators control several aspects of the subscription and stream process. First, they choose who initiates the subscription conversation -- the network device or the collector. Next, they selectively choose the information they want to collect. Standard data models, such as Yet Another Next Generation, OpenConfig or vendor proprietary models, help accomplish this process. Finally, admins choose the frequency that cadence-based data streams to a collector.








