5G driving IoT innovation: Key use cases and applications
5G's low latency, massive device density, energy efficiency and flexibility are tailor-made for the networking demands of a future IoT-connected world.
5G cellular represents a significant improvement over 4G for IoT applications because it provides a foundational network that can handle the unique and demanding requirements of a truly massive-scale, real-time connected world.
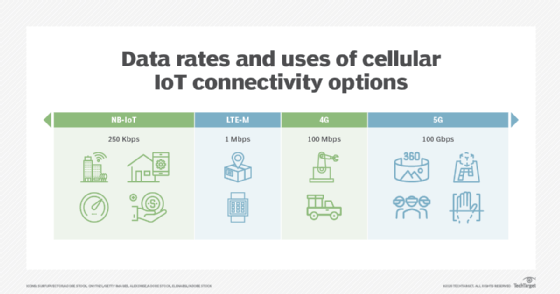
While 4G and its IoT-specific variants, such as long-term evolution for machines (LTE-M) and narrowband IoT (NB-IoT), have been successful in connecting millions of devices for simpler use cases, 5G's core design principles address and surpass the limitations of 4G, opening the door for new and more intricate capabilities and applications.
Top benefits of 5G for IoT
The improvements to IoT primarily relate to latency, device density, energy efficiency and coverage, as well as network and ecosystem flexibility.
Here's a breakdown.
Low latency
The most critical improvement is extremely low latency, which is the near-instantaneous speed at which data travels between devices on the network. 4G networks have a typical latency of around 50-100 milliseconds (ms), which is fine for streaming video or browsing the web but unacceptable for applications that require immediate feedback. 5G can reduce latency to as low as 1 ms, a transformative leap that enables time-sensitive use cases such as industrial automation and smart infrastructure. This low latency is essential for creating a genuinely responsive and automated IoT ecosystem.
Device density
Beyond speed, 5G's architecture is designed to support a vastly greater number of devices. Where 4G can support around 100,000 devices per square kilometer, 5G is engineered to handle up to 1 million devices in the same area. This massive IoT capability is crucial for smart city deployments, where countless sensors for traffic management, utility meters and environmental monitoring need to coexist on the same network without causing congestion.
The combination of low latency and massive device density enables real-time data transfer and analysis, which is crucial for applications such as industrial automation, remote control of assets and real-time video monitoring.
Network slicing
5G also introduces network slicing, which allows mobile operators to create dedicated, virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. This means an IoT application, such as a smart grid, can have its own customized slice of the network optimized for its specific needs, such as high reliability and low latency, without being affected by traffic from other applications. This flexibility ensures guaranteed quality of service for critical IoT uses.
IoT network support
5G cellular support of low-power wide area network (LPWAN) standards, including NB-IoT and LTE-M, delivers improvements over 4G by providing significantly better energy efficiency and deeper indoor and subterranean coverage, which are crucial for low-data, long-lifecycle IoT devices.
NB-IoT is a cellular-based LPWAN and a key component of 5G's massive machine type communications (mMTC) capabilities. It's designed for low-bandwidth, low-power IoT applications like smart meters, sensors and asset trackers.
LTE-M, which is also under the 5G mMTC umbrella, offers slightly higher bandwidth and supports mobility, making it suitable for things like fleet management and wearables. 5G networks deliver improved outcomes for LTE-M, not by replacing it but by enhancing its capabilities and integrating it into a more powerful and flexible ecosystem. Both NB-IoT and LTE-M operate on licensed cellular spectrum, which means governments have allocated specific frequencies to them to guard against interference and ensure performance and reliability.
Enhanced reliability
5G provides a more stable and robust connection, ensuring that mission-critical IoT devices, such as those in healthcare or manufacturing, can operate with consistent, uninterrupted service.
High-speed data
With speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G, 5G enables rapid data transfer for bandwidth-intensive IoT applications like high-definition video applications and real-time data analysis.
Improved energy efficiency
5G networks offer improved energy efficiency, a key benefit for IoT devices that often rely on batteries. By using technologies such as LPWAN and advanced sleep modes, 5G can extend the battery life of IoT devices like sensors and smart meters, making long-term deployments more practical.
5G powering IoT improvements
5G's mMTC capabilities are what enable it to support a significantly higher density of devices than 4G. They are essential for large-scale deployments such as smart cities and factories, where countless sensors and devices must communicate simultaneously without network congestion.
In addition, 5G's network slicing feature enables operators to create virtual, isolated networks tailored to the specific needs of an IoT application, ensuring guaranteed performance, security and bandwidth for specialized tasks, which is a significant step up from the one-size-fits-all approach of previous generations.
Here are the IoT use cases and applications that have gained substantially from 5G's capabilities:
- Autonomous vehicles. The ultra-low latency and high-bandwidth capabilities of 5G enable autonomous vehicles to communicate in real time with other vehicles (vehicle-to-vehicle, or V2V) and with infrastructure (V2I) and the cloud (V2C), allowing for instantaneous data exchange crucial for critical functions such as collision avoidance, cooperative maneuvering and dynamic route optimization.
- Manufacturing. 5G -- especially private 5G -- enhances manufacturing operations by enabling rapid rearrangement of factory floors, improving worker safety and product quality, and facilitating reliable, real-time collaboration.
- Mining, oil and gas. 5G networks enhance mining by enabling real-time remote control of heavy machinery, facilitating widespread deployment of IoT sensors for environmental and equipment monitoring, and improving worker safety through low-latency communication for autonomous vehicles and real-time location tracking.
- Healthcare. 5G has transformed healthcare by enabling remote robotic surgeries, facilitating real-time patient monitoring through connected medical devices, and powering secure, high-definition telehealth consultations -- all of which expand access to specialized care, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
- Robotics. IoT-enabled robotics benefit significantly from 5G connectivity due to its high bandwidth and low latency, which are essential for real-time data exchange. This enables robots to make instant, coordinated decisions and perform complex tasks such as autonomous navigation with greater precision and reliability.
New opportunities and applications 5G brings to IoT
Bolstered by 5G connectivity, IoT is set for significant growth over the next three to five years as the integration of AI and edge computing fuels innovations across an expanding array of industries, including the following:
- Smart cities. 5G can enable smart cities to deploy vast networks of interconnected IoT sensors and devices with more flexibility and intelligence, thereby augmenting real-time data collection and analysis to optimize traffic flow, manage energy grids, improve public safety and streamline waste management.
- Energy and utilities. The energy sector benefits from a smarter, more resilient grid through real-time monitoring and control, which allows for rapid detection and isolation of faults, efficient integration of renewable energy sources and dynamic demand-response programs that optimize energy use.
- Private 5G networks. Private 5G networks can enable a new wave of IoT applications by providing dedicated, intelligent, highly secure and ultra-low-latency networks that are essential for mission-critical operations and real-time automation in industries such as manufacturing, logistics and healthcare.
- Satellite coverage. The continued build-out of 5G networks, including low-band and satellite integration, can bring reliable IoT connectivity to remote and rural areas, unlocking new applications such as precision agriculture, environmental monitoring and asset tracking.
- Precision agriculture. 5G allows for automated monitoring and management of crops and widespread use of drones that rely on instantaneous communication for safe operation.
Thanks to its many advantages over 4G -- especially its massive device density, along with extremely low latency that enables near-instantaneous communication -- 5G marks a fundamental leap forward for IoT to support a truly large-scale, real-time connected world.
Ron Westfall is vice president and practice leader for infrastructure and networking at HyperFRAME Research, where he covers topics such as hybrid cloud, AI, security, edge computing, wired and wireless networking, 5G and IoT.







