bluebay2014 - Fotolia
DBMS keys: 8 types of keys defined
Here's a guide to primary, super, foreign and candidate keys, what they're used for in relational database management systems and the differences among them.
Database keys are essential components of a relational database management system. DBMS keys are used to specify identifying attributes in the rows of database tables so the data can be sorted and organized for use in applications. They also create links between different tables to reduce data duplication, while making it look like all the data in a table is a single entity.
Why are DBMS keys necessary?
DBMS keys bring several benefits for organizations when it comes to managing database tables. In large databases, there may be hundreds or thousands of rows of data, which may sometimes include duplicates. Without a DBMS key, it may be difficult or time consuming to accurately find the unique data row when it's needed. A single DBMS key can quickly identify the specific row of interest.
Additionally, DBMS keys can identify multiple rows and reveal relationships between data tables. Some of the eight DBMS keys discussed in this article use a single identifier for finding data, while others may use multiple attributes together as the key.
Types of keys in a DBMS
There are various types of database keys that serve different purposes in a DBMS, including primary, super, foreign and candidate keys. Let's look at each of these keys and the relationships and differences among them.
The main types of keys in a DBMS are the following:
- primary key
- candidate key
- super key
- foreign key
- alternate key
- surrogate key
- composite key
- compound key
Below is a description of each of these DBMS keys.
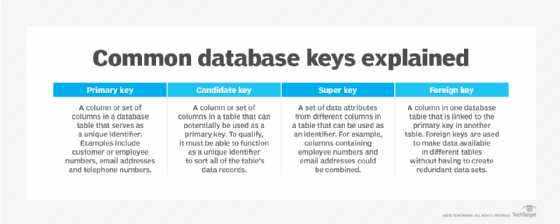
1. Primary key
A primary key is a column -- or a group of columns -- in a table that uniquely identifies the rows of data in that table. For example, in the table below, CustomerNo, which displays the ID number assigned to different customers, is the primary key.
| CustomerNo | FirstName | LastName |
| 1 | Sally | Thompson |
| 2 | Sally | Henderson |
| 3 | Harry | Henderson |
| 4 | Sandra | Wellington |
The data values placed in the primary key column must be unique to each row of data; no duplicates can be used. In addition, nulls are not allowed in primary key columns.
It is possible to use one or more columns as the primary key; however, how do you decide which columns -- and how many -- to choose?
Well, there are times when it is advisable or essential to use multiple columns. However, if you cannot see an immediate reason to use multiple columns, then use one. This isn't an absolute rule; it is simply advice.
However, primary keys made up of single columns are generally easier to maintain and faster in operation. This means that, if you query the database, you will usually get the answer back faster if the tables have a single primary key from a single column.
The next question you should ask is which column you should pick. The easiest way to choose a column to be a primary key -- and a method that is commonly employed -- is to get the database to automatically allocate a unique number to each row.
2. Candidate key
Often, there is only one choice for the primary key, as in the case above. However, if there are multiple DBMS keys, these can be called candidate keys -- the name reflects that they are candidates for the responsible job of the primary key.
A candidate key is a column that meets all the requirements of a primary key. In other words, it has the potential to be a primary key, like the CustomerNo column. On the other hand, in a table of customers or employees, clearly, a column like FirstName is a poor candidate to be a primary key because you cannot control people's first names.
If a candidate key is not the primary key of relation it is referred to as a unique key. Unlike primary keys, a unique key can accept null values in its table.
3. Super key
A super key is a set of attributes that can each uniquely identify a row in the data table. Now, given the definition above that a primary key can be made up of more than one column and must uniquely identify the rows, choose, for example, CustomerNo and a column containing customer phone numbers as the primary key. That fulfills the requirement, but it is clearly foolish because it's adding complexity for no reason.
It is also a great example of a super key with multiple unique identifiers. However, super, in this case, is not a synonym for great, but a contraction of supernumerary. It's recommended to avoid super keys in DBMSes.
4. Foreign key
Foreign keys are columns that point to primary key columns in other database tables. So, for example, OrderNo is the primary key of the ORDERS table below, and CustomerNo is a foreign key that points to the primary key in the CUSTOMERS table.
| OrderNo | EmployeeNo | CustomerNo | Supplier | Price | Item |
| 1 | 1 | 42 | Harrison | $235 | Desk |
| 2 | 4 | 1 | Ford | $234 | Chair |
| 3 | 1 | 68 | Harrison | $415 | Table |
| 4 | 2 | 112 | Ford | $350 | Lamp |
| 5 | 3 | 42 | Ford | $234 | Chair |
| 6 | 2 | 112 | Ford | $350 | Lamp |
| 7 | 2 | 42 | Harrison | $235 | Desk |
Foreign keys don't have to point to a primary key. The only true requirement of the column to which a foreign key points is that it must contain unique values. Imagine, for example, that our employee table looked like the EMPLOYEES table below.
| SsecurityNo | EmployeeNo | FirstName | LastName | DateOfBirth | DateEmployed |
| AF-23432334 | 1 | Manny | Tomanny | 12 Apr 1966 | 01 May 1999 |
| DQ-65444444 | 2 | Rosanne | Kolumns | 21 Mar 1977 | 01 Jan 2000 |
| GF-54354543 | 3 | Cas | Kade | 01 May 1977 | 01 Apr 2002 |
| JK-34333432 | 4 | Norma | Lyzation | 03 Apr 1966 | 01 Apr 2002 |
| VB-48565444 | 5 | Juan | Tomani | 12 Apr 1966 | 01 Apr 2002 |
| FG-23566553 | 6 | Del | Eats | 01 May 1967 | 01 May 2004 |
The Social Security number is actually the primary key of the table, but we also issue each person an employee number that is unique. Under these circumstances, ORDERS.EmployeeNo can be a foreign key pointing to EMPLOYEES.EmployeeNo, even though the latter column is not a primary key. So, the actual rule is slightly more subtle: A foreign key must point to a candidate key.
Having said this, I can also say that I cannot remember the last time I saw this done in a live production database. In practice, foreign keys almost always point to primary keys in a DBMS.
5. Alternate key
An alternate key is essentially all the keys in a data table that are not the primary key. Remember that only one key can be set as the primary key. Once the primary key is established, all others are now considered alternate keys. In the example above, the Social Security number is the identified primary key and all other keys are alternate.
6. Surrogate key
A surrogate key is an artificial key that is created strictly for the purposes of data analysis. It's sometimes also called a synthetic key or a pseudokey because it isn't derived from any application data. Instead, it is used to identify each record in the database.
7. Composite key
A composite key is a key that has more than one attribute. Any super key, primary key or candidate key can be a composite key as long as it meets the requirement of having more than one attribute. By combining two or more columns in a table into a key, it guarantees that the key refers to a specific row of data. This is the primary use of composite keys. A database tracking addresses could use the street name and house number as a composite key.
8. Compound key
A compound key is a particular type of composite key in which each attribute is a foreign key -- for example, a table tracking student enrollment. Tables for student ID and course ID may already exist, with both combining to make the compound key for enrollment.
While DBMS keys help organize and sort data, it's important for organizations to select the database management system that best fits their data needs.
Editor's note: Most of this information is from Inside Relational Databases, a book Mark Whitehorn coauthored with Bill Marklyn, published by Springer.