What is SAP Quality Management (QM)?
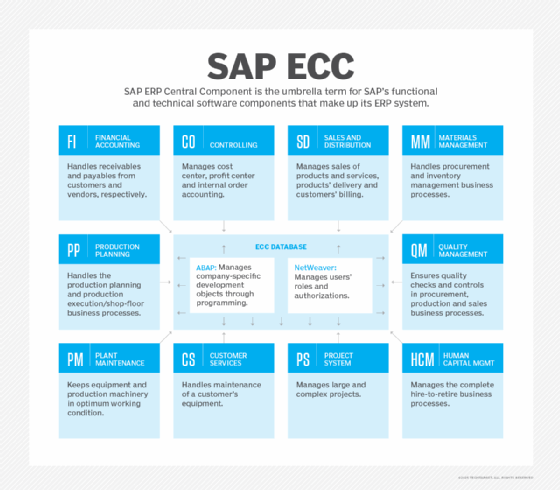
SAP Quality Management (QM) is a component of SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) that helps businesses implement and run quality control (QC) processes. It is designed to prevent defects, enable continuous process improvement and establish sustained QC programs. Potential benefits for the organization include compliance with manufacturing quality regulations, lower operating costs and customer satisfaction improvement.
Quality management is an essential process for many kinds of companies as it helps to ensure that their products, processes and services meet their market's and customers' expectations. A systematic and comprehensive QM process enables organizations to plan, execute and monitor quality inspections with the aim of producing high-quality output. Moreover, they can set up inspections for different scenarios and departments, such as procurement, production, sales and so on.
SAP QM, a feature with SAP ECC and SAP S/4HANA, enables businesses to set up sustainable and consistent processes for quality management and QC. By using this tool, they can prevent errors and other quality issues and implement programs for continuous improvement.
What is SAP QM used for?
SAP QM includes modules and functions that enable quality managers to streamline many aspects of quality management and QC. They can plan and execute multiple types of quality inspections to meet the needs of different scenarios and departments. They can also identify and process identified defects to eliminate them and prevent recurrence, thus improving product or service quality. SAP QM also provides quality-related data that enables companies to implement process improvements and thereby achieve their stated quality goals.
Within SAP ECC, the QM function can be used to perform quality inspections in SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) using the SAP Quality Inspection Engine (QIE). SAP EWM is a flexible warehouse management system offering digitized, cloud-based warehouse processes to manage high-volume warehouse operations and supply chain logistics. EWM triggers an inspection process and then calls QIE to carry it out.
In SAP S/4 HANA, QM can be used to implement a quality management system (QMS) in order to comply with various standards. One example is ISO 9000, a family of quality management standards aimed at helping organizations to improve the quality of their products and services.
Modules in SAP QM
SAP QM includes modules to help companies improve their QM processes and output quality. The main modules are the following:
- Basic data (QM-PT-BD). Here's where frequently used data about inspection methods, catalogs, sampling procedures, dynamic modification rules, sampling schemes, etc. is stored. Using the basic data as a model makes it easier for users to enter new data into the system for ongoing quality management and control.
- Inspection planning (QM-PT-IP). This module provides task lists and material specifications to plan inspections and define the criteria for each inspection, such as which material or criteria to inspect and required test equipment, streamlining the inspection process and assuring better results.
- Visual inspection planning (QM-PT-VP). With this module, users can create inspection plans from 3D models, derive the task list and define inspection criteria. By directly using 3D data, quality teams don't have to derive 2D drawing data or deploy additional software for file format conversions.
- Failure mode and effects analysis (QM-PT-FA). The module is designed for planning new products and processes and enables quality managers to detect potential failures in products and processes early and implement quality-specific actions to prevent those failures.
- Control in logistics (QM-PT-RP). This logistics component can be used to control the integration of the QM application component in logistical processes, like materials management, production, sales and distribution.
- Control plan (QM-PT-CP). Organizations looking to perform inspection planning and align it with the ISO/TS16949 standard can benefit from this module. When used with the QM-PT-FA component, QM-PT-CP helps to integrate inspection planning for goods production and goods receipt. Such integrations can help to prevent production defects early, thus reducing quality costs.
- Quality certificates (QM-CA). Companies can use this module to automatically create quality certificates for delivery items, inspection lots or batches. These certificates certify the quality of goods, which can aid in enhancing customer trust.
- Quality notifications (QM-QN). Through this module, businesses can record problems resulting from poor-quality goods, such as customer complaints. They can also analyze the issue, implement corrections and monitor the status of those corrections to prevent recurrence.
- Quality-related costs (QM-IM-IC). Here's where quality personnel record appraisal and nonconformity costs, which are expenses related to quality assurance (QA) to plan and assure product or service quality.
Benefits of SAP QM
The main benefit of SAP QM is that it enables organizations to implement effective quality management processes. These processes are vital to improving the quality of goods and services. Quality has a direct impact on sales, revenues, customer satisfaction and customer trust. High-quality products, services and processes can also lower operating costs by minimizing errors and reducing the need for rework.
Another potential benefit of SAP QM is compliance with manufacturing quality regulations. By achieving compliance, businesses can avoid noncompliance fines and penalties. They can also better control their internal processes and communicate their commitment to quality and safety to stakeholders.
SAP QM also includes capabilities to benefit other aspects of quality management, such as the following:
- Processing and managing samples during goods receipt and in goods production.
- Modifying and integrating inspection plans.
- Defining the quality criteria to determine how materials are inspected.
- Processing quality inspections on the basis of inspection lots.
- Performing quality inspections using test equipment defined and calibrated on the basis of specific performance criteria.
- Implementing customer enhancements, such as specific conditions for shipping certificates, additional data origins for specifications, layout, certificate printing, etc.
- Documenting processes involved in quality-relevant areas, e.g., production.
Integration with other SAP components
SAP QM integrates with other SAP components, including Materials Management, Plant Maintenance, Production Planning, Sales and Distribution, Finance, Controlling and Human Resources. Through these integrations, companies can incorporate the tasks and activities in SAP QM into the other components, thus instilling quality-oriented thinking and execution at each level.
Another benefit of integrating SAP QM into procurement and production is that it provides continuous QA. It also enables control over business processes and enables decision-makers to implement plans for continuous process improvement.
Explore ways companies can optimize SAP ECC and find ways to innovate.





