antenna
What is an antenna?
An antenna is a specialized transducer that converts electric current into electromagnetic (EM) waves or vice versa. Antennas are used to transmit and receive nonionizing EM fields, which include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation (IR) and visible light.
Radio wave antennas and microwave antennas are used extensively throughout most industries and in our day-to-day lives. Infrared and visible light antennas are less common. They're still deployed in a variety of settings, although their use tends to be more specialized.
How are antennas categorized?
Antennas are often categorized as either transmitting or receiving. However, many antennas can do both through a transceiver. A transmitting antenna receives current from a transmitting device. From this current, the antenna generates EM waves at a specific frequency that radiate out through the air, where they can then be received by one or more other antennas.
For example, a radio station might broadcast music as an FM signal, which is a type of radio wave in the EM spectrum. The station's transmitter sends the music to the antenna in the form of electric current at the desired frequency. The antenna converts the electric current to radio waves that are transmitted out in all directions.
A receiving antenna intercepts EM waves transmitted through the air. From these waves, the antenna generates a small amount of current, which varies depending on the strength of the signal. The current is passed to the receiving device, where it is transformed for its specific environment. For example, a car's antenna might pick up the FM signal from the radio station. The antenna converts the signal's radio waves to current, which is fed to the car's radio. The radio amplifies the current and in other ways transforms it and delivers it as music to the speakers.
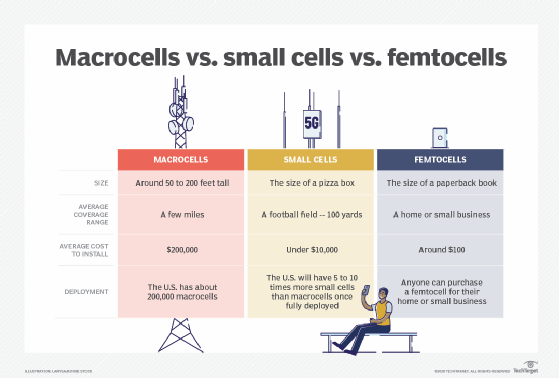
How is the electromagnetic spectrum divided?
The EM spectrum is typically divided into seven fields: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays and gamma rays. The field order is determined by wavelength and frequency.
Radio waves lie at one end of the spectrum, where wavelengths are at their longest and frequencies at their lowest. Gamma rays sit at the other end of the spectrum, where wavelengths are much shorter and frequencies are much higher.
According to estimates, radio wavelengths can be as long as 10,000 kilometers (km) and frequency rates below 3 kilohertz (kHz). At the other end of the radio range, wavelengths can be as short as 1 meter (m) and frequencies as high as 300 megahertz (MHz), which is where the microwave range begins.
Microwave wavelengths range from around 1 m to 1 millimeter (mm), and frequencies range from about 300 MHz to 300 gigahertz (GHz). However, the exact figures vary depending on the source. In addition, some sources treat microwaves as a type of radio wave, rather than a separate category.
Antennas are designed to transmit and receive EM waves at specific frequencies. Their design is also determined by such factors as direction, movement and signal strength. This is why antennas come in so many different shapes and sizes. For example, car antennas are designed much differently from television antennas, and both types of antennas are designed much differently from microwave antennas and cell phone antennas.
What are the main types of antennas?
Antennas support different use cases, depending on their design. To help distinguish between the different types, they are often grouped into specific categories, although there is no industry-wide agreement on what constitutes each group. Even so, several common categories are often used in describing and distinguishing one antenna type from another.
- Aperture. An antenna with an opening in its surface that helps direct EM transmission or reception to achieve larger gain. The antenna's size and shape depend on how the antenna is used. Aperture antennas are often deployed in situations that require a flush mounting, such as aircraft or spacecraft.
- Array. An antenna made up of smaller connected antennas that work together to produce a single radiation pattern. Array antennas can increase gain and reduce interference, while providing greater control over its directionality. Array antennas are used in a variety of settings, including wireless communications, 5G networks and military radar systems.
- Reflector. An antenna that includes one or more components that reflect the EM waves in order to better focus or direct them. Reflector antennas are often used in microwave and satellite communications. Many include a parabolic structure that reflects EM waves, such as those used in satellite dishes.
- Lens. An antenna that includes an embedded lens made up of glass, metal or a dielectric material. The antenna uses the convergence and divergence properties of the lens to transmit or receive EM waves, typically at higher frequencies. Lens antennas are often used for radar systems and microwave communications.
- Log periodic. A directional antenna with multiple elements that can support a broad range of frequencies. The supported range depends on the size of the elements and how they're arranged, which is based on a logarithmic function of frequency. Log periodic antennas can be useful in situations that require variable bandwidth or that support high-frequency communications, such as analog televisions, cellular communications or shortwave radios.
- Microstrip. A small antenna printed into a circuit board. The antenna itself is a patch made out of a conductive material that is mounted on a dielectric substrate, which itself sits on a ground plate. Microstrip antennas are used extensively in wireless communication and mobile devices including cell phones.
- Traveling-wave. A directional antenna in which the EM waves travel through the antenna in one direction, unlike many other types of antennas in which the waves travel in multiple directions. The unidirectional waves make it possible to support a wider range of frequencies. Traveling-wave antennas are used for analog televisions, amateur radios, telecommunications and other use cases.
- Wire. An antenna that is nothing more than a length of wire, connected at one end to a transmitter or receiver. Wire antennas are the simplest and most portable type of antenna. They're used extensively with radios, automobiles, ships, aircraft, buildings and a variety of other devices and structures.
How else are antennas categorized?
Antennas might also be categorized by whether they are internal or external or by their degree of directionality. There are also antennas that don't fit neatly into any of these categories, such as wearable antennas or near-field communication (NFC) antennas.
An antenna might also fit into multiple categories. For example, some log-periodic antennas can also be considered array antennas. At the same time, different types of antennas might be used to support the same use case, such as log periodic and traveling-wave antennas, which are both used for analog TV reception.
In some cases, an antenna is located at a distance from the transmitter or receiver, and the electric current is delivered to or from the antenna by means of a transmission line, also called a feed line or feeder.
Learn 5 benefits of Wi-Fi 6 for enterprise networks and check out our guide to enterprise 5G planning, architecture and benefits.








